(Press-News.org) ITHACA, N.Y. – When people go along with opinions that go against their better judgment, they feel more culpable for the decision if things go wrong than if they hadn’t received another opinion, new research from Cornell University finds.
The effect may seem counterintuitive, but going against one’s better judgment increases thoughts about better decisions that could have been made, which amplify feelings of control over the situation.
“If you have another person in the decision process, you would think that’s going to help spread the responsibility,” said Kaitlin Woolley, professor of marketing and management communications. “And yet not only do people not blame the adviser more, they’re blaming themselves more.”
Woolley and Sunita Sah, associate professor of management and organizations, published their findings in Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin.
The research included a 200-subject in-person experiment with physical prizes and four online studies, with up to 1,200 participants per experiment.
Participants chose between two lotteries, one with clearly superior prizes. Some subjects were offered input from an adviser who had no more knowledge about the choices. The adviser recommended the lesser lottery, and in four of the five studies participants received the lowest possible prize: 10 cents.
Across all studies, they found that participants’ feelings of culpability and the perception that they had control over the situation were greater in the group that received input than in the group that made an independent decision. Participants thought about how they could have ignored the advice and enjoyed the better prize.
“This effect could extend beyond small decisions. It can apply to major life choices, like wondering, ‘What if I had chosen a different career?’” Sah said.
In previous research, Sah, a physician turned organizational psychologist, found that people often followed obviously bad advice. This new research explored the downstream effects of regret, responsibility and blame after following bad advice – at least from an adviser who is not an expert.
“Our research highlights the importance of rejecting suggestions that go against our better judgments,” Sah said. “People often assume that following someone else’s suggestion will shield them from responsibility or regret. But in reality, the opposite happens. You end up feeling worse when you ignored what you knew was the better choice.”
END
Kicking yourself: Going against one’s better judgment amplifies self-blame
2025-02-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rice researchers harness gravity to create low-cost device for rapid cell analysis
2025-02-28
HOUSTON – (Feb. 28, 2025) – A team of researchers at the George R. Brown School of Engineering and Computing at Rice University has developed an innovative artificial intelligence (AI)-enabled, low-cost device that will make flow cytometry ⎯ a technique used to analyze cells or particles in a fluid using a laser beam ⎯ affordable and accessible.
The prototype identifies and counts cells from unpurified blood samples with similar accuracy as the more expensive and bulky conventional flow cytometers, provides results within minutes and is significantly cheaper and compact, making it highly attractive for point-of-care clinical ...
Revolutionary copper-infused microvesicles: a new era in biofunctional medicine
2025-02-28
In a study published today in Biofunctional Materials, Prof. Dr. Haidar, Founder and CEO of BioMAT’X I+D+I LABs in Santiago, Chile, unveils a groundbreaking advancement in dental care: Copper-incorporated microvesicles (CiMs). This innovative technology combines the healing power of copper with microvesicles to enhance tissue regeneration, promote healing, and combat oral diseases. With potential applications in dentistry, cranio-maxillo-facial surgery and beyond, CiMs; a promising leap forward in biomedical technology.
In an exciting breakthrough ...
Primary care practices with NPs are key to increasing health care access in less advantaged areas, Columbia Nursing study shows
2025-02-28
NEW YORK, NY (February 28, 2025) -- Primary care practices that employ nurse practitioners (NPs) are more likely to serve socioeconomically disadvantaged communities than practices with no NPs on staff, Columbia University School of Nursing researchers report in JAMA Network Open. Assistant Professor Monica O’Reilly-Jacob, PhD, led the study, published online February 28, 2025.
To better understand the distribution of NPs—who are increasingly critical to improving access to primary care—O’Reilly-Jacob and her colleagues looked ...
TTUHSC conducting study to help patients that experience traumatic blood loss
2025-02-28
The Texas Tech University Health Sciences Center is conducting a research study that will look at whether calcium, vasopressin, or both early in the course of treatment would help severely injured patients that lose a lot of blood survive their injuries.
The CAlcium and VAsopressin following Injury Early Resuscitation (CAVALIER) trial will include approximately 1,050 people aged 18 to 90. Patients who have traumatic injuries with loss of blood may be enrolled by participating emergency medical personnel during their transportation to the hospital or after arrival to University Medical Center Hospital.
CAVALIER is an Exception from Informed Consent (EFIC) trial, meaning that, the trial ...
Next top model: Competition-based AI study aims to lower data center costs
2025-02-28
NEWPORT NEWS, VA – Who, or rather what, will be the next top model?
Data scientists and developers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s Thomas Jefferson National Accelerator Facility are trying to find out, exploring some of the latest artificial intelligence (AI) techniques to help make high-performance computers more reliable and less costly to run.
The models in this case are artificial neural networks trained to monitor and predict the behavior of a scientific computing cluster, where torrents of numbers are constantly crunched. The goal is to help system administrators quickly identify and ...
Innovative startup awarded $10,000 to tackle cardiovascular disparities
2025-02-28
DALLAS, Feb. 28, 2025 — Cardiovascular disease disproportionately affects Black communities, with more than 57% of non-Hispanic Black adults living with some form of the disease. To drive solutions that address these disparities, the American Heart Association, a global force changing the future of health for all, launched the Heart of Innovation HBCU Challenge to empower the next generation of health tech entrepreneurs from Historically Black Colleges and Universities (HBCUs).
On Monday, Shadrach ...
Study compares indoor transmission-risk metrics for infectious diseases
2025-02-28
A recent study published in the journal Engineering delves into the complex world of assessing the transmission risk of infectious diseases in indoor spaces. With the ongoing impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, understanding how to accurately evaluate the effectiveness of non-pharmaceutical interventions (NPIs) has become crucial.
Governments worldwide implemented NPIs to control the spread of COVID-19. Many studies used simulations to measure the risk of infection transmission before and after implementing these measures. However, the choice of metric to quantify ...
Micro-expression detection in ASD movies: a YOLOv8-SMART approach
2025-02-28
Researchers have unveiled a groundbreaking AI-driven approach to improve the early diagnosis of Autism Spectrum Disorder by analyzing micro-expressions in movies. Micro-expressions, which are fleeting facial movements that reveal hidden emotions, are particularly challenging to detect in individuals with ASD. By employing the Cinemetrics method, the team successfully extracted micro-expressions from films featuring ASD patients and utilized an enhanced YOLOv8-SMART algorithm for precise detection. This advanced model significantly outperformed existing methods, achieving remarkable ...
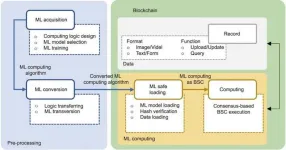
Machine learning on blockchain: A new approach to engineering computational security
2025-02-28
A new study published in Engineering presents a novel framework that combines machine learning (ML) and blockchain technology (BT) to enhance computational security in engineering. The framework, named Machine Learning on Blockchain (MLOB), aims to address the limitations of existing ML-BT integration solutions that primarily focus on data security while overlooking computational security.
ML has been widely used in engineering to solve complex problems, offering high accuracy and efficiency. However, it faces security threats such as data tampering and ...
Vacuum glazing: A promising solution for low-carbon buildings
2025-02-28
A new review article published in Engineering offers a comprehensive look at vacuum glazing, a technology that shows great potential in enhancing energy efficiency in buildings. As buildings account for around 40% of society’s total energy consumption, improving the thermal performance of glazing is crucial for achieving low-carbon building goals.
Vacuum glazing has gained attention for its heat preservation, sound insulation, lightweight features, and anti-condensation properties. The concept dates back to 1913, but it was not until 1989 that researchers in Australia successfully produced vacuum glazing with excellent thermal insulation performance. Since then, significant ...