(Press-News.org) March 10, 2025 — Perinatal interventions guided by reproductive justice principles can have positive effects on the perinatal mental health of Black birthing patients and, perhaps, the mental health development of their infants, states a systematic review published in a special issue of Harvard Review of Psychiatry, part of the Lippincott portfolio from Wolters Kluwer.
Mental health interventions incorporating reproductive justice principles "utilize a trauma-informed approach to address the psychosocial stress and trauma of racism and their negative effects on pregnant parents and offspring," Cristiane S. Duarte, PhD, MPH, of Columbia University Irving Medical Center (CUIMC) and New York State Psychiatric Institute in New York City, and colleagues explain. "They link the health of pregnant parents to the upstream structural determinant of racism and attempt to combat its negative effects on both physical and mental health by giving agency back to Black birthing communities."
High-level evidence-quantified intervention outcomes in multiple settings
Dr. Duarte’s team identified 12 randomized controlled trials of interventions explicitly designed to address reproductive justice or increase autonomy, community input, racial equity, and/or the cultural relevance of perinatal care for Black birthing people and their infants. The interventions were initiated during pregnancy or delivery and occurred in hospitals, prenatal clinics, and birthing centers, as well as during home visits. The trials measured maternal and/or infant mental health outcomes or developmental processes relevant to mental health.
Five studies employed interpersonal psychotherapy (IPT) or culturally tailored cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), two focused on group prenatal care, and four investigated culturally tailored home visiting programs with local community health workers or doulas. Ten studies measured maternal mental health, one included both infant mental development and maternal mental health outcomes, and one focused on infant mental development.
Positive mental health effects observed in a variety of outcomes
Seven studies had statistically significant positive results. Six found improvement in maternal mental health outcomes: reduction in ante/postpartum depressive symptoms (five studies), antepartum anxiety, and antepartum stress, and increase in postpartum adjustment. The other study identified a significant effect on infant mental health with REACH-Futures (Resources, Education, and Care in the Home by Black community health workers). One of the studies without significant findings was a pilot trial that did not evaluate for statistical significance.
"Effective intervention types included psychologically oriented modalities (IPT, culturally tailored/culturally sensitive CBT, CBT integrated into home visits), group prenatal care integrated with skill-building sessions (CenteringPregnancy Plus), and an educational intervention based on an interactive online platform (Birthly)," reports Simone Dreux, a CUIMC medical student and one of the article’s lead authors. "Of note, most effective interventions were specifically geared toward birthing people deemed at risk for developing mental health conditions—including antepartum and postpartum depression, and antepartum anxiety—as well as those with a previous history of mental health conditions."
Eight studies recruited predominantly low-income participants. Four of them found significant benefits for maternal mental health, and one study (REACH-Futures) found a significant benefit for infant mental development. "This finding is notable because low-income Black birthing people are at even higher risk of developing perinatal mental health conditions than low-income people of other races," the authors point out.
In their discussion, Dr. Duarte’s team suggests potential mechanisms related to their results: Engaging racially concordant community health workers “may increase social belonging, reduce isolation, and improve the emotional experience of pregnancy.” Culturally relevant, psychologically oriented interventions may improve mental health by focusing on “communication skills, goal setting, and problem-solving.” Additionally, group care affirms and respects the autonomy of birthing patients by allowing them to “take ownership of their prenatal care.”
Read Article: Reproductive Justice Interventions in Pregnancy: Moving Toward Improving Black Maternal Perinatal and Intergenerational Mental Health Outcomes
Wolters Kluwer provides trusted clinical technology and evidence-based solutions that engage clinicians, patients, researchers, and students in effective decision-making and outcomes across health care. We support clinical effectiveness, learning and research, clinical surveillance and compliance, as well as data solutions. For more information about our solutions, visit https://www.wolterskluwer.com/en/health.
###
About Wolters Kluwer
Wolters Kluwer (EURONEXT: WKL) is a global leader in information, software solutions and services for professionals in healthcare; tax and accounting; financial and corporate compliance; legal and regulatory; corporate performance and ESG. We help our customers make critical decisions every day by providing expert solutions that combine deep domain knowledge with technology and services.
Wolters Kluwer reported 2024 annual revenues of €5.9 billion. The group serves customers in over 180 countries, maintains operations in over 40 countries, and employs approximately 21,400 people worldwide. The company is headquartered in Alphen aan den Rijn, the Netherlands.
For more information, visit www.wolterskluwer.com, follow us on LinkedIn, Facebook, YouTube and Instagram.
END
Reproductive justice–driven pregnancy interventions can improve mental health
Principles aim to increase autonomy, community input, racial equity, and/or cultural relevance
2025-03-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Intranasal herpes infection may produce neurobehavioral symptoms, UIC study finds
2025-03-10
Herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) is commonly known for causing blisters and sores. But in some cases, the virus can migrate to the eye or nervous system, causing severe, chronic symptoms.
Now, a study from University of Illinois Chicago researchers finds that herpes infection through the nose can lead to anxiety, motor impairment and cognitive issues. The research is the first to show that, by exploiting a cellular enzyme, the virus can produce behavioral symptoms. The finding emphasizes the need for prevention and treatment of a virus carried by billions of people worldwide.
The research, published in mBio, is the latest from the College of Medicine group ...
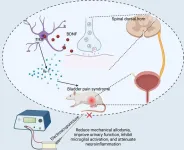
Developing treatment strategies for an understudied bladder disease
2025-03-10
Despite its increasing prevalence, a painful condition called bladder pain syndrome, or interstitial cystitis, remains understudied with limited treatment options. In a new eNeuro paper, Min-Zhi Su and colleagues, from Sun Yat Sen University, used a rat model of bladder pain syndrome to explore if electroacupuncture can alleviate pain and improve bladder function. Electroacupuncture nerve stimulation therapy has shown promise in treating conditions like Huntington’s disease and Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, but researchers have not explored its utility in this context. The researchers discovered that this ...
Investigating how decision-making and behavioral control develop
2025-03-10
Many psychiatric disorders are linked to altered functioning of brain networks that drive reward processing and executive functions like making decisions, taking risks, planning, and memory. But a better understanding of how these networks typically develop to support reward-related executive functions is needed. New in JNeurosci, Samuel Klein and Monica Luciana, from the University of Minnesota, led a longitudinal study to explore how brain networks for reward processing and executive functioning ...
Rutgers researchers revive decades-old pregnancy cohort with modern scientific potential
2025-03-10
The Camden Study, a pregnancy cohort of 4,765 women recruited between 1985 and 2006 from one of America’s poorest cities, has found new life at Rutgers University – where it promises to unlock critical insights into maternal and child health for researchers worldwide.
According to a recent paper in Nutrients, the project was designed to study nutritional status in adolescent pregnancies but expanded into a comprehensive repository of maternal and infant health data that yielded more than a decade of significant ...
Rising CO2 likely to speed decrease in ‘space sustainability’
2025-03-10
Currently more than 8,000 satellites are orbiting at altitudes of between 300 and 1000 km in the Earth’s upper atmosphere – also called the thermosphere. While changes in space weather, such as coronal mass ejections and solar flares, can cause temporary changes in the density of this region, scientists at the University of Birmingham suggest the effects caused by global warming are likely to be much longer term.
This is because of the effects caused by greenhouse gases (GHGs) ...
Study: Climate change will reduce the number of satellites that can safely orbit in space
2025-03-10
MIT aerospace engineers have found that greenhouse gas emissions are changing the environment of near-Earth space in ways that, over time, will reduce the number of satellites that can sustainably operate there.
In a study that will appear in Nature Sustainability, the researchers report that carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases can cause the upper atmosphere to shrink. An atmospheric layer of special interest is the thermosphere, where the International Space Station and most satellites orbit today. When the thermosphere contracts, the decreasing density reduces atmospheric drag— a force that pulls old satellites and other debris down to altitudes where they will ...
Mysterious phenomenon at center of galaxy could reveal new kind of dark matter
2025-03-10
A mysterious phenomenon at the centre of our galaxy could be the result of a different type of dark matter.
Dark matter, the mysterious form of unobserved matter which could make up 85% of the mass of the known universe, is one of science’s biggest manhunts.
In this first of its kind study, scientists have taken a step closer to understanding the elusive mystery matter. They believe a reimagined candidate for dark matter could be behind unexplained chemical reactions taking place in the Milky Way.
Dr Shyam Balaji, Postdoctoral Research Fellow at King’s College London and one of the lead authors of the study explains, “At the ...
Unlocking the secrets of phase transitions in quantum hardware
2025-03-10
Phase transitions, like water freezing into ice, are a familiar part of our world. But in quantum systems, they can behave even more dramatically, with quantum properties such as Heisenberg uncertainty playing a central role. Furthermore, various spurious effects can cause the systems to lose, or dissipate, energy to the environment. When they happen, theses “dissipative phase transitions” (DPTs) push quantum systems into new states.
There are different types or “orders” of DPTs. First-order DPTs are like flipping a switch, causing abrupt jumps between states. ...
Deep reinforcement learning optimizes distributed manufacturing scheduling
2025-03-10
A recent study published in Engineering presents a significant advancement in manufacturing scheduling. Researchers Xueyan Sun, Weiming Shen, Jiaxin Fan, and their colleagues from Huazhong University of Science and Technology and the Technical University of Munich have developed an improved proximal policy optimization (IPPO) method to address the distributed heterogeneous hybrid blocking flow-shop scheduling problem (DHHBFSP).
The DHHBFSP is a complex optimization challenge in manufacturing. In distributed manufacturing settings, jobs with diverse requirements arrive randomly at different hybrid flow shops. These shops have varying numbers of machines ...
AACR announces Fellows of the AACR Academy Class of 2025 and new AACR Academy President
2025-03-10
PHILADELPHIA – The American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) today announced its newly elected 2025 class of Fellows of the AACR Academy.
The mission of the Fellows of the AACR Academy is to recognize and honor extraordinary scientists whose groundbreaking contributions have driven significant innovation and progress in the fight against cancer. Fellows of the AACR Academy constitute a global brain trust of leading experts in cancer science and medicine, working to advance the AACR’s mission to prevent and cure all cancers through ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] Reproductive justice–driven pregnancy interventions can improve mental healthPrinciples aim to increase autonomy, community input, racial equity, and/or cultural relevance