(Press-News.org) Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), formerly known as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), is a global health challenge, affecting nearly 30% of adults worldwide. A significant subset of MASLD patients progresses to metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH), liver fibrosis, and even hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), yet no universally approved treatment exists outside resmetirom. The increasing prevalence of MASLD, driven by obesity and diabetes, highlights an urgent need for innovative therapeutic strategies.
A new review published in eGastroenterology sheds light on the mechanistic role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in MASLD and liver fibrosis. LncRNAs, which do not encode proteins but regulate gene expression, have emerged as critical players in metabolic and fibrotic pathways. This comprehensive review, authored by Dr. Henry Wade, Kaichao Pan, Bingrui Zhang, Dr. Wenhua Zheng, and Dr. Qiaozhu Su, provides insights into the complex interplay between lncRNAs, microRNAs, and key mediators of liver disease progression.
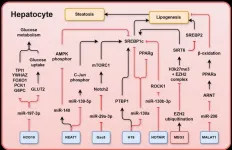
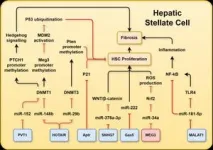
LncRNAs influence several metabolic pathways in hepatocytes, hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), and Kupffer cells, impacting lipid metabolism, inflammation, apoptosis, and fibrogenesis. Among the most studied lncRNAs, H19 has promoted hepatic lipid accumulation and fibrosis through interactions with sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs). Similarly, MALAT1 has been shown to exacerbate liver fibrosis by modulating inflammatory pathways via nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and toll-like receptors (TLRs).
One of the key findings discussed in the review is how lncRNAs regulate hepatic lipid homeostasis and fibrotic pathways. LncRNAs such as Gas5 and MEG3 appear to exert protective effects, inhibiting hepatocyte lipid accumulation and HSC activation. Conversely, lncRNAs like HOTAIR and NEAT1 drive liver disease progression by activating fibrotic and inflammatory responses. These opposing roles suggest that targeting lncRNAs could provide a dual approach—either suppressing pathogenic lncRNAs or enhancing protective ones—for MASLD treatment.
Additionally, the review explores how lncRNAs interact with microRNAs and transcription factors to regulate liver cell function. For instance, H19 interacts with miR-130a and heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1 (hnRNPA1) to promote steatosis, while HOTAIR regulates DNA methylation through interactions with miR-148b and DNMT1. These complex molecular networks underscore the potential of lncRNA-based interventions.
Dr. Qiaozhu Su, the corresponding author from Queen's University Belfast, notes that lncRNAs hold promise as both diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets. “Understanding how lncRNAs contribute to MASLD and fibrosis opens new avenues for therapeutic strategies. Given their regulatory roles in metabolism and inflammation, lncRNA-based therapies could be transformative,” said Dr. Su.
While the potential of lncRNA-targeted therapies is exciting, the review acknowledges significant challenges. LncRNAs exhibit species specificity, making translational research difficult. The review suggests that future studies should focus on identifying conserved lncRNAs across species to facilitate clinical applications. Developing delivery mechanisms for lncRNA-based therapeutics, such as nanoparticle-mediated RNA delivery, will be crucial for advancing this field.
This review underscores the urgent need for further investigation into lncRNAs as key regulators of liver disease. As MASLD prevalence continues to rise, unlocking the therapeutic potential of lncRNAs could mark a paradigm shift in liver disease management.
See the article:
Wade H, Pan K, Zhang B, et al. Mechanistic role of long non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease and fibrosis. eGastroenterology 2024;2:e100115. doi:10.1136/egastro-2024-100115
About eGastroenterology
eGastroenterology is a new, open-access, and open peer-reviewed BMJ Journal, which focuses on basic, clinical, translational, and evidence-based medicine research in all areas of gastroenterology (including hepatology, pancreatology, esophagology, and gastrointestinal surgery). eGastroenterology is now indexed by PubMed, Scopus, CAS, DOAJ, Dimensions, OpenAlex, ROAD, and COPE, with more to come!
For more information, please visit: egastroenterology.bmj.com and follow us on Twitter (@eGastro_BMJ).
Sign-up to Email Alerts for eGastroenterology: https://emails.bmj.com/k/Bmj/jausu/egastroenterology
END
McMaster University researchers have identified small molecules in the blood that may impact early childhood development, showing how dietary exposures, early life experiences, and gut health can influence a child's growth and cognitive milestones.
A McMaster team collaborated with Brazilian scientists to conduct an untargeted metabolomic analysis of blood samples taken from more than 5,000 children between the ages of six months and five years as part of the Brazilian National Survey of Child Nutrition study.
The McMaster team found several metabolites – small molecules that are by-products of human metabolism and microbial fermentation, ...
Giant pandas have digestive systems that are typical for carnivores. Yet, bamboo is their main source of food. They have evolved several features, for example pseudo thumbs to grasp bamboo and flat teeth that are well suited for crushing it, that make it possible for them to live off plants.
All living organisms have DNA, which stores the genetic information in a cell, and RNA, which carries and transfers this information. MicroRNAs (miRNA) are small non-coding RNAs that play an important role in gene expression, the process of turning the information encoded in a gene into a function. ...
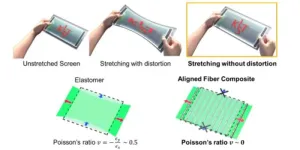
Stretchable display materials, which are gaining traction in the next-generation display market, have the advantage of being able to stretch and bend freely, but the limitations of existing materials have resulted in distorted screens and poor fit. General elastomeric substrates are prone to screen distortion due to the 'Poisson's ratio' phenomenon, in which stretching in one direction causes the screen to shrink in the vertical direction. In particular, electronics that are in close contact with the skin, such as wearable devices, are at risk of wrinkling or pulling on the skin during stretching and shrinking, resulting in ...
By Alistair Jones
SMU Office of Research – Even by the standards of medical terminology, photoplethysmography (PPG) is a mouthful. Yet it is widely used in clinical settings as a non-invasive, optical technique for measuring the oxygen saturation level in the blood, and the pulse rate, as vital signs of a patient. It is commonly encountered as a clip-on oximeter attached to a finger.
First developed in the 1930s, PPG emits light to illuminate the microvascular bed of the skin. Then a photodiode, positioned alongside the light emitter, captures the reflected light, termed the PPG waveform, which ...
By Vince Chong
SMU Office of Research – With the surfeit of trackable, wearable devices in modern life, there is little problem locating things and people outdoors by leveraging Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) solutions (GPS is an example of this type of solution) that use signals from satellites. Indoors on the other hand, is a different matter as GNSS signals are unavailable and other possible signals such as those from Wi-Fi systems are inconsistent, and often distorted.
And when this ability to swiftly, accurately locate indoor objects is starkly crucial to essential services that make the difference between life and death, upgrading ...
No one should have to fear food poisoning every time they eat or drink, but the reality, even in the 21st century, is that risks remain. An Osaka Metropolitan University-led Egypt-Japan research team found E. coli prevalent in over 25% of popular milk and dairy products in Egypt.
Of the 210 samples of raw milk, cheese, and yoghurt, 26.2% were positive for E. coli, with the highest being raw buffalo milk at 68%, and the lowest at 7.5% for rayeb, a type of fermented milk. The preference for raw milk instead of pasteurized milk and varying hygienic conditions at small dairies and markets could explain these results. Yet food poisoning ...
By Christie Loh
SMU Office of Research – When his parents heard that he had won an award at his workplace, they were naturally delighted, showering their son with a confetti of questions like what the prize was for, whether there was a formal ceremony, and that he must keep up the good work. Indeed, Monit Sharma is well aware that as encouraging as the SMU Research Staff Excellence Award is, the professional road he is on calls for both hard work and stamina.
The 23-year-old is a Research Engineer at SMU’s ...
A nationwide study has revealed that survivors of COVID-19 hospitalization face an increased risk of death or organ-related disorders for up to two-and-a-half years after discharge.
Published today in Infectious Diseases, the study of nearly 64,000 French residents provides valuable insights into the long-term health effects of COVID-19 and emphasises the need for continued healthcare and monitoring for people who have been hospitalised with SARS-CoV-2 infection.
“These findings are a stark reminder of the far-reaching impact of COVID-19, which extends far beyond the initial infection,” says lead author Dr Sarah Tubiana, who specializes ...
Document-level Role Filler Extraction exhibits a wide range of application value in natural language processing, including information retrieval, article summarization and trends analysis of world events. Existing document-level event role filler extraction methods face challenges in contextual modeling of long texts and ignore the explicit dependency relationships between event arguments displayed in long texts.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Zhengtao YU published their new research on 15 Feb 2025 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education Press and ...
New York, NY | February 27, 2025: Employee burnout is likely costing companies millions of dollars each year, ranging from approximately $4,000 to $21,000 per employee in the U.S., according to a study published in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine. That means a 1,000-employee company in the U.S. would on average be losing about $5 million annually. These estimates are based on a computational simulation model developed by the Public Health Informatics, Computational, and Operations Research (PHICOR) team based at the CUNY Graduate ...