(Press-News.org) Cardiac arrhythmias affect millions across the world and are responsible for a fifth of all deaths in the Netherlands. Currently there are multiple treatment options, ranging from life-long medication to invasive surgical procedures. Research from Amsterdam UMC and Johns Hopkins University, published today in the European Heart Journal, sets another important step in the hunt for a one-off gene therapy that could improve heart function and protect against arrhythmias.
"Arrhythmias often occur due to slowing of conduction of the electrical impulse through the heart. Rapid impulse conduction is needed for the heart to beat in a steady rhythm. When this is disturbed, the patient may experience a life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia. Among others, conduction slowing and arrhythmias can occur in patients who suffer from a heart attack, heart failure, or from a genetic cause,” says Gerard Boink, cardiologist at Amsterdam UMC and coordinating author of the study.
The research team aimed to resolve conduction slowing for the first time through the insertion of a novel gene into heart muscle cells.
"The search for a gene therapy is not a new one but until now we had the pretty fundamental problem that the potential effective genes we had identified were too large to be transported via a viral vector into heart muscle cells," says Boink. "Think of this vector like being a suitcase, up until now most of the relevant genes were just too big to fit in,” he adds.
Researchers from the department of Medical Biology at Amsterdam UMC have recently discovered a gene (SCN10a-short, S10s), which is small enough to fit into an AAV vector, the most efficient gene delivery platform for the heart.
"Finding a small enough gene was of course a crucial first step and in S10s we also have found a gene that may be able to reverse the conduction slowing and allow the heart to beat at its regular rhythm,” says Phil Barnett, who works as a senior researcher in the Department of Medical Biology.
The research team has shown for the first time in the current study that it is possible to introduce S10s into the heart with an AAV vector and that this leads to faster conduction and, thus, a potential therapeutic for the prevention of cardiac arrhythmias. This has been demonstrated in various animal models, but also in human heart muscle cells derived from stem cells and a computational model of the human heart.
"These are great early steps but now we need to continue our research in order to find out if this approach will really translate into clinical practice. If it does, then we should be able to significantly reduce the occurrence of arrythmias and make a meaningful impact on patient mortality,” says Boink.
To facilitate this, Boink has, together with fellow Amsterdam UMC cardiologist Hanno Tan and anaesthesiologist Otto Kirzner, launched a spin-off company called Pacing Cure. The company aims to "serve as a stepping stone" to facilitate quicker clinical progress.
These follow-up studies are being carried out in collaboration with the Amsterdam UMC, Departments of Medical Biology, Experimental Cardiology, Clinical Cardiology and the spin-off company PacingCure B.V., and will be financed by the European Innovation Council and the Dutch Heart Foundation.
END
A new gene identified in the search for a therapy to treat malignant cardiac arrythmia
2025-02-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
‘Fog harvesting’ could yield water for drinking and agriculture in the world’s driest regions
2025-02-20
With less annual rainfall than 1 mm per year, Chile’s Atacama Desert is one of the driest places in the world. The main water source of cities in the region are underground rock layers that contain water-filled pore spaces which last recharged between 17,000 and 10,000 years ago.
Now, local researchers have assessed if ‘fog harvesting,’ a method where fog water is collected and saved, is a feasible way to provide the residents of informal settlements with much needed water.
“This research represents a notable shift in the ...
Unveiling the intricate mechanisms behind oxysterol-induced cell death
2025-02-20
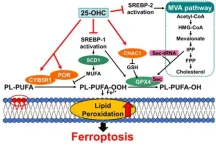
Oxysterols are a class of molecules derived from cholesterol via oxidation or as byproducts of cholesterol synthesis. Despite their relatively low concentration within our bodies, oxysterols are known to play many important biological roles, acting as transcriptional regulators, precursors for bile acid, and key players in brain development.
On the flip side, some pathologies are associated with imbalances in oxysterols. In particular, 25-hydroxycholesterol (25-OHC) has been shown to contribute to arteriosclerosis, cancer development, central nervous system ...
Closing the recycle loop: Waste-derived nutrients in liquid fertilizer
2025-02-20
Growing plants can be a joyous, yet frustrating process as plants require a delicate balance of nutrients, sun, and water to be productive.
Phosphorus and nitrogen, which are essential for plant growth, are often supplemented by chemical fertilizers to assure proper balance and output of produce. However, the amount of these nutrients on the planet is increasing due to excessive use, which in turn is causing various environmental problems. For this reason, there is a growing movement to promote sustainable agriculture through the recycling of phosphorus and nitrogen. In Japan, a target has been ...
vmTracking enables highly accurate multi-animal pose tracking in crowded environments
2025-02-20
Studying the social behavior of animals in their natural environments is necessary for advancing our understanding of neurological processes. To achieve this, tracking multiple individuals simultaneously and accurately as they interact in shared spaces is crucial. Traditional multi-animal tracking systems, such as multi-animal DeepLabCut (maDLC) and Social LEAP Estimates Animal Poses (SLEAP), use frame-by-frame identification to predict movements without the need for markers. While these tools effectively track poses, such as head direction, in simple scenarios, ...
A special collection to highlight recent advances in air pollution complex research in China
2025-02-20
Air pollution is a global environmental problem with serious impacts on human health, climate change, and ecological systems. In China, rapid development in the last several decades has led to a drastic increase in coal consumption and the number of vehicles. As a result, air pollution in China is complicated by the coexistence of high concentrations of primary and secondary trace gases and aerosol particles from multiple sources.
Air pollution complex is a term used to characterize the formation mechanisms of air pollution, and was first proposed by Professor Xiaoyan Tang in 1997. A better understanding of these complex mechanisms is critical for meeting the urgent societal ...
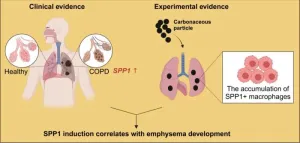
Macrophages express high level of Spp1, linking the environmental particle pollution exposure and the development of emphysema - an important finding for COPD
2025-02-20
This study is led by Dr. Lianyong Han and Dr. Tobias Stoeger in Germany (Institute of Lung Health and Immunity (LHI), Comprehensive Pneumology Center (CPC), Helmholtz Zentrum München, German Research Center for Environmental Health).
By analyzing multiple emphysema and COPD patient datasets, SPP1 is significantly upregulated in the lungs of patients, compared to healthy individuals. “These findings pointed out the clinical relevance of SPP1 induction during COPD development and has motivated us to understand their contributions ...
Fitness apps fuelling disordered eating
2025-02-20
With New Year resolutions in full swing and health tracking apps at our fingertips, new research reveals concerning links between health and fitness apps and disordered eating, body image concerns and excessive exercise.
“Diet and fitness apps are marketed as tools to improve health, however they may also have unintended negative consequences, such as creating pressure to meet goals, concerns about body image as well as provoking feelings of guilt if goals aren’t achieved,” says Ms Isabella Anderberg in the College of Education, Psychology and Social Work.
“Whilst there is evidence that these tools can be effective in increasing physical activity, we’re ...
Duke-NUS study targets proteins to reverse lung scarring
2025-02-20
Singapore, 20 February 2025—A discovery at Duke-NUS Medical School offers new hope in the battle against pulmonary fibrosis, a debilitating lung condition that progressively makes it harder for patients to breathe. Scientists have pinpointed proteins in immune cells that, when blocked, could significantly reduce lung tissue scarring.
Current treatments primarily manage symptoms and improving quality of life, without addressing the underlying cause of pulmonary fibrosis.
Although macrophages, a type of immune cell, had previously been known to contribute to inflammation ...
New toolkit empowers healthcare providers with evidence-based strategies for childhood obesity prevention and treatment
2025-02-20
Greaux Healthy—a public service initiative powered by Pennington Biomedical Research Center, in partnership with the State of Louisiana—is proud to announce the release of the Childhood Obesity Prevention, Evaluation and Treatment Toolkit, a comprehensive resource designed to equip healthcare providers with practical, evidence-based guidance for preventing, evaluating, and treating childhood obesity and its related comorbidities.
Developed in alignment with the 2023 American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) clinical practice guidelines, the toolkit synthesizes the latest scientific evidence and ...
UT MD Anderson and Texas Children’s Hospital announce joint venture to end childhood cancer
2025-02-20
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Texas Children’s Hospital have announced a transformational collaboration dedicated solely to pediatric cancer care. Approved by the UT System Board of Regents and the Texas Children’s Board of Trustees, this new, first-of-its-kind joint venture will unite the nation’s largest comprehensive pediatric system and a top pediatric cancer program with the nation’s leading comprehensive cancer center. The collaboration has a single ...