(Press-News.org) A new study from Tulane University suggests that repeated collapse and reopening of tiny alveoli—air sacs in the lungs essential for breathing—during mechanical ventilation may cause microscopic tissue damage, playing a key role in ventilator-related injuries that contribute to thousands of deaths annually.
Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), the study sheds light on ventilator-induced lung injury, a complication that gained increased attention during the COVID-19 pandemic, which led to a surge in patients requiring mechanical ventilation. These devices pump oxygen-rich air into a patient’s airways when they are unable to breathe adequately on their own.
The study identified that alveolar recruitment/derecruitment — when collapsed air sacs in the lungs repeatedly open and close — accounts for only 2-5% of energy dissipation during ventilation but correlates directly with lung injury in a model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
"It's like a tiny explosion at the delicate lung surface," said lead author Donald P. Gaver, a biomedical engineering professor at Tulane University School of Science and Engineering. "Though small in magnitude, it creates a power intensity of about 100 watts per square meter — comparable to sunlight exposure."
ARDS is a severe lung condition that affects roughly 10% of intensive care unit patients and carries a mortality rate of 30-40%, even with modern ventilation techniques. Using a pig model of ARDS, the team examined how ventilator energy is transferred and dissipated in the lungs.
The researchers found that reducing this type of energy dissipation led to rapid recovery, while patients continued to deteriorate when 5-10% of alveoli underwent repetitive recruitment/derecruitment.
The study suggests that minimizing these repetitive collapse-and-reopening cycles could significantly reduce ventilator-induced lung injury. Researchers noted that adjusting ventilation strategies to prevent such events may improve outcomes for critically ill patients.
The study’s findings could also help inform the development of new ventilation protocols aimed at reducing lung injury and improving patient care in intensive care units worldwide.
“Follow-up steps should include developing real-time monitoring devices to quantify reopening events and integrating this data into treatment strategies to optimize ventilation and improve patient outcomes,” Gaver said.
This research was completed in collaboration with the University of Vermont, the State University of New York Upstate Medical University (SUNY Upstate) and the University of Maryland Shock Trauma Center.
END
Study links intense energy bursts to ventilator-induced lung injury
2025-03-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
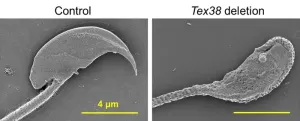
Uncovering the protein complex critical to male fertility
2025-03-03
Osaka, Japan – The human body is full of checks and balances that ensure correct growth, development, and function of all our different systems. Now, researchers from Japan have reported a newly discovered protein interaction that regulates sperm development.
In a study to be published soon in PNAS, a multi-institutional research team led by Osaka University has revealed that the interaction between two specific proteins is crucial for ensuring that sperm cells develop properly.
Sperm formation is a highly complex process that involves many changes ...
Scientists discover how a naturally occurring mechanism hampers fertility
2025-03-03
A Yale-led research team has uncovered how a naturally occurring biological mechanism found in mammals is able to prevent sperm cells from interacting with an egg, preventing fertilization.
The discovery, identified in rodent models, offers a new path for scientific research to help people grappling with infertility issues, while also opening a new line of study for developing contraceptive therapies. The findings appear in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
“This will have direct implications ...
Integrated framework for ecological security: A case study of the Daqing river basin
2025-03-03
In a recent study published in Engineering, researchers have developed an innovative analytical framework for ecological security assessment, prediction, and zoning management. Guided by the Social–Economic–Natural Complex Ecosystems (SENCE) theory, this framework aims to enhance ecological security for sustainable development.
The Daqing River Basin in the North China Plain was chosen as a case study due to its ecological significance and the increasing human-land conflicts. The research team established an assessment index system based on the pressure-state-response ...
New design paradigm boosts reconfigurable intelligent surface efficiency
2025-03-03
A recent study published in Engineering introduces an innovative design paradigm for reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs), aiming to enhance their design efficiency and versatility. This research, led by a team of scientists from Southeast University and Guangzhou University, offers a fresh approach to address the challenges in RIS design.
RISs, enabled by digital coding technology, are crucial for manipulating electromagnetic (EM) waves in real-time. They play a significant role in 5G and 6G research. However, traditional automatic RIS design methods face issues. Most involve extensive numerical simulations ...
Long-term cocaine use may increase impulsivity
2025-03-03
Researchers have widely accepted that impulsivity increases the risk of drug addiction, but the evidence to support this belief is mixed. Exploring the relationship between impulsivity and cocaine use in rats, Yihong Yang and colleagues from the National Institute on Drug Abuse found evidence that contradicts the prevailing view that high impulsivity predicts cocaine use.
One classification of impulsivity is impulsive choice, which can be studied with risky choice tasks and delay-discounting tasks (DDT). During DDT, impulsive individuals prefer smaller, ...
How London’s Ultra Low Emission Zone is changing the school run
2025-03-03
London’s Ultra Low Emission Zone (ULEZ) is transforming children’s journeys to school by making streets safer, improving perceptions of air quality and encouraging children to live healthier lives. A new study published today in BMJ Open, and funded by the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR), highlights its benefits, with many families noticing cleaner air and safer roads. However, it also reveals challenges, particularly for those living in outer boroughs who are more reliant on the car and may struggle to adapt.
Road traffic is a major source of air pollution in London, posing serious health risks. One in 11 children in the city has asthma, a condition ...
Breakthrough CRISPR-based test offers faster, more accurate diagnosis for fungal pneumonia
2025-03-03
Tulane University researchers have developed a CRISPR-based test that diagnoses Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) — a life-threatening fungal infection primarily affecting children and immunocompromised patients — more quickly and less invasively, according to a new study published in the Journal of Clinical Investigation.
The highly accurate test detects RNA from live fungi in blood samples and throat swabs, eliminating the need for invasive bronchoscopy procedures currently used for diagnosis.
"Current diagnostic methods haven't evolved in ...
3D-printed knee implants improves quality and reliability
2025-03-03
Customized 3D-printed medical implants are becoming more common, and a new study has taken this technology to the next level. Researchers at Naton Biotechnology have developed the world’s first laser 3D-printed total knee implant, which has received official approval from China’s National Medical Products Administration as an innovative medical device.
The study focused on improving the strength and consistency of cobalt-chromium-molybdenum (CoCrMo) alloy implants made using laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), a 3D printing process. The team discovered and corrected inconsistencies in the structure of the material ...
UC San Diego innovators to spotlight transformative science at SXSW 2025
2025-03-03
The South by Southwest (SXSW) Conference and Festivals — a renowned convergence of pioneers, storytellers, and global visionaries — will take place this year from March 7-15 in Austin, Texas, bringing together a vibrant mix of ideas and innovations. Once again, UC San Diego will take center stage, showcasing cutting-edge research, transformative discussions on critical global challenges and a film premiere.
“UC San Diego’s participation in the 2025 South by Southwest Conference and Festivals reinforces our institution’s passion for interdisciplinary ...
Burning question: How to save an old-growth forest in Tahoe
2025-03-03
On the shores of Lake Tahoe at Emerald Bay State Park grows what some consider to be the most iconic old-growth forest in the Lake Tahoe Basin. Giant ponderosa pines — some of the last remaining in the area — share space with at least 13 other tree species.
Yet despite its high conservation value and proximity to severely burned forests, the Emerald Point stand has not been managed to reduce its risk to drought or catastrophic wildfire. The fire-adapted forest has also not experienced fire for at least 120 years. This has led to massive increases in forest density, fuels, and insect- and drought-driven mortality.
A fire ...