(Press-News.org) A ‘chasm of misunderstanding and miscommunication’ is often experienced between clinicians and patients, leading to autoimmune diseases such as lupus and vasculitis being wrongly diagnosed as psychiatric or psychosomatic conditions, with a profound and lasting impact on patients, researchers have found.
A study involving over 3,000 participants – both patients and clinicians – found that these misdiagnoses (sometimes termed “in your head” by patients) were often associated with long term impacts on patients’ physical health and wellbeing and damaged trust in healthcare services.
The researchers are calling for greater awareness among clinicians of the symptoms of such diseases, which they recognise can be difficult to diagnose, and for more support for patients.
Autoimmune rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and vasculitis are chronic inflammatory disorders that affect the immune system and can damage organs and tissues throughout the body. They can be very difficult to diagnose as people report a wide range of different symptoms, many of which can be invisible, such as extreme fatigue and depression.
Dr Melanie Sloan from the University of Cambridge led a study exploring patient-reported experiences from two large groups, each of over 1,500 patients, and in-depth interviews with 67 patients and 50 clinicians. The results are published today in Rheumatology.
Patients who reported that their autoimmune disease was misdiagnosed as psychosomatic or a mental health condition were more likely to experience higher levels of depression and anxiety, and lower mental wellbeing. For example, one patient with multiple autoimmune diseases said: “One doctor told me I was making myself feel pain and I still can’t forget those words. Telling me I’m doing it to myself has made me very anxious and depressed.”
More than 80% said it had damaged their self-worth and 72% of patients reported that the misdiagnosis still upset them, often even decades later. Misdiagnosed patients also reported lower levels of satisfaction with every aspect of medical care and were more likely to distrust doctors, downplay their symptoms, and avoid healthcare services. As one patient reported, it “has damaged my trust and courage in telling doctors very much. I even stopped taking my immunosuppressive medicine because of those words”.
Following these types of misdiagnoses, patients often then blamed themselves for their condition, as one individual described: “I don’t deserve help because this is a disease I’ve brought on myself. You go back to those initial diagnosis, you’ve always got their voices in your head, saying you’re doing this to yourself. You just can’t ever shake that. I’ve tried so hard.”
One patient described the traumatising response their doctor’s judgement had on them: “When a rheumatologist dismissed me I was already suicidal, this just threw me over the edge. Thankfully I am terrible at killing myself, it’s so much more challenging than you think. But the dreadful dismissiveness of doctors when you have a bizarre collection of symptoms is traumatizing and you start to believe them, that it’s all in your head.”
Dr Melanie Sloan, from the Department of Public Health and Primary Care at the University of Cambridge, said: “Although many doctors were intending to be reassuring in suggesting a psychosomatic or psychiatric cause for initially unexplainable symptoms, these types of misdiagnoses can create a multitude of negative feelings and impacts on lives, self-worth and care. These appear to rarely be resolved even after the correct diagnoses. We must do better at helping these patients heal, and in educating clinicians to consider autoimmunity at an earlier stage.”
Clinicians highlighted how hard it was to diagnose autoimmune rheumatic diseases and that there was a high risk of misdiagnosis. Some doctors said they hadn’t really thought about the long-term problems for patients, but others talked about the problems in regaining trust, as one GP from England highlighted: “They lose trust in anything that anyone says…you are trying to convince them that something is OK, and they will say yes but a doctor before said that and was wrong.”
However, there was evidence that this trust can be rebuilt. One patient described having been “badly gaslit by a clinician”, but that when they told the clinician this, “She was shocked and had no idea … She was great. Took it on the chin. Listened and heard. Apologised profusely…For me, the scar of the original encounter was transformed into something much more positive.”
Mike Bosley, autoimmune patient and co-author on the study, said: “We need more clinicians to understand how a misdiagnosis of this sort can result in long-standing mental and emotional harm and in a disastrous loss of trust in doctors. Everyone needs to appreciate that autoimmune conditions can present in these unusual ways, that listening carefully to patients is key to avoiding the long-lasting harm that a mental health or psychosomatic misdiagnosis can cause.”
The study authors recommend several measures for improving support for patients with autoimmune rheumatological diseases. These are likely to apply for many other groups of patients with chronic diseases that are often misunderstood and initially misdiagnosed.
They propose that clinicians should talk about previous misdiagnoses with patients, discuss and empathise with their patients as to the effects on them, and offer targeted support to reduce the long-term negative impacts. Health services should ensure greater access to psychologists and talking therapies for patients reporting previous misdiagnoses, which may reduce the long-term impact on wellbeing, healthcare behaviours, and patient-doctor relationships. Education may reduce misdiagnoses by encouraging clinicians to consider systemic autoimmunity when they assess patients with multiple, seemingly unconnected, physical and mental health symptoms.
Professor Felix Naughton, from the Lifespan Health Research Centre at the University of East Anglia, said: “Diagnosing autoimmune rheumatic diseases can be challenging, but with better awareness among clinicians of how they present, we can hopefully reduce the risk of misdiagnoses. And while there will unfortunately inevitably still be patients whose condition is not correctly diagnosed, with the correct support in place, we may be able to lessen the impact on them.”
The research was funded by LUPUS UK and The Lupus Trust.
Reference
Sloan, M, et al. “I still can’t forget those words”: mixed methods study of the persisting impacts of psychosomatic and psychiatric misdiagnoses. Rheumatology; 3 Mar 2025; DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/keaf115
END
Chronic diseases misdiagnosed as psychosomatic can lead to long term damage to physical and mental wellbeing, study finds
2025-03-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Omalizumab treats multi-food allergy better than oral immunotherapy
2025-03-02
A clinical trial has found that the medication omalizumab, marketed as Xolair, treated multi-food allergy more effectively than oral immunotherapy (OIT) in people with allergic reactions to very small amounts of common food allergens. OIT, the most common approach to treating food allergy in the United States, involves eating gradually increasing doses of a food allergen to reduce the allergic response to it. Thirty-six percent of study participants who received an extended course of omalizumab could tolerate 2 grams or more of peanut protein, or about eight peanuts, and two other ...
Sleep apnea linked to increased risk of Parkinson’s, but CPAP may reduce risk
2025-03-02
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, SUNDAY, MARCH 2, 2025
Media Contacts:
Renee Tessman, rtessman@aan.com, (612) 928-6137
Natalie Conrad, nconrad@aan.com, (612) 928-6164
Sleep apnea linked to increased risk of Parkinson’s, but CPAP may reduce risk
Risk reduced if treatment started within two years of diagnosis
MINNEAPOLIS – People with obstructive sleep apnea have an increased risk of Parkinson’s disease, but if started early enough, continuous positive airway pressure ...
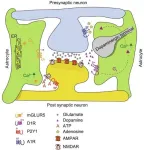
New insights into drug addiction: The role of astrocytic G protein-coupled receptors
2025-03-02
A recent study published in Engineering delves into the complex mechanisms of drug addiction, highlighting the crucial role of astrocytic G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). This research offers fresh perspectives on understanding and potentially treating substance-use disorders (SUDs).
For a long time, neuroscience research on drug addiction mainly focused on neuronal mechanisms. However, emerging evidence shows that astrocytes, the most abundant glial cells in the central nervous system, also play a significant part. Astrocytes ...
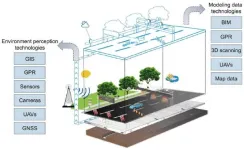
Digital twin technology: Transforming road engineering and its lifecycle applications
2025-03-02
A recent study published in the journal Engineering delves into the potential of digital twin (DT) technology in revolutionizing road engineering and its lifecycle applications. As road infrastructure worldwide faces the challenge of digitalization, DT has emerged as a promising solution.
The research, conducted by a team of scholars from Tongji University and Harbin Institute of Technology (Shenzhen), systematically reviews DT-enabling technologies, including model creation, condition sensing, data processing, and interaction. The development of DT in road engineering has been ...
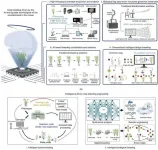
Next-generation AI and big data: Transforming crop breeding
2025-03-01
A new study published in Engineering explores how next-generation artificial intelligence (AI) and big data are revolutionizing crop breeding, with potential far-reaching implications for global food security.
Crop breeding has come a long way, evolving through distinct stages from domestication breeding to the current era of big data intelligent design breeding. The latest stage, “Breeding 4.0,” integrates biotechnology, big data, and AI. This convergence aims to achieve efficient, personalized breeding of new crop varieties, marking a significant shift from traditional “scientific” ...
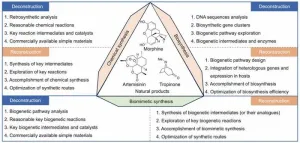
Biomimetic synthesis of natural products: Progress, challenges and prospects
2025-03-01
In a recent publication in Engineering, researchers from Jinan University in China and the University of Illinois Chicago in the US presented an in-depth perspective on the biomimetic synthesis of natural products. This research area, which bridges chemistry, biology, and pharmacy, has seen significant progress in recent years.
Natural products are crucial in drug discovery, providing essential scaffolds for developing new medications. However, obtaining sufficient quantities of these compounds for research and production is challenging due to resource limitations. Traditional chemical synthesis and biosynthesis methods also face their own set of ...
New limits found for dark matter properties from latest search
2025-03-01
Tokyo, Japan – A team led by a member of Tokyo Metropolitan University have made advances in the search for dark matter, observing galaxies using new spectrographic technology and the Magellan Clay Telescope. With a mere 4 hours of observations, precise measurements in the infrared range have set new limits on the lifetime of dark matter. Their findings highlight the crucial utility of their technology and extend the search to less explored parts of the spectrum.
Over the past century, cosmologists have grappled with an apparent inconsistency in what they saw in the universe. Observations of the rotation of galaxies, for example, imply that there is a lot of mass out ...
SCAI expresses disappointment over ABMS decision to deny independent cardiovascular medicine boar
2025-02-28
WASHINGTON– The Society for Cardiovascular Angiography & Interventions (SCAI) today expressed profound disappointment in the American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS) decision to deny the creation of the American Board of Cardiovascular Medicine (ABCVM).
The ABCVM was proposed by SCAI, the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association (AHA), the Heart Failure Society of America (HFSA), and the Heart Rhythm Society (HRS) as a necessary step to establish cardiology as its own distinct medical specialty, separate from internal ...
Rice researchers develop efficient lithium extraction method, setting stage for sustainable EV battery supply chains
2025-02-28
In the race to meet the growing global demand for lithium — a critical component in batteries for electric vehicles — a team of researchers from Rice University’s Elimelech lab has developed a breakthrough lithium extraction method that could reshape the industry.
In their study published in Science Advances, the researchers demonstrated near-perfect lithium selectivity by repurposing solid-state electrolytes (SSEs) as membrane materials for aqueous lithium extraction. While originally designed for the rapid conduction of lithium ions in solid-state batteries — where there are no other ions or liquid solvents — the highly ordered and confined structure ...
Statement on ABMS denying new cardiovascular board
2025-02-28
American Board of Cardiovascular Medicine Chair Jeffrey Kuvin, MD, issued the following statement in response to the American Board of Medical Specialties denial of an independent board for cardiology:
“We are deeply disappointed with the American Board of Medical Specialties’ decision not to approve the American Board of Cardiovascular Medicine as a new, independent board for cardiology.
The decision ignores the evolution of cardiovascular medicine into its own distinct medical specialty, separate from the field of internal medicine, requiring its own set of knowledge, skills, and competencies to sustain professional excellence and effectively ...