A new path to recovery: Scientists uncover key brain circuit in the fight against cocaine use disorder
2025-02-26
(Press-News.org) PHILADELPHIA (February 26, 2025) – Imagine a future where the grip of cocaine use disorder can be loosened, where cravings fade, and the risk of relapse diminishes. A new study published in Science Advances, led by Penn Nursing’s Heath Schmidt, PhD, brings this vision closer to reality. The research has identified a critical brain circuit that plays a pivotal role in regulating cocaine-seeking behavior.
Cocaine use disorder casts a long shadow, trapping individuals in a cycle of dependence and leaving limited options for effective treatment. This study delves deep into the brain, offering crucial insights into the underlying mechanisms of this complex disorder. By understanding how this intricate circuitry functions, scientists can pave the way for the development of more effective therapies, offering new hope to those struggling with this debilitating disorder.
At the heart of this discovery lies the role of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), a hormone known for its involvement in regulating food intake and blood sugar. The study reveals that chronic cocaine use is associated with reduced GLP-1 levels, effects that suggest that increasing central GLP-1 signaling could reduce cocaine seeking.
Further investigation pinpointed a specific brain circuit: GLP-1-producing neurons in the nucleus tractus solitarius (NTS) that project to the ventral tegmental area (VTA), a key brain region involved in reward and motivation. By manipulating this circuit, researchers were able to significantly reduce cocaine-seeking behavior in animal models.
The study also sheds light on the specific cells involved. GLP-1 receptors were found to be primarily located on GABA neurons within the VTA. GABA, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, plays a crucial role in regulating brain activity. Importantly, activating these GLP-1 receptors increases the activity of GABA neurons, which in turn reduces the activity of dopamine neurons, a key neurotransmitter involved in reward and addiction.
"This research provides exciting new insights into the brain mechanisms underlying cocaine seeking," said Schmidt, the Killebrew-Censits Chair of Undergraduate Education and a Professor of Neuroscience and Pharmacology in the Department of Biobehavioral Health Sciences. "By understanding how GLP-1 signaling influences brain activity in this context, we can potentially develop new GLP-1-based treatments to treat cocaine use disorder."
This research opens a new chapter in the fight against cocaine use disorder. The findings offer a promising avenue for developing innovative therapies that target this critical brain circuit, potentially offering a lifeline to individuals struggling to break free from the grip of this devastating disorder.
# # #
About the University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing
The University of Pennsylvania School of Nursing is one of the world’s leading schools of nursing. For the ninth year in a row, it is ranked the #1 nursing school in the world by QS University. Our Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN) is among the top ranked programs in the nation according to the 2025 U.S. News & World Report’s Best Colleges rankings. Our School also consistently ranks highly in the U.S. News & World Report annual list of best graduate schools and is ranked as one of the top schools of nursing in funding from the National Institutes of Health. Penn Nursing prepares nurse scientists and nurse leaders to meet the health needs of a global society through innovation in research, education, and practice. Follow Penn Nursing on: Facebook, X, LinkedIn, YouTube, & Instagram.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-02-26
Education experts at the University of South Australia are encouraging schools to consider problem-based learning (PBL) in a move to improve engagement and creativity among high school students.
The call follows new Productivity Commission data that shows national school attendance rates over the past year have decreased from 88.8% in Year 7 to 84% in Year 10. Government schools are worst hit, with only 73% of public-school students completing year 12, as compared with nearly 80% in 2017.
New UniSA research demonstrates how hands-on, community-based projects can deliver successful ...
2025-02-26
Please mention in your story that the study is published in Neurology, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
MINNEAPOLIS — ALS, or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, can sometimes be difficult to diagnose or to predict how quickly the disease is likely to progress. A new study helps determine which blood tests are best at identifying and monitoring ALS. The study is published in the February 26, 2025, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Having an effective biomarker can be highly valuable—in addition to helping ...
2025-02-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, FEBRUARY 26, 2025
Media Contacts:
Renee Tessman, rtessman@aan.com, (612) 928-6137
Natalie Conrad, nconrad@aan.com, (612) 928-6164
Drug may prevent some migraine attacks in children and teens
MINNEAPOLIS – For children and teens living with migraine, there may be a new preventive treatment, according to a preliminary study released today, February 26, 2025, that will be presented at the American Academy of Neurology’s 77th Annual Meeting taking place April 5–9, 2025, in San Diego ...
2025-02-26
Although preventing all the consequences of climate change is now impossible, we can adopt policies to mitigate its impact. In a set of policy recommendations produced by the University of Jyväskylä, researchers examine the development of sustainable livelihoods in the Sundarbans, a coastal region of India and Bangladesh that is vulnerable to the impacts of climate change. The Sundarbans is one of the largest threatened mangrove ecosystems, which efficiently store carbon dioxide and protect coastal areas from cyclones.
In a research project funded by the Research Council ...
2025-02-26
Shark sightings by scuba divers reveal the movements of marine predators throughout the year, according to a study published February 26, 2025 in the open-access journal PLOS One by George Balchin, William Hughes and colleagues at the University of Sussex, U.K., and Aquaplanet Dive Center, South Africa.
Many sharks move through different habitats as they follow food or search for mates. Since they are major predators, they change the shape of the ecosystems they visit. Examining these movements is key to understanding the health of ocean habitats as well as the impacts of human activity, but it is notoriously ...
2025-02-26
Eavesdropping on baleen whale songs in the Pacific Ocean reveals year-to-year variations that track changes in the availability of the species they forage on, reports a new study led by John Ryan, of the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (MBARI), U.S., published February 26, 2025 in the open-access journal PLOS One.
In the vast oceans, monitoring populations of large marine animals can be a major challenge for ecologists. Scientists deploy underwater microphones called hydrophones to study and track baleen whales, which communicate ...
2025-02-26
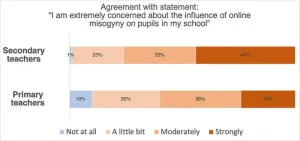
In a survey study of 200 U.K. teachers, 76 percent of secondary school teachers and 60 percent of primary school teachers expressed extreme concern about the influence of online misogyny on their students. Harriet Over of the University of York, U.K., and colleagues present these findings in the open-access journal PLOS One on February 26, 2025.
Prior research has shown that young students are increasingly exposed to social media content created by misogynistic influencers, such as Andrew Tate and members of the incel movement. However, few researchers have examined ...
2025-02-26
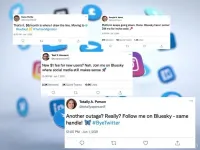
A comprehensive analysis of social media platform Bluesky provides insights into its structure, polarization and political leanings, in a new study published in open-access journal PLOS One on February 26, 2025, by Dorian Quelle and Alexandre Bovet, from the University of Zurich, Switzerland.
Many social media platforms rely on proprietary algorithms to recommend content, a methodology that has received increasing backlash over the years. However, Bluesky instead allows users the ability to curate their experiences. The authors of the present study analyzed the social media site’s trajectory from its invite-only launch ...
2025-02-26
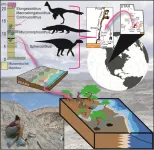
Fossil eggshells from Utah's Cedar Mountain Formation include Cretaceous period eggs from 3 feathered bird-like dinosaurs, 2 herbivorous dinosaurs, and a crocodile-like species found for the first time outside Europe
Article URL: https://plos.io/42XpPYx
Article title: Fossil eggshell diversity of the Mussentuchit Member, Cedar Mountain Formation, Utah
Author countries: U.S., South Africa
Funding: This research was supported by Canyonlands Natural History Association, Global Creatures, and MagicSpace ...
2025-02-26
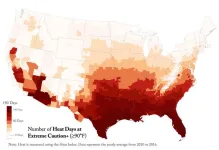
A new USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology study suggests greater exposure to extreme heat may accelerate biological aging in older adults, raising new concerns about how climate change and heat waves could affect long-term health and aging at the molecular level.
People in neighborhoods that experience more days of high heat show greater biological aging on average than residents of cooler regions, said Jennifer Ailshire, senior author of the study and professor of gerontology and sociology at the USC Leonard Davis School.
Biological age is a measure of how well the body functions at the molecular, cellular, and system ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] A new path to recovery: Scientists uncover key brain circuit in the fight against cocaine use disorder