(Press-News.org) A new USC Leonard Davis School of Gerontology study suggests greater exposure to extreme heat may accelerate biological aging in older adults, raising new concerns about how climate change and heat waves could affect long-term health and aging at the molecular level.
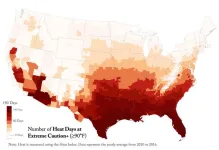
People in neighborhoods that experience more days of high heat show greater biological aging on average than residents of cooler regions, said Jennifer Ailshire, senior author of the study and professor of gerontology and sociology at the USC Leonard Davis School.
Biological age is a measure of how well the body functions at the molecular, cellular, and system levels, as opposed to chronological age based on one’s birthdate; having a biological age greater than one’s chronological age is associated with higher risk for disease and mortality. While exposure to extreme heat has itself long been associated with negative health outcomes, including increased risk of death, heat’s link to biological aging has been unclear.
Measuring epigenetic changes
Ailshire and her coauthor Eunyoung Choi, USC Leonard Davis PhD in Gerontology alumna and postdoctoral scholar, examined how biological age changed in more than 3,600 Health and Retirement Study (HRS) participants aged 56 and older from throughout the U.S. Blood samples taken at various time points during the six-year study period were analyzed for epigenetic changes, or changes in the way individual genes are turned “off” or “on” by a process called DNA methylation.
The researchers used mathematical tools called epigenetic clocks to analyze methylation patterns and estimate biological ages at each time point. They then compared participants’ changes in biological age to their location’s heat index history and number of heat days reported by the National Weather Service from 2010 to 2016.
The National Weather Service Heat Index Chart categorizes heat index values into three levels based on the potential risk of adverse health effects. The “Caution” level includes heat index values ranging from 80°F to 90°F, the “Extreme Caution” level includes values between 90°F and 103°F, and the “Danger” level includes values between 103°F and 124°F. Days in all three levels were included as heat days in the study.
The analysis revealed a significant correlation between neighborhoods with more days of extreme heat and individuals experiencing greater increases in biological age, Choi said. This correlation persisted even after controlling for socioeconomic and other demographic differences, as well as lifestyle factors such as physical activity, alcohol consumption and smoking, she added.
“Participants living in areas where heat days, as defined as Extreme Caution or higher levels (≥90°F), occur half the year, such as Phoenix, Arizona, experienced up to 14 months of additional biological aging compared to those living in areas with fewer than 10 heat days per year,” she said. “Even after controlling for several factors, we found this association. Just because you live in an area with more heat days, you're aging faster biologically.”
All three epigenetic clocks employed in the study – PCPhenoAge, PCGrimAge, and DunedinPACE – revealed this association when analyzing epigenetic aging over a 1- to 6-year period. PCPhenoAge also showed the association after short (7 days) and medium (30-60 days) periods of time, indicating that heat-related epigenetic changes could happen relatively quickly, and some of them may accumulate over time.
Climate implications for communities
Older adults are particularly vulnerable to the effects of high heat, Ailshire said. She noted that the study used heat index, rather than just air temperature, to take relative humidity into account as they analyzed results.
“It's really about the combination of heat and humidity, particularly for older adults, because older adults don't sweat the same way. We start to lose our ability to have the skin-cooling effect that comes from that evaporation of sweat,” she explained. “If you’re in a high humidity place, you don’t get as much of that cooling effect. You have to look at your area’s temperature and your humidity to really understand what your risk might be.”
The next steps for the researchers will be to determine what other factors might make someone more vulnerable to heat-related biological aging and how it might connect to clinical outcomes. In the meantime, the study results could also prompt policymakers, architects, and others to keep heat mitigation and age-friendly features in mind as they update cities’ infrastructure, from placing sidewalks and building bus stops with shade in mind to planting more trees and increasing urban green space, Ailshire said.
“If everywhere is getting warmer and the population is aging, and these people are vulnerable, then we need to get really a lot smarter about these mitigation strategies,” she said.
---
The study, “Ambient Outdoor Heat and Accelerated Epigenetic Aging among Older Adults in the U.S.,” appeared in the journal Science Advances on February 26, 2025. Funding for the study included the USC/UCLA Center on Biodemography and Population Health through a grant from the National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health (P30AG017265) and The Network on Life Course Health Dynamics and Disparities in 21st Century America funded by the National Institute on Aging, National Institutes of Health (R24AG045061).
END
Study: Extreme heat may speed up aging in older adults
People in neighborhoods that experience more days of high heat show faster aging at the molecular level than residents of cooler regions, say USC researchers
2025-02-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A springtail-like jumping robot
2025-02-26
Springtails, small bugs often found crawling through leaf litter and garden soil, are expert jumpers. Inspired by these hopping hexapods, roboticists in the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have made a walking, jumping robot that pushes the boundaries of what small robots can do.
Published in Science Robotics, the research glimpses a future where nimble microrobots can crawl through tiny spaces, skitter across dangerous ground, and sense their environments without ...
When the wild things are: URI team reports on mammalian daily activity with surprising results
2025-02-26
KINGSTON, R.I. – Feb. 26, 2025 – Animal antics have captured public attention and viral views across the U.S. in the last few years with the advent of mini cameras that capture the movements of animals in front yards nationwide, from bear to deer.
A University of Rhode Island-based group has taken the camera concept one step further and then some, generating a massive dataset of animal images, not for entertainment, but for science.
When the Global Animal Diel Activity Project results were analyzed, researchers made some unique discoveries.
Put together, researchers across the country and around the world generated a more focused picture of animal ...
Morphing robot turns challenging terrain to its advantage
2025-02-26
From mountain goats that run up near-vertical rock faces to armadillos that roll into a protective ball, animals have evolved to adapt effortlessly to changes in their environment. In contrast, when an autonomous robot is programmed to reach a goal, each variation in its pre-determined path presents a significant physical and computational challenge.
Researchers led by Josie Hughes in the CREATE Lab in EPFL’s School of Engineering wanted to develop a robot that could traverse diverse environments as adeptly as animals by changing form on the fly. With GOAT (Good Over All Terrains) they have achieved just that – and created a new paradigm for robotic ...
New study reveals how rogue planetary-mass objects form in young star clusters
2025-02-26
A groundbreaking study published in Science Advances sheds new light on the mysterious origins of free-floating planetary-mass objects (PMOs)—celestial bodies with masses between stars and planets.
Led by Dr. DENG Hongping of the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, an international team of astronomers used advanced simulations to uncover a novel formation process for these enigmatic objects. The research suggests that PMOs can form directly through violent interactions between circumstellar disks in young star clusters.
The Mystery of Rogue Planetary-Mass ...
School of rock: Properties of rocks in fault zones contribute to earthquake generation
2025-02-26
ANN ARBOR—Earthquakes occur along fault lines between continental plates, where one plate is diving beneath another. Pressure builds between each plate, called fault stress. When this stress builds enough to release, the plates slip and grind against each other, causing an earthquake.
Researchers have long thought that this force is the central driver of earthquakes. But another force is also in the mix: the properties of the rocks in the fault zones along the plate interface. This includes both the structure of the rock as well as how the rocks are arranged along the zones.
Now, a University of Michigan study looking at a small ...
Aston University microbiologist calls for public vigilance and urgent action on the danger of raw sewage in UK seas
2025-02-26
Dr Jonathan Cox writes in Microbiology about the pathogens in raw sewage and the “significant” danger to public health when it ends up in the sea
He contracted a lung infection in 2024, likely from exposure to raw sewage in the sea where he had been swimming
He urges people to check for sewage reports before heading to the beach and calls for investment to improve infrastructure.
Aston University microbiologist Dr Jonathan Cox has written an article for the journal Microbiology on ...
Supercomputing illuminates detailed nuclear structure
2025-02-26
Using the Frontier supercomputer at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory, researchers have developed a new technique that predicts nuclear properties in record detail.
The study revealed how the structure of a nucleus relates to the force that holds it together. This understanding could advance efforts in quantum physics and across a variety of sectors, from to energy production to national security.
“Our reliable predictions will bring new insights to the study of nuclear forces and structure,” said Zhonghao Sun of Louisiana State University, formerly of ORNL.
The team’s findings, published in the ...
Ohio tests new model for providing mental health resources to youth in rural communities
2025-02-26
During and after the height of the COVID-19 pandemic, telehealth appointments became a more common part of the American health care system. But even as telehealth options grow, barriers such as long waitlists or a lack of a stable internet connection mean many communities still do not have access to care, particularly for mental health services.
The University of Cincinnati, the Adams County Health Department (ACHD) and other local partners are testing a new collaborative care model that aims to remove these barriers and provide more students access to telemental health care. The team recently received a $1.75 million grant from the Health ...
Breast-conserving surgery improves sexual well-being compared to breast reconstruction
2025-02-26
February 26, 2025 — For women with breast cancer, breast-conserving therapy (BCT) is associated with improved sexual well-being, compared to mastectomy followed by breast reconstruction, reports a study in the March issue of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery®, the official medical journal of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS). The journal is published in the Lippincott portfolio by Wolters Kluwer.
"In our study, patients undergoing BCT scored consistently higher on a measure of sexual well-being, compared to total mastectomy and breast reconstruction," comments Jonas A. Nelson, MD, MPH, of Memorial ...
What can theoretical physics teach us about knitting?
2025-02-26
The practice of purposely looping thread to create intricate knit garments and blankets has existed for millennia. Though its precise origins have been lost to history, artifacts like a pair of wool socks from ancient Egypt suggest it dates back as early as the 3rd to 5th century CE. Yet, for all its long-standing ubiquity, the physics behind knitting remains surprisingly elusive.
“Knitting is one of those weird, seemingly simple but deceptively complex things we take for granted,” says ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
UF research finds a gentler way to treat aggressive gum disease
Strong alcohol policy could reduce cancer in Canada
Air pollution from wildfires linked to higher rate of stroke
Tiny flows, big insights: microfluidics system boosts super-resolution microscopy
Pennington Biomedical researcher publishes editorial in leading American Heart Association journal
New tool reveals the secrets of HIV-infected cells
HMH scientists calculate breathing-brain wave rhythms in deepest sleep
Electron microscopy shows ‘mouse bite’ defects in semiconductors
Ochsner Children's CEO joins Make-A-Wish Board
Research spotlight: Exploring the neural basis of visual imagination
Wildlife imaging shows that AI models aren’t as smart as we think
Prolonged drought linked to instability in key nitrogen-cycling microbes in Connecticut salt marsh
Self-cleaning fuel cells? Researchers reveal steam-powered fix for ‘sulfur poisoning’
Bacteria found in mouth and gut may help protect against severe peanut allergic reactions
Ultra-processed foods in preschool years associated with behavioural difficulties in childhood
A fanged frog long thought to be one species is revealing itself to be several
Weill Cornell Medicine selected for Prostate Cancer Foundation Challenge Award
[Press-News.org] Study: Extreme heat may speed up aging in older adultsPeople in neighborhoods that experience more days of high heat show faster aging at the molecular level than residents of cooler regions, say USC researchers