(Press-News.org) Fred Hutch Cancer Center announced 10 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award, which recognizes the exceptional achievements of graduate studies in the biological sciences.
This year’s recipients represent both national and international research institutions, with a variety of thesis topics including the structural organization of neural networks, a hereditary basis for metastatic breast cancer, gene editing tools for neurodegenerative diseases and the brain’s ability to control the tongue.
“We congratulate the impressive group of domestic and international applicants this year and commend their scientific achievements. Their work shows how creative thinking and dedicated research can spark discoveries,” said Jihong Bai, PhD, a professor in Fred Hutch’s Basic Sciences Division who co-leads the Weintraub awards committee.
“We celebrate the awardees and hope they inspire more students to follow their passion in biomedical science,” Bai added.
Fred Hutch established the annual award in 2000 to honor the bold and pioneering spirit of Dr. Harold “Hal” Weintraub, who died from brain cancer in 1995 at 49. Weintraub earned deep respect and admiration, and the award honors his legacy as a caring mentor and supportive colleague.
Nominations are submitted internationally each year. Awardees are chosen by a committee of Fred Hutch faculty and students, who select winners based on quality, originality and scientific significance as well as representing a diverse range of topics.
This award is supported by the Weintraub/Groudine Fellowship for Science and Human Disease, which aims to foster intellectual exchange through programs for graduate students and the Weintraub Symposium.
2025 Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award recipients:
Pilar Baldominos Flores
PhD; Biotechnology
Universidad Politécnica de Valencia
Roman Barth
PhD; Bionanoscience
Delft University of Technology
Dawn Chen
PhD; Systems, Synthetic and Quantitative Biology Program
Harvard University
Leila Elabbady
PhD; Neurobiology and Biophysics
University of Washington
Jeremy Hollis
PhD; Molecular and Cellular Biology (MCB)
Fred Hutch Cancer Center
Brendan Ito
PhD; Neurobiology & Behavior (NBB)
Cornell University
Connor McKenney
PhD; Biochemistry, Cellular and Molecular Biology
Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine
Wenbin Mei
PhD; The David Rockefeller Graduate Program
The Rockefeller University
Edwin Neumann
PhD; Biological Engineering
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Tong Zhang
PhD; Biology
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
###
Media contact:
Shayla Ring
sring@fredhutch.org
Fred Hutch Cancer Center unites individualized care and advanced research to provide the latest cancer treatment options while accelerating discoveries that prevent, treat and cure cancer and infectious diseases worldwide.
Based in Seattle, Fred Hutch is an independent, nonprofit organization and the only National Cancer Institute-designated cancer center in Washington. We have earned a global reputation for our track record of discoveries in cancer, infectious disease and basic research, including important advances in bone marrow transplantation, immunotherapy, HIV/AIDS prevention and COVID-19 vaccines. Fred Hutch operates eight clinical care sites that provide medical oncology, infusion, radiation, proton therapy and related services. Fred Hutch also serves as UW Medicine’s cancer program.
END
Fred Hutch announces 10 recipients of the 2025 Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Award honors graduate students in biological sciences from across the world
2025-03-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
30 million euros for a novel method of monitoring the world's oceans and coastal regions using telecommunications cables
2025-03-04
Summary
The worldwide network of telecommunications cables lying on the bottom of the world's oceans offers unique potential for scientific use if the fibre-optic cables themselves are used as or equipped with sensors. Based on this, the GFZ Helmholtz Centre for Geosciences in Potsdam and the GEOMAR Helmholtz Centre for Ocean Research Kiel are now setting up the research infrastructure SAFAtor (SMART Cables And Fiber-optic Sensing Amphibious Demonstrator), that can be used to monitor the world's oceans. It will be included in the portfolio of the major Helmholtz infrastructures and funded by ...
New multicenter study shows: Which treatment helps best with high-risk acute pulmonary embolism
2025-03-04
A current study involving the University Hospital Bonn (UKB) has investigated which treatment strategy offers the best chances of survival in high-risk acute pulmonary embolism. The results, now published in the renowned journal "Intensive Care Medicine", provide crucial information for the future treatment of this life-threatening disease.
High-risk acute pulmonary embolism affects around five percent of all pulmonary embolisms and can take a dramatic course even in young people. Acute obstruction of the pulmonary circulation by a blood clot can lead to circulatory failure with a high mortality rate. The study, which was carried out in collaboration with 34 European centers ...
Hidden dangers and myths: What you need to know about HPV and cancer
2025-03-04
COLUMBUS, Ohio – While the human papillomavirus (HPV) is most associated with cervical cancer risk and women, a new survey commissioned by The Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center – Arthur G. James Cancer Hospital and Richard J. Solove Research Institute (OSUCCC – James) shows that the majority of people are unaware that the virus is actually more common among men than women and is associated with rising rates of other cancers that directly impact men.
The consumer survey sought to understand the public’s knowledge of the lesser known but common virus – specifically how it is spread and its impact on cancer risk.
Survey ...
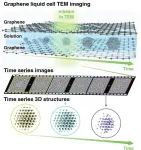
SNU researchers develop world’s first technology to observe atomic structural changes of nanoparticles in 3D
2025-03-04
Seoul National University College of Engineering announced that Professor Jungwon Park’s research team from the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering has developed a groundbreaking technology to observe atomic structural changes of nanoparticles in three dimensions.
This study, recognized as a revolutionary achievement that resolves a long-standing challenge even past Nobel laureates could not solve, was published online in Nature Communications, one of the most prestigious international journals, on January 29.
Recently, nanoparticles have garnered significant attention as they are widely used in developing functional materials for cutting-edge industries ...
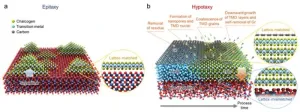
SNU researchers develop a new synthesis technology of single crystal 2D semiconductors, “Hypotaxy,” to enhance the commercialization of next-generation 2D semiconductors
2025-03-04
College of Engineering at Seoul National University announced that a research team led by Professor Gwan-Hyoung Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with the research teams of Professors Hyejin Jang and Jeong Woo Han from the same department, has successfully developed the new synthesis technology of 2D semiconductors. This groundbreaking technique enables the direct growth of wafer-scale single-crystal 2D semiconductors on various substrates.
The research were published in "Nature," the world's most ...
Graphene production method offers green alternative to mining
2025-03-04
Researchers in Sweden report a green alternative to reduce reliance on mining graphite, the raw source behind the next wonder material, graphene.
In the latest volume of the scientific journal Small, researchers at KTH Royal Institute of Technology say they have developed a reproducible and scalable method for producing graphene oxide (GO) nanosheets from commercial carbon fibers, marking a breakthrough in sustainable nanomaterial synthesis.
The process involves exfoliating carbon fibers with nitric acid, which provides high yields of one-atom-thick sheets of graphene oxide with characteristics comparable ...
Researchers discover a cause of leptin resistance—and how to reverse it
2025-03-04
Worldwide obesity rates have more than doubled since 1990, with nearly a billion people now falling into the category. Though a complex interplay of genes, diet, and environment contribute, 90% of cases share one thing in common: leptin resistance.
In lean individuals, fat cells produce the hormone leptin, which suppresses appetite. But in most individuals with obesity, this signal fails to register. Why this happens has been a mystery for more than three decades, ever since Jeffrey M. Friedman’s laboratory at the Rockefeller University cloned the leptin gene in 1994.
But now Bowen Tan, Kristina Hedbacker, ...
Heat from the sun affects seismic activity on Earth
2025-03-04
WASHINGTON, March 4, 2025 – Seismology has revealed much of the basics about earthquakes: Tectonic plates move, causing strain energy to build up, and that energy eventually releases in the form of an earthquake. As for forecasting them, however, there’s still much to learn in order to evacuate cities before catastrophes like the 2011 magnitude 9.0 Tōhoku earthquake that, in addition to causing a tsunami that led to the Fukushima nuclear disaster, resulted in more than 18,000 deaths.
In recent years, research has focused on a possible correlation between ...
Postoperative aspiration pneumonia among adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
2025-03-04
About The Study: This cohort study found no significant association between the preoperative use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) and short-term postoperative aspiration pneumonia despite growing concerns about the adverse effects of these medications after surgery. This finding suggests that it may be beneficial to reassess the preoperative withholding guidelines for GLP-1 RAs.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Eric L. Smith, M.D., email esmith@nebh.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.0081)
Editor’s ...
Perceived discrimination in health care settings and care delays in patients with diabetes and hypertension
2025-03-04
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest that higher perceived discrimination in health care settings is positively associated with delaying health care due to nervousness about seeing a health care professional. The largest mediation proportion observed was among younger adults and racial and ethnic minority groups. By prioritizing better patient-clinician communication, health care delays associated with patient apprehension related to perceived discrimination may be reduced.
Corresponding author: To contact the corresponding author, Maryam Jafari Bidgoli, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] Fred Hutch announces 10 recipients of the 2025 Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student AwardAward honors graduate students in biological sciences from across the world