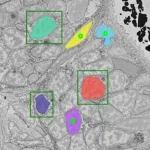
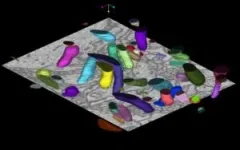
(Press-News.org) UdeM reproductive biologist Greg FitzHarris and his team show for the first time that sister cells can communicate with each other through a bridge that allows them to die in a coordinated way.
Sister cells are a pair of cells that share the same mother cell. In a new study published in Developmental Cell, researchers led by Université de Montréal (UdeM) professor Greg FitzHarris show how the early mouse embryo gets rid of the defective or unneeded cells in pairs.
“Such a mechanism could serve to ensure the elimination of cells with a common adverse history, such as DNA damage or aneuploidy, an abnormal number of chromosomes in cells known to be one of the main causes of infertility,” said FitzHarris, a researcher at the UdeM-affiliated hospital research centre, the CRCHUM.
In the new study, first author Filip Vasilev, a former postdoctoral fellow in FitzHarris’ laboratory, shows that abscission, the final step of cell division, is delayed in the early mouse embryo, leaving sister cells connected by a stable cytoplasmic bridge.
This bridge between sister cells allows the exchange of molecules that promote apoptosis, the process of programmed cell death in which the body rids itself of unneeded cells.
In humans, apoptosis occurs during early development to eliminate unwanted cells, such as those between the fingers of a developing hand. It also plays an important role in the proper closure of the neural tube—the part of an embryo where the brain and spinal cord develop—and in the normal development of major heart vessels.
Death bridge
“One consequence of this bridge is that sister cells undergo apoptosis in unison,” said FitzHarris. “In other words, if one cell dies, so does its sister. In our study, we have shown that the apoptotic pairing is prevented when the bridge is eliminated. It plays a key role.”
The bridge acts as a true cell-to-cell communication channel, coordinating the clearance of pairs of cells with a similar developmental history.
The question of whether the coordination mechanisms observed by researchers in mice can be extrapolated to humans remains unanswered. FitzHarris’ team is currently studying human embryos.
Science writing: Bruno Geoffroy
###
About this study
“Long-lived cytokinetic bridges coordinate sister-cell elimination in mouse embryos,” by Filip Vasilev under the supervision of Greg FitzHarris et al., was published online Jan. 24, 2025, in Developmental Cell. Funding was provided by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research and the Fondation Jean-Louis Lévesque. The research was supported by the CRCHUM’s animal facility and the genetic engineering and animal modelling core facility.
About the CHUM Research Centre (CRCHUM)
Université de Montréal's affiliated hospital research centre, the CRCHUM, is one of North America’s leading hospital research centres. It strives to improve the health of adults through a continuum of research spanning disciplines such as basic science, clinical research and population health. About 2,130 people work at CRCHUM. These include more than 550 researchers and nearly 530 graduate students and postdoctoral fellows. crchum.com
About Université de Montréal
Deeply rooted in Montréal and dedicated to its international mission, Université de Montréal is one of the top universities in the French-speaking world. Founded in 1878, Université de Montréal today has 13 faculties and schools, and together with its two affiliated schools, HEC Montréal and Polytechnique Montréal, constitutes the largest centre of higher education and research in Québec and one of the major centres in North America. It brings together 2,300 professors and researchers and has close to 67,000 students. umontreal.ca
END
Identifying and delineating cell structures in microscopy images is crucial for understanding the complex processes of life. This task is called “segmentation” and it enables a range of applications, such as analysing the reaction of cells to drug treatments, or comparing cell structures in different genotypes. It was already possible to carry out automatic segmentation of those biological structures but the dedicated methods only worked in specific conditions and adapting them to new conditions was costly. An international ...
AURORA, Colo. (Feb. 25, 2025) – A new study, published today in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, tested whether a set of interventions to keep lungs expanded before, during, and after abdominal surgery could lower the risk of serious breathing problems in patients compared to the usual care at 17 academic hospitals in the U.S. The research has determined that these interventions for open abdominal surgery do not result in less severe breathing problems as compared to the usual care in those hospitals.
Adult abdominal surgery patient enrollees were either given a lung expansion set of interventions or the typical care plan to follow at each hospital. ...
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, TUESDAY, FEBRUARY 25, 2025
Media Contacts:
Renee Tessman, rtessman@aan.com, (612) 928-6137
Natalie Conrad, nconrad@aan.com, (612) 928-6164
Microplastics in ocean linked to disabilities for coastal residents
Mobility, self-care, independent living disability higher in areas with high microplastics
MINNEAPOLIS – Tiny bits of plastic found in the ocean may be tied to a higher risk of disability for people who live in coastal areas with high levels, according to a preliminary study released today, ...
ROCKVILLE, MD – The 10 winners of the annual Undergraduate Poster Award Competition (UPAC) were recognized at the 69th Biophysical Society Annual Meeting Awards Ceremony on February 17, 2025. After two rounds of judging, judges from every career level selected these students for their outstanding presentations during the poster competition. Seventy-four students participated in the competition.
The 2025 UPAC winners are:
Adam Gatch, Clemson University, USA – “AΒ42 Accelerates Pathogenic Structural Transformation Within ...
How can the loss of species and habitats in agricultural landscapes be stopped? Up to now, measures have mostly been implemented by individual farms. In contrast, agri-environmental measures that are planned across farms at landscape level offer greater potential for creating suitable habitats for different species as a mosaic in the landscape. However, successful landscape level approaches also require cooperation between farms and other stakeholders from local governments, politics and nature conservation. Researchers at the University of Göttingen have therefore identified ...
LA JOLLA, CA—Scientists at La Jolla Institute for Immunology (LJI) have found a potential new target for treating Parkinson's disease. Their new research reveals how a protein in brain cells may drive Parkinson's onset—and offers a possible explanation for why Parkinson's is much more common in men.
In recent years, LJI scientists have found increasing evidence that autoimmunity plays a role in the onset of Parkinson's disease. Their recent study in The Journal of Clinical Investigation shows that PINK1 appears to mark ...
WASHINGTON—The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) has published an expert consensus statement that provides interventional cardiologists, cardiothoracic surgeons, and heart teams with practical guidance for selecting patients and performing alternative access transaortic valve replacement (TAVR).
TAVR has seen substantial growth over the past decade, becoming a standard of care for many patients with asymptomatic aortic stenosis. However, some patients face challenges due to inadequate femoral vascular access. The new guidelines address this gap by recommending alternative access ...
The efficient architecture of our joints, which allows our skeletons to be flexible and sturdy, originated among our most ancient jawed fish ancestors, according to a study published February 25th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Neelima Sharma of the University of Chicago and colleagues.
Synovial joints are a key feature of most vertebrate skeletons, providing more mobility and stability compared to other joint types. A synovial joint allows bones or cartilage to slide past each other with the aid of a lubricated cavity between them. These joints are present in land vertebrates and bony fish, suggesting this feature had evolved in the common ancestors of these groups, but ...
A world of microbes resides within the gut of every human being. This vast microbial community, the microbiome, which includes bacteria and viruses, has repeatedly demonstrated its ability to actively contribute to both health and disease.
Researchers have learned a good deal about the bacterial communities that live in the human gut. For instance, they have discovered that these bacteria extensively metabolize the food we eat, drive normal development of the immune system and, to our detriment, include some opportunistic microorganisms that can cause disease under certain conditions.
On the other hand, the contributions of viruses in the gut microbiome ...
WHAT:
Lowering the body temperature of preterm infants (born at 33 to 35 weeks of pregnancy) with hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE)—a type of brain damage caused by oxygen loss—offers no benefits over standard care, according to a study funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Previous studies of near-term and term infants (born after 36 weeks) with HIE found that this cooling treatment, which lowers body temperature to about 92 degrees Fahrenheit, significantly reduced the risk of death or disability by age 18 months (corrected for prematurity). However, the current findings show ...