(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. –Using underwater microphones and machine learning (ML), Cornell University researchers have developed a new method to estimate North Atlantic right whale numbers — offering a potentially safer and more cost-effective way to monitor this critically endangered species.
Their study, published in Endangered Species Research, demonstrates how microphones combined with ML and traditional aerial survey methods can help track right whale populations in Cape Cod Bay, a crucial feeding ground where the whales gather each spring.
To track this endangered species, researchers rely on costly and dangerous surveys by airplanes, or use sound recordings to identify their presence, or absence.
“Using sound recordings to monitor whale populations isn’t new,” said lead author Marissa Garcia of the Cornell Lab of Ornithology’s K. Lisa Yang Center for Conservation Bioacoustics. “What makes our study unique is that we were able to take those recordings and go beyond getting information on the presence or absence of whales to getting an approximate number of whales in an area.”
The team set out an array of marine autonomous recording units (MARU) across Cape Cod Bay to capture right whale sounds.
Following deployment of the MARUs, the team trained, validated and applied a deep-learning model that could automatically detect right whale sounds with 86% precision.
“By analyzing their distinctive upcall vocalizations, we can detect their presence continuously, day and night,” Garcia said. “This kind of round-the-clock monitoring that results from passive acoustic monitoring just isn’t possible with traditional aerial surveys, which can only happen in daylight hours and in good weather.”
Garcia says there’s still some uncertainty in the counts that the team needs to address in future research, but the team is optimistic that monitoring whale vocalizations holds promise for estimating the abundance of right whales to aid in conservation and management efforts.
Having the ability to expand monitoring efforts across larger areas of the ocean will help scientists better assess the species’ population numbers across the full extent of its range. Garcia said right whales have been traditionally thought of as a conservation challenge in New England, but right whales are found all along the East Coast.
“Using passive acoustic data and deep-learning tools, we can expand the area we can safely monitor and keep track of this critically endangered species,” Garcia said.
The work comes at a critical time for North Atlantic right whales, whose population has declined to fewer than 370 individuals due to ship strikes, fishing gear entanglement and changing ocean conditions affecting their food sources.
For additional information, see this Cornell Chronicle story.
END
Underwater mics and machine learning aid right whale conservation
2025-02-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Solving the case of the missing platinum
2025-02-21
For nearly two decades, scientists have tried to understand how negatively polarized platinum electrodes corrode, a costly mystery that plagues water electrolyzers, a promising energy technology for making hydrogen, as well as electrochemical sensors using platinum electrodes.
Now, a close collaboration between researchers at the Department of Energy’s SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and the Leiden University has finally identified the culprit, potentially paving the way for cheaper hydrogen energy production and more reliable electrochemical sensors. The results were published in Nature Materials.
Electrolyzers ...
Glass fertilizer beads could be a sustained nutrient delivery system
2025-02-21
Agricultural fertilizers are critical for feeding the world’s population, restoring soil fertility and sustaining crops. Excessive and inefficient use of those resources can present an environmental threat, contaminating waterways and generating greenhouse gases such as nitrous oxide. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Agricultural Science & Technology have addressed those challenges with glass fertilizer beads. The beads control nutrient release, and the researchers say they’re environmentally compatible.
“The results show that glass fertilizers can be tailored to plant needs, slowly and sustainably releasing ...
Biobased lignin gels offer sustainable alternative for hair conditioning
2025-02-21
Researchers at Stockholm University have developed a fully biobased hair conditioner using lignin gel emulsions, offering a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to conventional haircare products.
Hair conditioners typically contain 20–30 ingredients, many derived from petroleum and oleochemicals, raising concerns about sustainability and environmental impact. A new study published in Science Advances, demonstrates that micellar lignin gels can effectively stabilize emulsions with natural oils, reducing the need for synthetic surfactants and complex stabilizers commonly used in commercial formulations. The research team, led by Mika Sipponen at Stockholm University, ...
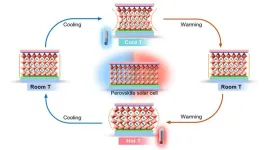
Perovskite solar cells: Thermal stresses are the key to long-term stability
2025-02-21
Perovskite solar cells are highly efficient and low cost in production. However, they still lack stability over the decades under real weather conditions. An international research collaboration led by Prof. Antonio Abate has now published a perspective on this topic in the journal Nature Reviews Materials. They explored the effects of multiple thermal cycles on microstructures and interactions between different layers of perovskite solar cells. They conclude that thermal stress is the decisive factor in the degradation of metal-halide perovskites. Based on this, they derive the most promising strategies to increase the long-term stability of perovskite solar cells.
Perovskites ...
University of Houston professors named senior members of the National Academy of Inventors
2025-02-21
University of Houston professors Birol Dindoruk, Megan Robertson and Francisco Robles Hernandez have joined the prestigious list of Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors.
The University of Houston now has 39 faculty members in the NAI.
“We congratulate these three esteemed colleagues on being named NAI Senior Members,” said Ramanan Krishnamoorti, vice president for energy and innovation at UH. “This recognition is a testament to their dedication, research excellence and pursuit of real-world impact by knowledge and technologies. Their achievements continue to elevate the University as a leader in innovation and entrepreneurship.”
NAI Senior Members ...
Unraveling the mystery of the missing blue whale calves
2025-02-21
Only two blue whale births have ever been recorded in human history, both decades ago. This remains an extraordinary mystery given there used to be hundreds of thousands of blue whales before whaling started — even today blue whales number around 10,000 to 25,000 — and they give birth every two to three years.
Not only are births very stealthy, but calves are also only rarely sighted — far less than would be expected from their pregnancy rates. Calves closely follow their moms and are sighted as mother-calf pairs, but why are so few detected?
A new University ...
UTA partnership boosts biomanufacturing in North Texas
2025-02-21
The University of Texas at Arlington is joining forces with the Texas A&M Engineering Experiment Station (TEES) to operate the new National Center for Therapeutics Manufacturing Satellite Campus at Pegasus Park (NCTM2) in Dallas.
UTA’s Institute of Biomanufacturing and Precision Medicine (IMPRINT) is partnering with TEES on NCTM2, an extension of the National Center for Therapeutics Manufacturing (NCTM) in College Station. The collaboration will expand UTA’s biomanufacturing capabilities and provide NCTM2 with access to financial ...
Kennesaw State researcher earns American Heart Association award for innovative study on heart disease diagnostics
2025-02-21
Kennesaw State University researcher Chen Zhao has earned the 2025 American Heart Association Institutional Research Enhancement Award (AIREA) for his unique research on non-invasive blood flow prediction in cardiovascular disease diagnosis.
The $194,032 award will allow Zhao to continue developing technology aimed at evaluating Fractional Flow Reserve (FFR), a measurement used to diagnose coronary artery disease (CAD). According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, CAD is the leading cause of death in the United States, with an average of 375,000 to ...
Self-imaging of structured light in new dimensions
2025-02-21
Researchers of photonics from Tampere University, Finland, and Kastler-Brossel Laboratory, France, have demonstrated how self-imaging of light, a phenomenon known for nearly two centuries, can be applied to cylindrical systems, facilitating unprecedented control of light’s structure with great potential for advanced optical communication systems. In addition, a new type of space-time duality is explored for powerful analogies bridging different fields of optics.
In 1836, Henry F. Talbot performed an experiment, where ...
Study highlights successes of Virginia’s oyster restoration efforts
2025-02-21
Virginia has made significant investments in the restoration of oyster reefs in the Chesapeake Bay, and now a study led by William & Mary’s Batten School & VIMS suggests those management practices are literally paying off in the Rappahannock River. The study, recently published in the Journal of Environmental Management, was led by Batten School of Coastal & Marine Sciences Ph.D. student Alexandria Marquardt, who presented the results to the Virginia Marine Resources Commission’s (VMRC) Shellfish Management Advisory Committee ...