(Press-News.org) A UC Riverside computer science team has developed a sensor-based technology that could revolutionize commercial beekeeping by reducing colony losses and lowering labor costs.
Called the Electronic Bee-Veterinarian, or EBV, the technology uses low-cost heat sensors and forecasting models to predict when hive temperatures may reach dangerous levels. The system provides remote beekeepers with early warnings, allowing them to take preventive action before their colonies collapse during extreme hot or cold weather or when the bees cannot regulate their hive temperature because of disease, pesticide exposure, food shortages, or other stressors.
“We convert the temperature to a factor that we are calling the health factor, which gives an estimate of how strong the bees are on a scale from zero to one,” said Shamima Hossain, a Ph.D. student in computer science at UCR and lead author of a paper explaining the technology.
This simplified metric — with a score of ‘one' meaning the bees are at full strength — allows beekeepers unfamiliar with the underlying model to assess hive health quickly.
Boris Baer, a UCR professor of entomology, believes the technology could revolutionize beekeeping, which is essential to vast sectors of global agriculture. Honeybees pollinate more than 80 crops and contribute an estimated $29 billion annually to U.S. agriculture. Yet bee populations have declined due to various factors, including habitat loss, pesticide exposure, parasites, and climate change.
“Over the last year, the U.S. lost over 55% of its honeybee colonies,” Baer said, citing data from Project Apis m., which monitors beehive losses throughout the U.S. “We are experiencing a major collapse of bee populations, and that is extremely worrying because about one-third of what we eat depends on bees.”
Beekeepers now rely on their own judgment and manual inspections to detect problems, often leading to delayed interventions. With EBV, they can get real-time insights and predict conditions days in advance, significantly reducing labor costs, said Baer, who collaborated with Hossain and other scientists at UCR’s Bourns College of Engineering.
“People have dreamed of these sensors for a very long time,” Baer said. “What I like here is that this system is fully integrated into the hive setup that beekeepers already use.”
Temperature fluctuations are among the first responses to any kind of threats to a hive’s health. Honeybees maintain a precise internal hive temperature between 33 and 36 degrees Celsius (91.4–96.8°F), a requirement for proper brood development and colony survival, Baer said.
The EBV method is based on thermal diffusion equations and control theory, making its predictions interpretable to both scientists and beekeepers, Hossain said. The model uses temperature data collected from low-cost sensors installed inside the hive, feeding that information into an algorithm that predicts hive conditions several days in advance.
In tests conducted at UCR’s apiary, the EBV method analyzed data from 10 hives during initial development and later expanded to 25 hives. The technology has already proven its effectiveness, detecting conditions that required beekeeper intervention.
“When I looked at the dashboard and saw the health factor dropped below an empirical threshold, I contacted our apiary manager,” Hossain recalled. “When we went to check the hive, we found that there was actually something wrong, and they were able to take action to manage the situation.”
Hyoseung Kim, an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at UCR, explained that keeping costs low — under $50 per hive — is a high priority.
“There are commercial sensors available, but they are too expensive,” Kim said. “We decided to create a very cheap device using off-the-shelf components so that beekeepers can afford it.”
The research team is already working on the next phase, which is to develop automated hive climate controls that can be installed on hives and respond to EBV’s predictions, adjusting hive temperatures automatically.
“Right now, we can only issue warnings,” Hossain said. “But in the next phase, we are working on designing a system that can automatically heat or cool the hive when needed.”
The title of Hossain’s paper is “Principled Mining, Forecasting and Monitoring of Honeybee Time Series with EBV+” In addition to Hossain, Baer and Kim, the co-authors are Christos Faloutsos, professor of computer science at Carnegie Mellon University, and Vassilis Tsotras, professor of computer science and engineering at UCR.
All the authors are with UCR’s Center for Integrative Bee Research, one of the largest pollinator health research hubs in the nation.
END
Beehive sensors offer hope in saving honeybee colonies
Innovation allows for remote monitoring of beehive health
2025-02-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Award-winning research may unlock universe’s origins
2025-02-25
University of Texas at Arlington physicist Ben Jones has received an international honor for his contributions to developing advanced instruments used in particle physics research.
Dr. Jones, an associate professor of physics, was awarded the 2025 International Committee for Future Accelerators (ICFA) Early Career Researcher Instrumentation Award. Presented by the ICFA Instrumentation Innovation and Development Panel, the award recognizes significant advancements in the innovation and development of new instrumentation for future accelerator experiments.
He accepted the award last week at the 2025 Vienna ...
BRCA1 gene mutations may not be key to prostate cancer initiation, as previously thought
2025-02-25
Mutations in the BRCA1 gene that are either inherited (germline) or acquired (somatic) might not be key to the initiation of prostate cancer, as previously thought, suggests the first study of its kind, published online in the open access journal BMJ Oncology.
If confirmed in further studies, the findings suggest that it may be time to reassess current treatment with PARP (poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase) inhibitor drugs, which block the ability of cells, including cancer cells, to repair DNA damage, in men with BRCA1 genetic variants, say the researchers.
A linked editorial suggests that the findings pave the way for greater refinement of genetic ...
Melatonin supplementation may help offset DNA damage linked to night shift work
2025-02-25
Melatonin supplementation may help offset the DNA damage associated with night shift work by boosting the body’s ability to repair it, suggest the findings of a small clinical trial published online in the journal Occupational & Environmental Medicine.
Larger studies looking at varying doses and the potential long term effects of melatonin supplementation are now warranted, conclude the researchers.
Normal night-time production of the body clock hormone, melatonin, is suppressed in night shift workers. This compromises the body’s ability to repair oxidative DNA damage, the by-product of normal cellular processes, heightening the risk of ...
Common gynaecological disorders linked to raised heart and cerebrovascular disease risk
2025-02-25
Having one or more common gynaecological disorders, such as endometriosis or heavy or irregular periods, may be linked to a heightened risk of heart disease and conditions that affect blood flow to the brain (cerebrovascular disease), finds a pooled data analysis of the available evidence published online in the journal Heart.
Although the quality of the studies included in the analysis was variable, the researchers nevertheless conclude that clinicians and the public need to be more aware of these associations to potentially mitigate the risks.
Long term non-cancerous gynaecological disorders ...
Nerve fibers in the inner ear adjust sound levels and help compensate for hearing loss in mice, study finds
2025-02-25
The brain may play a role in helping the ear regulate its sensitivity to sound and compensate for hearing loss by sending a signal to a structure in the inner ear known as the cochlea, according to a study that was just published in the Journal of Neuroscience. The discovery could help researchers develop treatments for tough-to-treat hearing disorders such as hyperacusis, where everyday sounds seem uncomfortably loud, and tinnitus, a sensation of ringing, buzzing or other sound in the ear when there is no external source.
The findings were powered by a new ...
ECMWF – Europe’s leading centre for weather prediction makes forecast data from AI model available to all
2025-02-25
Embargo: 25 February 2025 00.01 AM GMT
ECMWF – Europe’s leading centre for weather prediction makes forecast data from AI model available to all
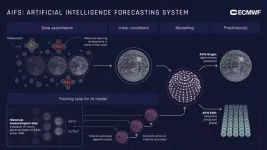
A newly operational model, known as the Artificial Intelligence Forecasting System (AIFS), has been launched by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF), an intergovernmental centre and leader in numerical weather prediction. For many measures including tropical cyclone tracks, the AIFS outperforms state-of-the-art physics-based models, with gains ...
New paper-based device boosts HIV test accuracy from dried blood samples
2025-02-24
In parts of the world where traveling to a clinic for routine blood tests is a financial and logistical challenge, HIV patients increasingly have the option to collect and ship a drop of their blood in paper-based devices that absorb the sample and store it for analysis in far-away labs.
While this technology is helpful for tracking someone’s adherence to their drug regimen or monitoring disease progression, the most frequently used devices don’t control how much blood they collect, potentially leading to inaccurate readings of a person’s infection.
Understanding this limitation, Charlie Mace, an associate professor at Tufts University’s ...
Pay-for-performance metrics must be more impactful and physician-controlled
2025-02-24
Pay-for-Performance Metrics Must Be More Impactful and Physician-Controlled
Background: This editorial builds on a study by Brulin and Teoh, released ahead of the March/April 2025 issue of Annals of Family Medicine, which found that performance-based reimbursement is associated with lower perceived quality of care by increasing illegitimate tasks and moral distress for primary care physicians.
Editorial Stance: Quality metrics and pay-for-performance initiatives are far more expensive than many patients, clinicians, or administrators realize. The authors call for more rigorous review through cluster randomized controlled trials both before and after implementation—and ...
GLP-1RAs may offer modest antidepressant effects compared to DPP4is but not SGLT-2is
2025-02-24
Follow @Annalsofim on X, Facebook, Instagram, threads, and Linkedin
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
Performance-based reimbursement increases administrative burden and moral distress, lowers perceived quality of care
2025-02-24
Performance-Based Reimbursement Increases Administrative Burden and Moral Distress, Lowers Perceived Quality of Care
Background and Goal: Performance-based reimbursement (PBR) is a payment system in which clinics receive compensation based on the quality and outcomes of care they deliver, rather than the volume of services provided. Although designed to improve efficiency and effectiveness, the growth of PBR systems has been linked to increased administrative work for physicians. This study examined how PBR affects doctors' perceived ability to provide quality ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
[Press-News.org] Beehive sensors offer hope in saving honeybee coloniesInnovation allows for remote monitoring of beehive health