(Press-News.org)
The intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) do not attain a stable secondary or tertiary structure and rapidly change their conformation, making structure prediction particularly challenging. These proteins although exhibit chaotic and ‘disordered’ structures, they still perform essential functions.
The IDPs comprise approximately 30% of the human proteome and play important functional roles in transcription, translation, and signalling. Many mutations linked to neurological diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), are located in intrinsically disordered protein regions (IDRs).
Powerful machine-learning algorithms, including AlphaFold and RoseTTAFold, cannot provide realistic representations of these ‘disordered’ and ‘chaotic’ protein regions as a whole. This is because they have not been trained on such data and because these proteins exhibit inherent dynamic behaviour, adopting a range of conformations rather than a single stable one.
Now, a team of researchers from BSRC Fleming and the Centre for Misfolding Diseases at the University of Cambridge has found an efficient way to predict the structures of a significant fraction of all human proteins that were previously considered “dark” and notoriously difficult to observe.
The team developed and used an algorithm called ‘AlphaFold-Metainference’, which was trained on data from available protein structure databases as well as molecular dynamics simulations. The findings of the study were recently published in Nature Communications.
“AlphaFold has transformed structural biology by providing accurate predictions of protein structures. We have now shown how to extend these predictions to IDPs, which make up about a third of the human proteome and are implicated in virtually all major diseases,” says Michele Vendruscolo, Professor of Biophysics at the Centre for Misfolding Diseases at the University of Cambridge.
“We were surprised to find that although AlphaFold does not accurately predict the three-dimensional structure of IDPs, it can predict the distances between amino acids with quite good accuracy. We then incorporated this information into molecular dynamics simulations, allowing us to accurately predict the three-dimensional structures these disordered proteins adopt and their motion,” explains Dr Faidon Brotzakis, a senior postdoctoral researcher in the lab of Dr Georgios Skretas at the Institute for Bioinnovation of the Biomedical Sciences Research Center “Alexander Fleming” (BSRC Fleming) and the study's first author.
The algorithm was tested on proteins containing both disordered and non-disordered regions, including TDP-43 (associated with ALS), ataxin-3 (linked to Machado-Joseph disease), and the prion protein (implicated in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease).
“We tested the algorithm on a total of eleven IDPs and six PDPs, but we focused particularly on proteins associated with serious diseases. In all cases, the algorithm outperformed AlphaFold in accuracy. In fact, in 80% of cases, it matched or exceeded the accuracy of molecular dynamics simulations. This demonstrates the algorithm’s advantage in the structural characterization of IDPs,” explains Dr. Brotzakis.
Scientists now have a faster and more accurate way to determine the structures of disordered proteins, especially in cases where experimental data are unavailable. “In the future, we can use this information to discover molecules of pharmaceutical interest that can interact strongly with these proteins and modify their dynamics. This could prevent their problematic folding into toxic forms, such as amyloid fibrils, which are observed in many neurodegenerative diseases,” says Brotzakis.
Next steps are to apply the algorithm to other biomolecules, such as DNA and RNA.
END
A new study by researchers including those at the University of Tokyo revealed that atmospheric gravity waves play a crucial role in driving latitudinal air currents on Mars, particularly at high altitudes. The findings, based on long-term atmospheric data, offer a fresh perspective on the behaviors of Mars' middle atmosphere, highlighting fundamental differences from Earth’s. The study applied methods developed to explore Earth’s atmosphere to quantitatively estimate the influence of gravity waves on Mars’ planetary circulation.
Despite it being a very cold planet, Mars is quite a hot topic these days. With human visitation seemingly ...
A team of scientists from University College Cork (UCC) , the University of Connecticut, and the Natural History Museum of Vienna have uncovered how plants responded to catastrophic climate changes 250 million years ago. Their findings, published in GSA Bulletin, reveal the long, drawn-out process of ecosystem recovery following one of the most extreme periods of warming in Earth’s history: the ‘End-Permian Event’.
With more than 80% of ocean species wiped out, the end-Permian event was the worst mass extinction of all time. But the impacts of this event for life on land have been elusive. By examining fossil plants and ...
ANN ARBOR, Mich. – A new clinical trial will allow researchers to study 3D-printed bioresorbable devices aimed at treating children with rare and life-threatening airway condition tracheobronchomalacia.
The trial, launched by Michigan Medicine and Materialise, marks a crucial step towards full Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for the innovative devices designed to support the airways of infants with the severest forms of the disease.
Tracheobronchomalacia causes the airway to collapse, making breathing difficult and, in severe cases, can be fatal. Currently, infants with this ...
Background and objectives
Sepsis involves a complex cascade of inflammatory reactions and immune system dysregulation. Neutrophils play a crucial role in modulating the anti-inflammatory response, which is vital for managing sepsis. Impaired chemotaxis of granulocytes can significantly impact the outcome of sepsis. Shenfu Decoction, by tonifying Qi and warming Yang, enhances the propelling function of Qi for promoting the chemotactic function of neutrophils. This study aimed to investigate the effects of Shenfu Decoction on the chemotactic function of neutrophils in septic mice and the underlying ...
Various full and partial scholarships will be available for three premier programs of ESMT: Bringing Technology to Market, the General Management Seminar, and the Executive Transition Program.
By offering financial support and access to distinguished executive education, ESMT is committed to fostering greater diversity in senior leadership. The initiative empowers professionals from various backgrounds to make a lasting impact in their industries and beyond.
The scholarships are aimed at senior leaders preparing for top executive positions, particularly transitioning from leading corporate divisions into board level as well as accomplished managers holding global responsibilities ...
PULLMAN, Wash. — When a product is hard to buy, more people want it. A new Washington State University study reveals that wineries producing “cult wines” can boost long-term profits by keeping their prices low, creating excess demand that fuels their brand’s prestige and future revenue.
Economists in WSU’s School of Economic Sciences (SES) analyzed data on cult wines: rare, luxury bottles only available to consumers who secure a spot on a winery’s allocation list or purchase the product via the secondary market. The study, published in the Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, focused solely on Washington, ...
Researchers have discovered how antibodies help to protect against contagious bacterial infections caused by Strep A, including strep throat. And the findings are already contributing to efforts to accelerate the development of a Strep A vaccine.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI), Monash University and the University of Auckland, using the world’s only human challenge model for Strep A, has uncovered how antibodies respond to strep throat infections.
MCRI Dr ...
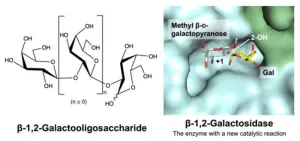
Carbohydrate chains, or glycans, are complex sugar-like compounds that play important roles in various biological processes and structures in our bodies. Galactosides are a type of glycan found in plants, animals, and microorganisms. For example, galactosides are present in plant cell walls and in certain types of beneficial sugars known as prebiotic oligosaccharides, which support gut health. Many glycans containing galactose are also added to processed foods like juice and powdered milk due to their potential health ...
A new study published in the journal Human-Animal Interactions has revealed that exposure to wildlife and forest walks can help ease the symptoms of Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) in US war veterans.
Researchers from UMass Chan Medical School studied 19 veterans with PTSD or PTSD symptoms and found that walking in the forest, assisting with wildlife care in a rehabilitation centre, seeing wildlife in a sanctuary, and bird watching improved psychological symptoms, especially reducing anxiety.
Those that took part in the near four-month study in Massachusetts ...
[Vienna, 06.02.2025]—"In this study, we use the spatial social connections of people within the 50 largest cities in the US to test whether the built environment—in this case, urban highways— is indeed a barrier to social ties, as has long been assumed in urban studies. For the first time, we are also finding quantitatively that this is the case,” explains co-author Sándor Juhász. During his postdoctoral fellowship at the Complexity Science Hub (CSH), Juhász participated in the study.
This ...