Advancements in artificial ligaments for ACL reconstruction: A leap towards improved outcomes
2025-02-27
(Press-News.org)
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injuries are common, especially among athletes. Each year, over 400 000 ACL reconstruction (ACLR) surgeries are carried out globally. While the success rate of ACLR is reported to be over 90%, a significant number of patients still face issues like revision surgery and long-term osteoarthritis. This has spurred research into better graft materials, and artificial ligaments have emerged as a potential solution. A recent review article published in Engineering delves into the current state and future prospects of artificial ligaments for ACLR.
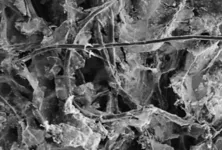
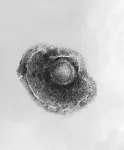
Artificial ligaments have been in use since the 1950s. They offer advantages such as eliminating donor-site morbidity and the risk of disease transmission, which are associated with autografts and allografts. However, they also have drawbacks. Some artificial ligaments have shown a high incidence of complications like chronic effusions, synovitis, and graft failure. For example, the Gore-Tex ligament, made of PTFE, has had issues with a declining Lysholm score over time and a relatively high rate of graft failure, effusion, and infection.
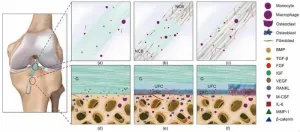
The healing process of a reconstructed ACL involves two crucial parts: graft–bone integration inside bone tunnels and intra-articular ligamentization. Autografts are considered the gold standard due to their bioactive properties that facilitate cell adhesion, proliferation, and osteogenesis. In contrast, artificial ligaments often lack these bioactive features, which has led researchers to focus on enhancing their bioactivity.
In recent years, there have been numerous attempts to modify artificial ligaments and fixation devices. One approach is to add bioactive components to ligament scaffolds. For instance, adding ECM components like hyaluronic acid and collagen can enhance cell adhesion and proliferation. Another promising modification is the use of magnesium-based materials in fixation devices. Magnesium has been shown to promote osteogenesis by increasing the release of calcitonin gene-related polypeptide (CGRP), which in turn upregulates osteogenic genes.
The review also points out that future research on artificial ligaments should focus on several key areas. Advanced manufacturing processes such as electrospinning and 3D printing could improve the physical and biological properties of artificial ligaments. Direct modification of materials, like using natural silk with its good mechanical properties and cell affinity, holds great potential. Additionally, understanding the biological features of components and their key upstream biological effects is essential for optimizing artificial ligaments.
Although there are still challenges in balancing the mechanical and biological properties of artificial ligaments, these recent advancements bring hope for better clinical outcomes in ACLR. As research continues, artificial ligaments may one day provide a more effective and reliable alternative to traditional grafts.
The paper “Current Advances of Artificial Ligaments for Anterior Cruciate Ligament Reconstruction: From Biocompatibility to Bioactivity,” authored by Haozhi Zhang, Xin Chen, Michael Tim-Yun Ong, Lei Lei, Lizhen Zheng, Bingyang Dai, Wenxue Tong, Bruma Sai-Chuen Fu, Jiankun Xu, Patrick Shu-Hang Yung, Ling Qin. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.10.018. For more information about the Engineering, follow us on X (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) & like us on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringJrnl).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-02-27
1 Gene Variant Is Poised to Cure a Devastating Inherited Disease
Scientists compared five families and multiple generations to find a gene variant that prevents COPA Syndrome and opens the door to a new gene therapy for the condition.
For more than 15 years, Anthony Shum, MD, a pulmonologist at UC San Francisco, has tried to understand the random path of devastation that a rare genetic condition carves through the families it affects.
While many of those who carry the mutation develop severe lung hemorrhaging as children others never get the disease ...
2025-02-27
In the rapidly developing contest between human creativity and artificial intelligence algorithms, professional artists still have an edge in producing more creative AI-assisted artwork than the AI programs themselves or novice artists, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
The rapid advancement of AI raises some existential questions about the nature of creativity, said lead researcher Paul Seli, PhD, an assistant professor of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University.
“Creativity ...
2025-02-27
Despite improvements to air filtration technology in the aftermath of the COVID-19 pandemic, some of the smallest particles — those of automobile and factory emissions — can still make their way through less efficient, but common filters. An interdisciplinary team of researchers from Drexel University’s College of Engineering have introduced a new way to improve textile-based filters by coating them with a type of two-dimensional nanomaterial called MXene.
Recently published in C Journal ...
2025-02-27
Digital Science has today announced new enhancements to Symplectic Elements, which will now offer the ability to embed AI-generated summaries for publication abstracts within a researcher’s public profile.
Symplectic Elements, a leading research information management system (RIMS), enables the creation of comprehensive public profiles. These profiles are hosted on sleek, modern, and intuitive online portals that offer advanced search and discovery capabilities while ensuring alignment with organizational branding. Profiles can be made available not only for researchers and faculty but also for ...
2025-02-27
New University of Sheffield research shows that combining solar panels with farming (agrivoltaics) can meet UK solar energy targets without sacrificing agricultural land
The coverage potential for the technology is so high that it could meet UK electricity demand more than four times over
Regions identified for the effective deployment of agrivoltaics include Cambridgeshire, Essex, Lincolnshire, and the broader East and South East of England
The approach counters criticism of traditional solar farms, which are often opposed ...
2025-02-27
Biomass burning—whether from wildfires, wood stoves or agricultural fires—sends massive amounts of tiny particles and chemicals into the air. These emissions are not just an environmental issue; they pose serious health risks, especially for our lungs. An Environmental Pollution study, co-authored by Dr. Jason Surratt, a professor in the Department of Chemistry at UNC-Chapel Hill, reveals how two key components of biomass smoke—levoglucosan and 4-nitrocatechol—affect human lung cells. Their findings suggest that aged ...
2025-02-27
For a few hundred dollars, a bedroom can be refreshed with the latest flat-pack offerings. Wood particleboard furniture is affordable and generally easy to assemble, but particleboard is often held together with formaldehyde-based resins that make it hard or impossible to recycle. Now, with the help of science, old pressed-wood furnishings could be repurposed, and new modular decor could incorporate more environmentally friendly materials. Four articles published in ACS journals reveal how. Reporters can request free access to these papers ...
2025-02-27
Biological tissues are made up of different cell types arranged in specific patterns, which are essential to their proper functioning. Understanding these spatial arrangements is important when studying how cells interact and respond to changes in their environment, as well as the intricacies of pathologies like cancer. Spatial transcriptomics (ST) techniques, which have been rapidly evolving over the past decade, allow scientists to map gene activity within tissues while keeping their structure intact, ...
2025-02-27
The varicella zoster virus (VZV), an infectious virus from the herpes virus family, is primarily known to cause varicella in children and shingles in adults. But lately, this virus has also been reported to trigger severe complications like central nervous system (CNS) infections. Researchers from Fujita Health University, Japan, conducted a comprehensive study spanning 10 years (2013–2022), to identify the VZV-related infections affecting the CNS. Their study reveals a marked increase in adult VZV-related CNS infections, ...
2025-02-27
CABI has led a team of scientists who have used DNA barcodes to narrow down the possible sources of introductions of an invasive banana skipper butterfly, with implications as to the threat of it spreading to Africa and tropical America.
The banana skipper, Erionota torus Evans (Lepidoptera, Hesperiidae, Hesperiinae, Erionotini) is a South-east Asian pest of banana that, in the last 60 years, has spread to the southern Philippines, Taiwan, Japan, India, Sri Lanka, Mauritius and La Réunion.
The new research, published in the journal CABI Agriculture and Bioscience, analysed a partial library of DNA barcodes from the indigenous and introduced ranges and suggests that aircraft are likely ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Advancements in artificial ligaments for ACL reconstruction: A leap towards improved outcomes