(Press-News.org) Kayunta Johnson-Winters, an associate professor of chemistry and biochemistry at The University of Texas at Arlington, has been named a 2025 fellow of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
The honor recognition recognizes her contributions to biochemistry and molecular biology and her efforts to support junior faculty, women in science and student mentorship.
“This is a tremendous honor and recognizes Kay’s important work in advancing our understanding of disease while mentoring junior faculty and student researchers,” said Morteza Khaledi, dean of UTA’s College of Science. “I’m pleased to see her talent and efforts recognized.”
Dr. Johnson-Winters’ research group uses kinetics to study F420-dependent enzymes, focusing on proteins involved in diseases like tuberculosis and energy generation in cells. Her work has expanded understanding of these proteins and paved the way for potential treatments of metabolic disorders.
“Receiving this award from my peers at the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology is an incredible honor, and I am deeply grateful to all those who have supported me,” Johnson-Winters said. “This is a testament to the those who encouraged me, offered great mentorship and collaborated with me over the years.”
Her research has been supported by grants from prestigious organizations like the National Institutes of Health and the National Science Foundation. She is currently working on a Welch Foundation-sponsored project to explore why some F420-dependent enzymes can use multiple substrates, unlike the Mycobacterial enzyme linked to tuberculosis.
Johnson-Winters also serves as director of undergraduate research, where she has helped triple UTA’s investment in paid research opportunities for students. She is also piloting a travel grant program that enables select students to present their work at national and international conferences.
She earned her undergraduate degree in biology and chemistry from Alverno College in Milwaukee and her doctorate in biochemistry from the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee. She completed a postdoctoral fellowship in chemistry and biochemistry at the University of Arizona before joining UTA in 2010.
Founded in 1906, the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology and its 12,000 members are committed to better understanding the molecular nature of life.
Johnson-Winters will officially be honored at the organization’s annual meeting on April 12-15 in Chicago.
About The University of Texas at Arlington (UTA)
Located in the heart of the Dallas-Fort Worth Metroplex, The University of Texas at Arlington is a comprehensive teaching, research, and public service institution dedicated to the advancement of knowledge through scholarship and creative work. With an enrollment of approximately 41,000 students, UT Arlington is the second-largest institution in the UT System. UTA’s combination of outstanding academics and innovative research contributes to its designation as a Carnegie R-1 “Very High Research Activity” institution, a significant milestone of excellence. The University is designated as a Hispanic Serving-Institution and an Asian American Native American Pacific Islander-Serving Institution by the U.S. Department of Education and has earned the Seal of Excelencia for its commitment to accelerating Latino student success. The University ranks in the top five nationally for veterans and their families (Military Times, 2024), is No. 4 in Texas for advancing social mobility (U.S. News & World Report, 2025), and is No. 6 in the United States for its undergraduate ethnic diversity (U.S. News & World Report, 2025). UT Arlington’s approximately 270,000 alumni occupy leadership positions at many of the 21 Fortune 500 companies headquartered in North Texas and contribute to the University’s $28.8 billion annual economic impact on Texas.
END
Biochemist’s impact on science and students honored
UTA’s Kayunta Johnson-Winters named American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology fellow
2025-03-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
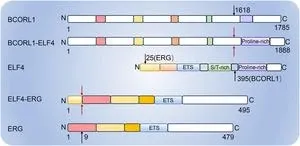
ELF4: A key transcription factor shaping immunity and cancer progression
2025-03-10
ELF4, a transcription factor belonging to the ETS family, has emerged as a pivotal regulator in cell differentiation, immune system function, and cancer progression. This newly published review underscores its molecular complexity and clinical significance, shedding light on its dual role in tumor suppression and oncogenesis.
ELF4 is highly expressed in various tissues, including hematopoietic cells, placenta, and the gastrointestinal tract. Its activity is tightly controlled through post-translational modifications and intricate signaling pathways, allowing it to modulate key physiological processes. Notably, ELF4 plays a critical ...
Updated chronic kidney disease management guidelines recommend SGLT2 inhibitors regardless of diabetes or kidney disease type
2025-03-10
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 10 March 2025
Follow @Annalsofim on X, Facebook, Instagram, threads, and Linkedin
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
New research explores how AI can build trust in knowledge work
2025-03-10
In today’s economy, many workers have transitioned from manual labor toward knowledge work, a move driven primarily by technological advances, and workers in this domain face challenges around managing non-routine work, which is inherently uncertain. Automated interventions can help workers understand their work and boost performance and trust. In a new study, researchers explored how artificial intelligence (AI) can enhance performance and trust in knowledge work environments. They found that when AI systems provided feedback in real-time, performance and trust increased.
The study, by researchers at Carnegie Mellon ...
Compound found in common herbs inspires potential anti-inflammatory drug for Alzheimer’s disease
2025-03-10
LA JOLLA, CA—The herb rosemary has long been linked with memory: “There’s rosemary, that’s for remembrance,” says Ophelia in Shakespeare’s Hamlet. So it is fitting that researchers would study a compound found in rosemary and sage—carnosic acid—for its impact on Alzheimer’s disease. In the disease, which is the leading cause of dementia and the sixth leading cause of death in the US, inflammation is one component that often leads to cognitive decline.
Carnosic acid is an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound that works by activating enzymes that make up the body’s natural defense system. ...
Inhaled COVID vaccine begins recruitment for phase-2 human trials
2025-03-10
Researchers at McMaster University have started a phase-2 clinical trial on a next-generation, inhaled COVID-19 vaccine.
The AeroVax study, supported by $8M in funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), will test needle-free vaccines developed to provide protection from SARS-CoV-2.
Led by Fiona Smaill and Zhou Xing, members of the Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Infectious Disease Research (IIDR) at McMaster, the multi-centre trial will evaluate the new vaccine in a broad study group, while also confirming ...
What’s in a label? It’s different for boys vs. girls, new study of parents finds
2025-03-10
A decades-old riddle poses the following scenario: A boy is injured in a car crash in which the father dies and is taken to the emergency room, where the doctor says, “I cannot operate on him—he’s my son.” Who, then, is the doctor? Many over the years have been stumped in not recognizing the answer: the mother.
Similarly, research has shown that adults instinctively think of men when asked to think of a person—they describe the most “typical” person they can imagine as male and assume storybook characters without a specified gender are men. A new study by psychology researchers shows that the way parents ...
Genes combined with immune response to Epstein-Barr virus increase MS risk
2025-03-10
In multiple sclerosis (MS), antibodies to the common Epstein-Barr virus can accidentally attack a protein in the brain and spinal cord. New research shows that the combination of certain viral antibodies and genetic risk factors can be linked to a greatly increased risk of MS. The study has been published in the journal PNAS and led by researchers at Karolinska Institutet, Sweden, and Stanford University School of Medicine, USA.
An estimated 90 to 95 percent of adults are carriers of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and have formed antibodies against it. Many become infected as children with few or no symptoms, but in young adults, the virus can cause glandular ...
Proximity and prejudice: Gay discrimination in the gig economy
2025-03-10
University of Queensland research has found discrimination based on sexual orientation is common in the gig economy, but only for tasks requiring close physical proximity.
Dr David Smerdon, Dr Samuel Pearson and Dr Sabina Albrecht ran an experiment on a popular online marketplace involving more than 1,100 job posts across 6 Australian cities.
“To test whether workers discriminate against gay men, we created hundreds of fictitious male ‘requester’ profiles, with some clearly signalling they were gay by referring to their male partner or with a couple profile photo,” Dr Pearson said.
“The requested tasks were either inside the home – such as moving ...
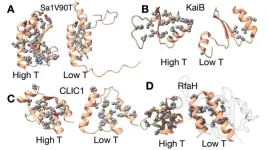
New paper suggests cold temperatures trigger shapeshifting proteins
2025-03-10
Metamorphic proteins can be thought of as the “shapeshifters” of human, animal and bacterial cells. Their ability to drastically switch between two different shapes enables them to adapt to changing environments and carry out diverse functions.
Little is known about how metamorphic proteins transform despite their usefulness in living organisms. To help tackle this mystery, a new paper in the “Perspectives” section of the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) offers a “bold theory,” said co-author John Orban, a professor in the University of Maryland’s Department ...
Reproductive justice–driven pregnancy interventions can improve mental health
2025-03-10
March 10, 2025 — Perinatal interventions guided by reproductive justice principles can have positive effects on the perinatal mental health of Black birthing patients and, perhaps, the mental health development of their infants, states a systematic review published in a special issue of Harvard Review of Psychiatry, part of the Lippincott portfolio from Wolters Kluwer.
Mental health interventions incorporating reproductive justice principles "utilize a trauma-informed approach to address the psychosocial stress and trauma of racism and their negative effects on pregnant parents and offspring," Cristiane S. Duarte, PhD, MPH, of Columbia University ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Biochemist’s impact on science and students honoredUTA’s Kayunta Johnson-Winters named American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology fellow