Intelligent covert communication: a leap forward in wireless security
2025-03-10
(Press-News.org)
In the ever-evolving landscape of wireless communication, security remains a paramount concern. A recent study published in Engineering delves into the realm of intelligent covert communication, exploring its latest advancements and future research trends.
Covert communication, also known as low probability of detection (LPD) communication, is a technique that aims to conceal the existence of communication, thereby safeguarding private information. As the volume of private data transmitted via wireless systems continues to soar in the big data era, the need for robust security measures has become more pressing than ever. Unlike traditional encryption and physical layer security techniques, covert communication focuses on hiding the communication behavior itself, adding an extra layer of protection.
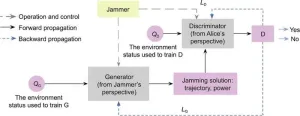
The researchers first introduced the basic concepts and performance metrics of covert communication. A typical system model involves a sender (Alice) transmitting data to a recipient (Bob) without being detected by an adversary (Willie). Performance is measured through metrics such as error detection probability, detection probability, covert outage probability, and effective covert rate. These metrics help in evaluating the effectiveness of covert communication systems and designing better strategies.
The paper then reviewed existing covert communication techniques across different domains. In the time domain, random time-slot selection and time-hopping techniques add an element of randomness to evade detection, although they come with issues like increased transmission delay. Frequency domain techniques, such as spread spectrum and frequency-hopping, reduce the signal power density, making it harder for eavesdroppers to detect the signal. However, they face limitations due to spectrum resources and receiver sensitivity.
Spatial domain technologies, including beamforming, millimeter wave, terahertz communication, and frequency diverse array (FDA), enhance covertness by controlling signal propagation direction and leveraging the unique properties of high-frequency waves. In the power domain, power adaption and artificial noise methods introduce uncertainty to prevent detection, but they pose challenges for legitimate receivers. In the modulation domain, random modulation schemes and waveform overlay techniques improve covertness, with optimal probabilistic constellation shaping further enhancing the covert rate.
Looking ahead, the study identified several future research directions. Intelligent cooperative covert communication, which uses generative adversarial networks (GANs) and deep reinforcement learning (DRL), aims to adapt to complex and dynamic wireless environments. However, it faces challenges in terms of computational complexity. Intelligent parasitic covert communication, which involves spectral superposition, requires careful management of inter-system interference. Multidimensional covert waveform design holds promise in meeting the demands of complex electromagnetic environments but is hampered by high transceiver complexity.
The development of active detection by adversaries also calls for enhanced cognitive capabilities in covert communication systems. Additionally, integrating sensing and communication (ISAC) in covert communication shows potential, but it needs to address issues related to information leakage and mutual interference.
This research provides a comprehensive overview of intelligent covert communication, highlighting its significance in securing future wireless networks. As technology continues to advance, these findings will guide the development of more secure and efficient covert communication methods.
The paper “Intelligent Covert Communication: Recent Advances and Future Research Trends,” authored by Zan Li, Jia Shi, Jiangbo Si, Lu Lv, Lei Guan, Benjian Hao, Zhuangzhuang Tie, Danyang Wang, Chengwen Xing, Tony Q.S. Quek. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.12.007. For more information about the Engineering, follow us on X (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) & like us on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringJrnl).
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-10
LOS ANGELES – March 10, 2025 – Stand Up To Cancer® (SU2C) today announced changes to its Scientific Advisory Committee (SAC), which is composed of cancer research leaders from academic, government, industry and advocacy fields. The SAC oversees SU2C’s scientific research in collaboration with SU2C’s president and CEO Julian Adams, Ph.D.
The new SAC members are:
Scott A. Armstrong, M.D., Ph.D., SVP for drug discovery and chief research strategy officer at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and David G. Nathan professor of pediatrics at Harvard ...
2025-03-10
Two years ago, Chance Ward began opening boxes of horse remains that had been shipped to the University of Colorado Museum of Natural History from other institutions around the country. What he saw made his heart sink.
At the time, Ward was a master’s student in Museum and Field Studies at CU Boulder. The researcher, who had grown up riding horses, was taking part in a large-scale study exploring the history of these iconic animals in the American West. But when he looked inside the packages, he sometimes found ...
2025-03-10
Since the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, workers have spent countless hours in videoconferences—now a fixture of office life. As more people work and live remotely, videoconferencing platforms such as Zoom, MS Teams, FaceTime, Slack, and Discord are a huge part of socializing among family and friends as well. Some exchanges are more enjoyable and flow better than others, raising questions about how the medium of online meetings could be improved in order to raise both efficiency and job satisfaction.
A team of New York University scientists has developed an AI model that can identify aspects ...
2025-03-10
(New York, NY – March 10) – For the third straight year, The Mount Sinai Hospital is ranked the top hospital in New York State on Newsweek/Statista’s “World’s Best Hospitals” list for 2025. The Mount Sinai Hospital moved up to No. 7 in the United States and No. 19 in the world on the same list.
Hospitals within the Mount Sinai Hospital Health System continue to make gains on the global and local stage, with Mount Sinai Morningside and Mount Sinai West ranked at no. 4 in New York City and no. 8 statewide on the same list, which recognizes and ranks 600 leading hospitals across the nation as well as the top hospitals from 30 countries.
“These honors ...
2025-03-10
EMBARGOED: FOR RELEASE 7:01 A.M. (ET), MARCH 10, 2025
Tempe, Ariz., March 10, 2025 – Life with a dog is a matter of give and take. Especially when it comes to communication. With no common human-dog language, our ability to communicate relies on understanding and reading our pet, and vice versa. That process can seem seamless. You give your dog a treat, you look into her eyes and she says “I am delighted to have that cookie.” With a slight wag of her tail, she accepts the treat ...
2025-03-10
Whales are not just big, they’re a big deal for healthy oceans. When they poop, whales move tons of nutrients from deep water to the surface. Now new research shows that whales also move tons of nutrients thousands of miles—in their urine.
In 2010, scientists revealed that whales, feeding at depth and pooping at the surface, provide a critical resource for plankton growth and ocean productivity. Today, a new University of Vermont-led study shows that whales also carry huge quantities ...
2025-03-10
University of Florida researchers are addressing a critical gap in medical genetic research — ensuring it better represents and benefits people of all backgrounds.
Their work, led by Kiley Graim, Ph.D., an assistant professor in the Department of Computer & Information Science & Engineering, focuses on improving human health by addressing "ancestral bias" in genetic data, a problem that arises when most research is based on data from a single ancestral group. This bias limits advancements in precision medicine, Graim said, and leaves large portions ...
2025-03-10
It is widely believed that Earth’s atmosphere has been rich in oxygen for about 2.5 billion years due to a relatively rapid increase in microorganisms capable of performing photosynthesis. Researchers, including those from the University of Tokyo, provide a mechanism to explain precursor oxygenation events, or “whiffs,” which may have opened the door for this to occur. Their findings suggest volcanic activity altered conditions enough to accelerate oxygenation, and the whiffs are an indication of this taking place.
Take a deep breath. Do you ever think about the air entering your lungs? It’s ...
2025-03-10
Water is unique. It is one of the only substances that can exist in nature as a solid, liquid and gas at the same time under ambient conditions (think of solid ice over a pond, which is liquid underneath while storm clouds float overhead). It is also one of the only substances whose solid form is less dense than its liquid — this is why ice floats.
Now scientists from the University of California San Diego have uncovered a key finding to another unique property: at high pressure and low temperature, liquid water separates into two distinct liquid phases — one high-density ...
2025-03-10
The Biodiversity Data Journal (BDJ) became the second open-access peer-reviewed scholarly title to make use of the hosted portals service provided by the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF): an international network and data infrastructure aimed at providing anyone, anywhere, open access to data about all types of life on Earth.
The Biodiversity Data Journal portal, hosted on the GBIF platform, is to support biodiversity data use and engagement at national, institutional, regional and thematic scales by facilitating access and reuse of data by users with various expertise ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Intelligent covert communication: a leap forward in wireless security