(Press-News.org) A novel tool for rapidly identifying the genetic “fingerprints” of cancer cells may enable future surgeons to more accurately remove brain tumors while a patient is in the operating room, new research reveals. Many cancer types can be identified by certain mutations, changes in the instructions encoded in the DNA of the abnormal cells.
Led by a research team from NYU Langone Health, the new study describes the development of Ultra-Rapid droplet digital PCR, or UR-ddPCR, which the team found can measure the level of tumor cells in a tissue sample in only 15 minutes while also being able to detect small numbers of cancer cells (as few as five cells per square millimeter).
The researchers say their tool is fast and accurate enough, at least in initial tests on brain tissue samples, to become the first practical tool of its kind for detecting cancer cells directly using mutations in real time during brain surgery.
The researchers showed that UR-ddPCR had markedly faster processing speed than standard ddPCR, short for droplet digital polymerase chain reaction. Standard ddPCR can accurately quantify tumor cells, but it typically takes several hours to produce a result, making it impractical as a surgical guide.
“For many cancers, such as tumors in the brain, the success of cancer surgery and preventing the cancer’s return is predicated on removing as much of the tumor and surrounding cancer cells as is safely possible,” said study co-senior investigator and neurosurgeon Daniel Orringer, MD.
“With Ultra-Rapid droplet digital PCR, surgeons may now be able to determine what cells are cancerous and how many of these cancer cells are present in any particular tissue region at a level of accuracy that has never before been possible,” said Orringer, an associate professor in the Departments of Neurosurgery and Pathology at NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
Publishing in the Cell Press journal Med online Feb. 25, the study showed that UR-ddPCR produced the same results as standard ddPCR and genetic sequencing in more than 75 tissue samples from 22 patients at NYU Langone undergoing surgery to remove glioma tumors, a type of brain cancer. Results from UR-ddPCR were also checked against known samples with cancer cells and samples without any cancer.
“Our study shows that Ultra-Rapid droplet digital PCR could be a fast and efficient tool for making a molecular diagnosis during surgery for brain cancer, and it has potential to also be used for cancers outside the brain,” said study co-senior investigator Gilad Evrony, MD, PhD. Evrony is a geneticist at the Center for Human Genetics and Genomics at NYU Grossman School of Medicine and also serves as an assistant professor in the Departments of Pediatrics and Neuroscience at NYU Grossman School of Medicine.
To develop UR-ddPCR, researchers looked for efficiencies in each of the steps involved in standard ddPCR. The team shortened the time needed to extract DNA from tumor samples from 30 minutes to less than five minutes in a manner that is still compatible with subsequent ddPCR. The researchers also found efficiencies by increasing the concentrations of the chemicals used in testing, reducing the overall time needed for some steps from two hours to less than three minutes. Time savings were also achieved by using reaction vessels prewarmed to each of the two temperatures required by the PCR rather than repeatedly cycling the temperature of a single reaction vessel between two temperatures.
For the study, researchers used UR-ddPCR to measure the levels of two genetic mutations, IDH1 R132H and BRAF V600E, which are prevalent in brain cancers. They combined UR-ddPCR with another technique the researchers developed earlier, called stimulated Raman histology, to calculate both the fraction and the density of tumor cells within each tissue sample.
Researchers caution that widespread use of the tool awaits further refinements and clinical trials. They say their next step is to automate UR-ddPCR to make it faster and simpler to use in the operating room. Subsequent clinical trials will be necessary to compare patient outcomes using their tool compared to current diagnostic technologies. They also plan to develop the technology to identify other common genetic mutations for other cancer types.
Funding for the study was provided by National Institutes of Health grant R01CA226527. Study supplies were donated by Bio-Rad, the manufacturer of the ddPCR equipment used in the research, which had no other involvement in the study.
Besides Orringer and Evrony, other NYU Langone researchers involved in this study are lead investigator Zachary Murphy and Emilia Bianchini, and co-investigators Andrew Smith, Lisa Körner, Teresa Russell, David Reinecke, Nader Maarouf, Yuxiu Wang, John Golfinos, Alexandra Miller, and Matija Snuderl.
Orringer, Evrony, Murphy, and NYU have a patent application pending on their development of UR-ddPCR.
Orringer is a shareholder in Invenio Imaging, a company that develops and markets imaging equipment. He has also received consulting fees from Servier, a company involved in the production of anticancer therapies. Orringer and Snuderl also have financial interests in Imagenomix. Snuderl has served as an advisor to and has financial interests in Heidelberg EPignostix and Halo Dx. He has also been a paid advisor to Arima Genomics and InnoSIGN, and received research funding support from Lilly. All of these arrangements are being managed in accordance with the policies and practices of NYU Langone Health.
###
About NYU Langone Health
NYU Langone Health is a fully integrated health system that consistently achieves the best patient outcomes through a rigorous focus on quality that has resulted in some of the lowest mortality rates in the nation. Vizient, Inc., has ranked NYU Langone the No. 1 comprehensive academic medical center in the country for three years in a row, and U.S. News & World Report recently placed nine of its clinical specialties among the top five in the nation. NYU Langone offers a comprehensive range of medical services with one high standard of care across six inpatient locations, its Perlmutter Cancer Center, and more than 300 outpatient locations in the New York area and Florida. With $14.2 billion in revenue this year, the system also includes two tuition-free medical schools, in Manhattan and on Long Island, and a vast research enterprise with over $1 billion in active awards from the National Institutes of Health.
Media Inquiries:
David March
212-404-3528
david.march@nyulangone.org
STUDY DOI:
10.1016/j.medj.2025.100604
END
“Ultra-rapid” testing unlocks cancer genetics in the operating room
2025-02-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Mimicking shark skin to create clean cutting boards
2025-02-25
WASHINGTON, Feb. 25, 2025 – Keeping work surfaces clean during meat processing is a challenge. Bacteria from meat can attach, grow, and build up to create a biofilm that is difficult to remove, even on stainless steel surfaces used in industrial facilities. It can also aggregate, clumping together into an invisible mass that is stronger than individual cells, making it harder to kill using food-grade antibacterial surface cleaners.
In a paper published this week in Journal of Laser Applications, from AIP Publishing and the Laser Institute of America, researchers from the Hopkirk Research Institute, New Zealand Food Safety Science and Research Centre, ...
Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and obesity-linked cancer risk
2025-02-25
About The Study: The findings of this study indicate that higher adherence to the Mediterranean diet is associated with a modest reduction in the risk of obesity-related cancers, independent of adiposity measures. Further research is needed to clarify the mechanisms by which the Mediterranean diet may contribute to cancer prevention.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Inmaculada Aguilera-Buenosvinos, PhD, email iaguilerabuenosvinos@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.61031)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
New technique reveals how the same mutations give rise to very different types of leukaemia
2025-02-25
Barcelona, 25 February 2025 - Myeloid leukaemias are among the most aggressive blood cancers and have low survival rates. Today, leukaemia patients undergo genetic analysis to identify mutations and select the most appropriate treatment. However, even among patients with the same mutation, disease progression and response to therapy can vary significantly.
A study led by ICREA researcher Dr. Alejo Rodríguez-Fraticelli at IRB Barcelona, and funded by Fundación CRIS contra el cáncer, has now revealed these differences can be explained by the fact that not all blood stem cells ...
New insights into how gut cells respond to bacterial toxins
2025-02-25
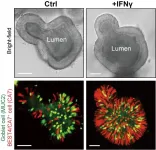
Researchers from the Organoid group at the Hubrecht Institute have found that specific gut cells, BEST4/CA7+ cells, regulate electrolyte and water balance in response to bacterial toxins that cause diarrhea. Their findings, published in Cell Stem Cell, show that these cells greatly increase in number when exposed to the cytokine interferon-γ (IFNγ), presenting a promising target for therapeutic strategies.
In the gut, a variety of cell types collaborate to keep a balance of electrolyte and water. Bacterial infections can disrupt this balance, leading ...
Designing self-destructing bacteria to make effective tuberculosis vaccines
2025-02-25
Working toward more effective tuberculosis (TB) vaccines, researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine have developed two strains of mycobacteria with "kill switches" that can be triggered to stop the bacteria after they activate an immune response. Two preclinical studies, published, Jan. 10 in Nature Microbiology, tackle the challenge of engineering bacteria that are safe for use in controlled human infection trials or as better vaccines. While TB is under control in most developed countries, the disease still kills over a million people a year worldwide.
Spreading easily through ...
SwRI-led PUNCH spacecraft poised for launch into polar orbit
2025-02-25
SAN ANTONIO — February 25, 2025 —Four small suitcase-sized spacecraft, designed and built by Southwest Research Institute headquartered in San Antonio, are poised to launch from Vandenberg Space Force Base in California no earlier than Feb. 28. NASA’s Polarimeter to Unify the Corona and Heliosphere, or PUNCH, spacecraft is sharing a ride to space with the Spectro-Photometer for the History of the Universe, Epoch of Reionization and Ices Explorer (SPHEREx) observatory.
“The PUNCH mission will study the solar corona, the Sun’s outer atmosphere, and the solar wind that fills ...
Orthopedic team from Peking Union Medical College Hospital publishes longest-term follow-up study on post-TKA outcomes in Chinese patients with knee osteoarthritis
2025-02-25
Knee osteoarthritis (KOA) is prevalent among middle-aged and elderly populations, can cause disability and significantly impairs quality of life. Total knee arthroplasty (TKA) is an effective treatment for end-stage KOA; however, long-term outcome and prosthesis survivorship were limited reported, particularly in Chinese cohorts.
Led by Professor Weng Xi-sheng and Professor Feng Bin, the orthopedic team at Peking Union Medical College Hospital conducted a landmark follow-up study spanning over two decades. The research analyzed KOA patients who underwent primary ...
Lung abnormalities seen in children and teens with long COVID
2025-02-25
OAK BROOK, Ill. – An advanced type of MRI uncovers significant lung abnormalities in children and adolescents with long COVID, according to a new study published today in Radiology, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Post-COVID-19 condition, commonly known as long COVID, can affect individuals of all ages and is diagnosed when symptoms persist for more than 12 weeks after an initial COVID-19 infection. Children and adolescents typically experience a milder form of the condition, but common symptoms such as chronic fatigue, headaches and poor concentration can negatively impact school performance and social activities.
While ...
NBA and NBA G League Player Ambassadors urge fans to learn lifesaving CPR in 90 seconds
2025-02-25
DALLAS, February 25, 2025 — More than half of people who experiencing sudden cardiac arrest out of hospital don’t receive immediate cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), contributing to a high death rate. A many as 9 out of 10 people who experience sudden cardiac arrest die[1]. CPR, especially if performed immediately, can double or triple a person’s chance of survival. To save more lives, the American Heart Association, a global force changing the future of health for all, and National Basketball Association/NBA G League players are working to educate about the lifesaving skill.
More Americans than ...
Hormones may have therapeutic potential to prevent wrinkles, hair graying
2025-02-25
WASHINGTON—Hormones may be leveraged to treat and prevent signs of aging such as wrinkles and hair graying, according to a new study published in the Endocrine Society journal Endocrine Reviews.
Until now, only a limited number of hormones, mainly topical retinoids (retinol and tretinoin) and estrogen which is typically used to treat side effects of menopause, have been used in clinical practice as anti-skin aging compounds. This study reviews a new class of hormones and their anti-aging properties.
“Our paper highlights key hormone players that orchestrate pathways of skin aging such as ...