(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON (Feb. 20, 2025)--A new study analyzes the disease burden and the risk factors for severity among people who suffer from a condition called cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome. Researchers at the George Washington University say the condition occurs in people who are long-term regular consumers of cannabis and causes nausea, uncontrollable vomiting and excruciating pain in a cyclical pattern that often leads to repeated trips to the hospital.
“This is one of the first large studies to examine the burden of disease associated with this cannabis-linked syndrome,” says Andrew Meltzer, professor of emergency medicine at the GW School of Medicine & Health Sciences and lead author of the study. “Our findings suggest that cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome could represent a costly and largely hidden public health problem.” While the exact prevalence of the condition is unknown, many experts say that the condition is on the rise as the number of daily or near daily users of cannabis has increased in the US.
To assess the burden of disease, Meltzer and his colleagues conducted a survey of 1,052 people who report suffering from cannabinoid hyperemesis syndrome. The researchers asked questions about frequency of use, duration of the habit, the age they started using the drug, and need for emergency department or hospital care.
Key findings of the study:
85% reported at least 1 emergency department visit and 44% reported at least 1 hospitalization associated with the hyperemesis symptoms.
Early age of cannabis initiation was associated with higher odds of emergency department visits.
Daily use of cannabis before the onset of the syndrome was nearly universal, with over 40% of respondents reporting they used marijuana more than 5 times a day.
Prolonged use was common with 44% reporting using regularly for more than 5 years before onset of syndrome.
The new research suggests that the condition may impose a heavy burden on individuals who suffer from it as it often results in pain, vomiting and costly trips to the hospital. Emergency room doctors can stabilize the patient and help alleviate the acute symptoms but the only known way to stop the episodes of excruciating abdominal pain and repeated vomiting is to stop using cannabis, Meltzer says.
Although this study had some limitations, including self reported use of cannabis, Meltzer says it suggests a substantial risk of this painful and costly condition, especially for users who begin daily use of cannabis as adolescents. He says more research is needed to understand why some people suffer from the condition after prolonged cannabis exposure and others do not. In addition, it is unclear why cannabis changes from a drug that has been known to ease nausea and vomiting, especially among patients undergoing chemotherapy, to causing nausea and vomiting in a subset of people.
Meltzer says it is important for clinicians to advise those with frequent cannabinoid use or hyperemesis about the risks and subsequent disease burden. He says many patients don’t realize that the syndrome is connected with their use of cannabis. Physicians should explain that and advise patients on resources to help them quit, he says.
The study, Cannabinoid Hyperemesis Syndrome is Associated with High Disease Burden: An Internet-based Survey, was published in the Annals of Emergency Medicine on Feb. 20, 2025.
Andrew Meltzer explains more about the study in this GW video.
END
Daily cannabis use linked to public health burden
New study suggests daily users who start in their teens at higher risk of a syndrome that causes vomiting, pain and repeated trips to the hospital
2025-02-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A new gene identified in the search for a therapy to treat malignant cardiac arrythmia
2025-02-20
Cardiac arrhythmias affect millions across the world and are responsible for a fifth of all deaths in the Netherlands. Currently there are multiple treatment options, ranging from life-long medication to invasive surgical procedures. Research from Amsterdam UMC and Johns Hopkins University, published today in the European Heart Journal, sets another important step in the hunt for a one-off gene therapy that could improve heart function and protect against arrhythmias.
"Arrhythmias often occur due to slowing of conduction of the electrical impulse through the heart. Rapid impulse conduction is needed for ...
‘Fog harvesting’ could yield water for drinking and agriculture in the world’s driest regions
2025-02-20
With less annual rainfall than 1 mm per year, Chile’s Atacama Desert is one of the driest places in the world. The main water source of cities in the region are underground rock layers that contain water-filled pore spaces which last recharged between 17,000 and 10,000 years ago.
Now, local researchers have assessed if ‘fog harvesting,’ a method where fog water is collected and saved, is a feasible way to provide the residents of informal settlements with much needed water.
“This research represents a notable shift in the ...
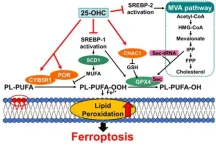
Unveiling the intricate mechanisms behind oxysterol-induced cell death
2025-02-20
Oxysterols are a class of molecules derived from cholesterol via oxidation or as byproducts of cholesterol synthesis. Despite their relatively low concentration within our bodies, oxysterols are known to play many important biological roles, acting as transcriptional regulators, precursors for bile acid, and key players in brain development.
On the flip side, some pathologies are associated with imbalances in oxysterols. In particular, 25-hydroxycholesterol (25-OHC) has been shown to contribute to arteriosclerosis, cancer development, central nervous system ...
Closing the recycle loop: Waste-derived nutrients in liquid fertilizer
2025-02-20
Growing plants can be a joyous, yet frustrating process as plants require a delicate balance of nutrients, sun, and water to be productive.
Phosphorus and nitrogen, which are essential for plant growth, are often supplemented by chemical fertilizers to assure proper balance and output of produce. However, the amount of these nutrients on the planet is increasing due to excessive use, which in turn is causing various environmental problems. For this reason, there is a growing movement to promote sustainable agriculture through the recycling of phosphorus and nitrogen. In Japan, a target has been ...
vmTracking enables highly accurate multi-animal pose tracking in crowded environments
2025-02-20
Studying the social behavior of animals in their natural environments is necessary for advancing our understanding of neurological processes. To achieve this, tracking multiple individuals simultaneously and accurately as they interact in shared spaces is crucial. Traditional multi-animal tracking systems, such as multi-animal DeepLabCut (maDLC) and Social LEAP Estimates Animal Poses (SLEAP), use frame-by-frame identification to predict movements without the need for markers. While these tools effectively track poses, such as head direction, in simple scenarios, ...
A special collection to highlight recent advances in air pollution complex research in China
2025-02-20
Air pollution is a global environmental problem with serious impacts on human health, climate change, and ecological systems. In China, rapid development in the last several decades has led to a drastic increase in coal consumption and the number of vehicles. As a result, air pollution in China is complicated by the coexistence of high concentrations of primary and secondary trace gases and aerosol particles from multiple sources.
Air pollution complex is a term used to characterize the formation mechanisms of air pollution, and was first proposed by Professor Xiaoyan Tang in 1997. A better understanding of these complex mechanisms is critical for meeting the urgent societal ...
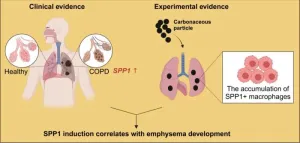
Macrophages express high level of Spp1, linking the environmental particle pollution exposure and the development of emphysema - an important finding for COPD
2025-02-20
This study is led by Dr. Lianyong Han and Dr. Tobias Stoeger in Germany (Institute of Lung Health and Immunity (LHI), Comprehensive Pneumology Center (CPC), Helmholtz Zentrum München, German Research Center for Environmental Health).
By analyzing multiple emphysema and COPD patient datasets, SPP1 is significantly upregulated in the lungs of patients, compared to healthy individuals. “These findings pointed out the clinical relevance of SPP1 induction during COPD development and has motivated us to understand their contributions ...
Fitness apps fuelling disordered eating
2025-02-20
With New Year resolutions in full swing and health tracking apps at our fingertips, new research reveals concerning links between health and fitness apps and disordered eating, body image concerns and excessive exercise.
“Diet and fitness apps are marketed as tools to improve health, however they may also have unintended negative consequences, such as creating pressure to meet goals, concerns about body image as well as provoking feelings of guilt if goals aren’t achieved,” says Ms Isabella Anderberg in the College of Education, Psychology and Social Work.
“Whilst there is evidence that these tools can be effective in increasing physical activity, we’re ...
Duke-NUS study targets proteins to reverse lung scarring
2025-02-20
Singapore, 20 February 2025—A discovery at Duke-NUS Medical School offers new hope in the battle against pulmonary fibrosis, a debilitating lung condition that progressively makes it harder for patients to breathe. Scientists have pinpointed proteins in immune cells that, when blocked, could significantly reduce lung tissue scarring.
Current treatments primarily manage symptoms and improving quality of life, without addressing the underlying cause of pulmonary fibrosis.
Although macrophages, a type of immune cell, had previously been known to contribute to inflammation ...
New toolkit empowers healthcare providers with evidence-based strategies for childhood obesity prevention and treatment
2025-02-20
Greaux Healthy—a public service initiative powered by Pennington Biomedical Research Center, in partnership with the State of Louisiana—is proud to announce the release of the Childhood Obesity Prevention, Evaluation and Treatment Toolkit, a comprehensive resource designed to equip healthcare providers with practical, evidence-based guidance for preventing, evaluating, and treating childhood obesity and its related comorbidities.
Developed in alignment with the 2023 American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) clinical practice guidelines, the toolkit synthesizes the latest scientific evidence and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Daily cannabis use linked to public health burdenNew study suggests daily users who start in their teens at higher risk of a syndrome that causes vomiting, pain and repeated trips to the hospital