Traditional Chinese medicine unlocks new potential in treating diseases through ferroptosis regulation
2025-03-10
(Press-News.org)
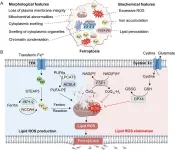
Innovative insights into the role of ferroptosis, a unique form of programmed cell death, are reshaping the landscape of disease treatment. This growing field highlights how Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) can effectively modulate ferroptosis, offering novel therapeutic approaches for various conditions, including cancer, cardiovascular diseases, neurodegenerative disorders, and organ injuries. The powerful bioactive compounds in TCM have demonstrated the ability to regulate iron metabolism, lipid peroxidation, and redox balance, positioning them as key players in advancing modern medicine.
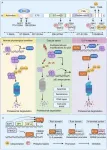
With its rich history of holistic healing, TCM is emerging as a major force in precision medicine, providing targeted treatments that align with the body's natural processes. Certain TCM compounds and monomers exhibit remarkable efficacy in enhancing or inhibiting ferroptosis, thereby offering a dual strategy to either suppress tumor growth or protect healthy tissues from oxidative stress. These findings reinforce the importance of harnessing natural medicinal chemistry to refine therapeutic interventions, ultimately reducing side effects and improving patient outcomes.
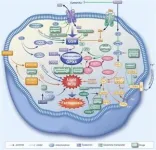
The intricate mechanisms of ferroptosis involve a delicate interplay between glutathione metabolism, iron homeostasis, and oxidative stress pathways. The ability of TCM formulations to fine-tune these biological processes underscores their therapeutic versatility. By leveraging polyphenols, flavonoids, alkaloids, and terpenoids, researchers have unlocked potent strategies to either induce ferroptosis in malignant cells or prevent its harmful effects in conditions like neurodegeneration and ischemia-reperfusion injury.
As advancements in pharmacological research and molecular biology continue to unfold, TCM-based ferroptosis modulation may become an integral part of clinical innovation. The ability to integrate traditional herbal wisdom with cutting-edge biomedical science presents an opportunity to redefine treatment protocols, paving the way for safer, more effective, and personalized medical solutions. Future research and technological breakthroughs will further illuminate the full potential of TCM in ferroptosis-targeted therapy, reinforcing its status as a valuable asset in next-generation healthcare. This growing body of knowledge highlights the synergistic potential between ancient healing traditions and contemporary biomedical advancements.
# # # # #
Genes & Diseases publishes rigorously peer-reviewed and high quality original articles and authoritative reviews that focus on the molecular bases of human diseases. Emphasis is placed on hypothesis-driven, mechanistic studies relevant to pathogenesis and/or experimental therapeutics of human diseases. The journal has worldwide authorship, and a broad scope in basic and translational biomedical research of molecular biology, molecular genetics, and cell biology, including but not limited to cell proliferation and apoptosis, signal transduction, stem cell biology, developmental biology, gene regulation and epigenetics, cancer biology, immunity and infection, neuroscience, disease-specific animal models, gene and cell-based therapies, and regenerative medicine.
Scopus CiteScore: 7.3
Impact Factor: 6.9
# # # # # #
More information: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/
Editorial Board: https://www.keaipublishing.com/en/journals/genes-and-diseases/editorial-board/
All issues and articles in press are available online in ScienceDirect (https://www.sciencedirect.com/journal/genes-and-diseases ).
Submissions to Genes & Disease may be made using Editorial Manager (https://www.editorialmanager.com/gendis/default.aspx ).
Print ISSN: 2352-4820
eISSN: 2352-3042
CN: 50-1221/R
Contact Us: editor@genesndiseases.com
X (formerly Twitter): @GenesNDiseases (https://x.com/GenesNDiseases )
# # # # # #
Reference
Shuai Liu, Xianzhen Yang, Sanxia Zheng, Changjing Chen, Lei Qi, Xiangdong Xu, Denglu Zhang, Research progress on the use of traditional Chinese medicine to treat diseases by regulating ferroptosis, Genes & Diseases, Volume 12, Issue 3, 2025, 101451, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2024.101451
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-10
MSU has a satellite uplink/LTN TV studio and Comrex line for radio interviews upon request.
EAST LANSING, Mich. – A team of researchers at Michigan State University and the University of Michigan found new insights on the timing of prenatal stress and its effect on infant stress reactivity and temperament — including differences between genders.
The study, published in Psychoneuroendocrinology, is the first to examine weekly stress across 27 weeks of pregnancy to pinpoint when it most affects a newborn’s stress response and temperament — two measures that indicate infant biobehavioral reactivity.
“Prenatal ...
2025-03-10
Kayunta Johnson-Winters, an associate professor of chemistry and biochemistry at The University of Texas at Arlington, has been named a 2025 fellow of the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.
The honor recognition recognizes her contributions to biochemistry and molecular biology and her efforts to support junior faculty, women in science and student mentorship.
“This is a tremendous honor and recognizes Kay’s important work in advancing our understanding of disease while mentoring junior faculty and student researchers,” said Morteza Khaledi, dean of UTA’s College of Science. “I’m pleased ...
2025-03-10
ELF4, a transcription factor belonging to the ETS family, has emerged as a pivotal regulator in cell differentiation, immune system function, and cancer progression. This newly published review underscores its molecular complexity and clinical significance, shedding light on its dual role in tumor suppression and oncogenesis.
ELF4 is highly expressed in various tissues, including hematopoietic cells, placenta, and the gastrointestinal tract. Its activity is tightly controlled through post-translational modifications and intricate signaling pathways, allowing it to modulate key physiological processes. Notably, ELF4 plays a critical ...
2025-03-10
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 10 March 2025
Follow @Annalsofim on X, Facebook, Instagram, threads, and Linkedin
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
2025-03-10
In today’s economy, many workers have transitioned from manual labor toward knowledge work, a move driven primarily by technological advances, and workers in this domain face challenges around managing non-routine work, which is inherently uncertain. Automated interventions can help workers understand their work and boost performance and trust. In a new study, researchers explored how artificial intelligence (AI) can enhance performance and trust in knowledge work environments. They found that when AI systems provided feedback in real-time, performance and trust increased.
The study, by researchers at Carnegie Mellon ...
2025-03-10
LA JOLLA, CA—The herb rosemary has long been linked with memory: “There’s rosemary, that’s for remembrance,” says Ophelia in Shakespeare’s Hamlet. So it is fitting that researchers would study a compound found in rosemary and sage—carnosic acid—for its impact on Alzheimer’s disease. In the disease, which is the leading cause of dementia and the sixth leading cause of death in the US, inflammation is one component that often leads to cognitive decline.
Carnosic acid is an antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compound that works by activating enzymes that make up the body’s natural defense system. ...
2025-03-10
Researchers at McMaster University have started a phase-2 clinical trial on a next-generation, inhaled COVID-19 vaccine.
The AeroVax study, supported by $8M in funding from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR), will test needle-free vaccines developed to provide protection from SARS-CoV-2.
Led by Fiona Smaill and Zhou Xing, members of the Michael G. DeGroote Institute for Infectious Disease Research (IIDR) at McMaster, the multi-centre trial will evaluate the new vaccine in a broad study group, while also confirming ...
2025-03-10
A decades-old riddle poses the following scenario: A boy is injured in a car crash in which the father dies and is taken to the emergency room, where the doctor says, “I cannot operate on him—he’s my son.” Who, then, is the doctor? Many over the years have been stumped in not recognizing the answer: the mother.
Similarly, research has shown that adults instinctively think of men when asked to think of a person—they describe the most “typical” person they can imagine as male and assume storybook characters without a specified gender are men. A new study by psychology researchers shows that the way parents ...
2025-03-10
In multiple sclerosis (MS), antibodies to the common Epstein-Barr virus can accidentally attack a protein in the brain and spinal cord. New research shows that the combination of certain viral antibodies and genetic risk factors can be linked to a greatly increased risk of MS. The study has been published in the journal PNAS and led by researchers at Karolinska Institutet, Sweden, and Stanford University School of Medicine, USA.
An estimated 90 to 95 percent of adults are carriers of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and have formed antibodies against it. Many become infected as children with few or no symptoms, but in young adults, the virus can cause glandular ...
2025-03-10
University of Queensland research has found discrimination based on sexual orientation is common in the gig economy, but only for tasks requiring close physical proximity.
Dr David Smerdon, Dr Samuel Pearson and Dr Sabina Albrecht ran an experiment on a popular online marketplace involving more than 1,100 job posts across 6 Australian cities.
“To test whether workers discriminate against gay men, we created hundreds of fictitious male ‘requester’ profiles, with some clearly signalling they were gay by referring to their male partner or with a couple profile photo,” Dr Pearson said.
“The requested tasks were either inside the home – such as moving ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Traditional Chinese medicine unlocks new potential in treating diseases through ferroptosis regulation