(Press-News.org)
A recent study published in Engineering presents an innovative acoustofluidics-based approach for intracellular nanoparticle delivery. This method offers a new way to transport various functional nanomaterials into different cell types, potentially revolutionizing therapeutic applications and biophysical studies.
The efficient delivery of biomolecular cargos into cells is crucial for biomedical research, including gene therapies and drug delivery. However, traditional delivery methods such as endocytosis of nano-vectors, microinjection, and electroporation have limitations. They may require time-consuming processes, complex operations, or expensive equipment. Additionally, issues like low delivery efficiency and potential cell damage still exist.
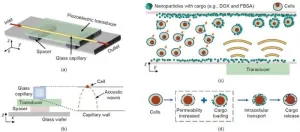
The newly developed acoustofluidics-based method addresses these challenges. It uses standing acoustic waves generated in a glass capillary coated with cargo-encapsulated nanoparticles. By tuning the frequency of the acoustic waves, cells flowing through the capillary are pushed towards the capillary wall. This enables controllable contact between cells and nanoparticles, facilitating nanoparticle attachment to the cell membrane. The acoustic radiation force also increases membrane stress, which slightly deforms the cells and enhances membrane permeability, helping nanoparticles enter the cells.
In the study, researchers used two types of cargos, doxorubicin (DOX) and fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled bovine serum albumin (FBSA), to test the method. They loaded these cargos into zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanoparticles. The results showed that the method could successfully deliver nanoparticles loaded with different cargos into U937 and HeLa cells. The delivery efficiency was significantly enhanced compared to approaches without using acoustofluidics. What’s more, this method does not need bubbles or special acoustic contrast agents, which are often required in conventional sonoporation methods.
The researchers also investigated the properties of the cargo-encapsulated ZIF-8 nanoparticles and the impact of the delivery process on cell viability. They found that the nanoparticles had suitable characteristics for cargo encapsulation and release, and the acoustic waves and ZIF-8 decomposition had minimal effects on cell viability.
This acoustofluidics-based intracellular delivery approach provides a new option for achieving efficient and controllable intracellular delivery of biomolecular cargos. In the future, the research team plans to explore its application in delivering other types of cargo and in treating different cell types, including primary human cells. The findings of this study have the potential to contribute to the development of gene and cellular therapies, as well as fundamental research in cell mechanics.
The paper “Acoustofluidics-Based Intracellular Nanoparticle Delivery,” authored by Zhishang Li, Zhenhua Tian, Jason N. Belling, Joseph T. Rich, Haodong Zhu, Zhehan Ma, Hunter Bachman, Liang Shen, Yaosi Liang, Xiaolin Qi, Liv K. Heidenreich, Yao Gong, Shujie Yang, Wenfen Zhang, Peiran Zhang, Yingchun Fu, Yibin Ying, Steven J. Jonas, Yanbin Li, Paul S. Weiss, and Tony J. Huang. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.11.030. For more information about the Engineering, follow us on X (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) & like us on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringJrnl).
END
Sulfate-reducing bacteria break down a large proportion of the organic carbon in oxygen-free zones of the Earth, and in the seabed in particular. Among these important microbes, the Desulfobacteraceae family of bacteria stands out because its members are able to break down a wide variety of compounds – including some that are poorly degradable – to their end product, carbon dioxide (CO2).
A team of researchers led by Dr Lars Wöhlbrand and Prof. Dr Ralf Rabus from the University of Oldenburg, Germany, has investigated the role ...
When spiders spin their webs, they use their hind legs to pull silk threads from their spinnerets. This pulling action doesn’t just help the spider release the silk, it’s also a crucial step in strengthening the silk fibers for a more durable web.
In a new study, Northwestern University researchers have discovered why the role of stretching is so important. By simulating spider silk in a computational model, the team discovered the stretching process aligns the protein chains within the fibers and increases the number of bonds between those ...
On ten thousand to million years time scales, climate dynamics on the Earth’s surface are driven by both external and internal processes. Earth`s interior provides heat from radioactive decay and chemical compounds by volcanic degassing, such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and carbon dioxide (CO2). Quasiperiodic changes in Earth’s orbit around the sun regulate the amount of incoming solar radiation on the planet’s surface as well as its distribution across latitudes, affecting the length and intensity ...
High levels of ammonia kill liver cells by damaging the mitochondria that power the cells. But this can be prevented using an existing drug due to start clinical trials, finds a new study in mice led by researchers from UCL.
The study, published in Science Advances, is the first to observe that build-up of ammonia (hyperammonaemia) can harm liver cells and describe how this damage occurs in mouse models that are clinically relevant for humans.
Hyperammonaemia is known to cause brain dysfunction in those with liver disease, ...
Philadelphia, March 7, 2025 – After many decades of research, the dairy sector has a significant body of peer-reviewed research showing that feed additives can effectively reduce methane, the greenhouse gas that makes up most of dairy’s environmental footprint. Yet the practical use of this knowledge on farms—as well as general awareness around additive effectiveness and safety—is still gaining momentum. At this critical point in the dairy sector’s pathway to a net-zero future, the Journal of Dairy Science, the leading general dairy research journal from ...
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. — Eradivir, a clinical-stage small molecule immunotherapy biotech company, announced it has begun a Phase 2 challenge study with its antiviral therapeutic, EV25. The study will provide safety and efficacy data gathered from otherwise healthy participants infected with influenza then later treated with EV25.
EV25 was built on a platform created in Philip Low’s lab. Low is the Presidential Scholar for Drug Discovery and the Ralph C. Corley Distinguished Professor of Chemistry in Purdue University’s College of Science. Low is Eradivir’s chief scientific officer and on its board of directors.
The European Medicines ...
Puerto Madryn, Argentina – A new study published in PeerJ Life and Environment reveals that the teeth of South American sea lions (Otaria byronia) hold valuable clues about past population dynamics. Researchers from the Instituto de Biología de Organismos Marinos, the Centro para el Estudio de Sistemas Marinos, and the Universidad Nacional de la Patagonia San Juan Bosco analysed changes intooth size and growth layer groups (GLGs) over the ...
East Hanover, NJ – March 7, 2024 – The employment rate for people with disabilities saw a slight dip in February but continued to fluctuate around a steady plateau of approximately 37.5%. While these dips can trigger speculation about broader policy implications, nTIDE experts cautioned that it is premature to attribute changes to recent shifts in federal employment policies. The employment-to-population ratio for people with disabilities remained stable. nTIDE is issued by Kessler Foundation and the ...
Researchers in the Michael E. DeBakey Department of Surgery at Baylor College of Medicine, the QIMR Berghofer Medical Research Institute in Brisbane, Australia, and collaborating institutions report a groundbreaking discovery in cardiac regeneration that offers new hope for the treatment of ischemic heart failure. Published in npj Regenerative Medicine, the study reveals a novel approach to promoting cardiomyocyte proliferation.
“When the heart cannot replace injured cardiomyocytes with healthy ones, it becomes progressively ...
Elevated concentrations of fluoride can occur in well water, and in some countries, it is added to drinking water to counteract caries in the population. A study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden now supports a few previous studies indicating that exposure to fluoride during the fetal stage or early childhood may impair cognition in children. The study is published in the journal Environmental Health Perspectives.
Fluoride occurs naturally as fluoride ions in drinking water, but the concentrations are generally low in ...