(Press-News.org)
A recent study published in the journal Engineering delves into the application of tissue engineering in spinal cord injury (SCI) repair, presenting a comprehensive review of the latest research and potential treatment strategies.
SCI is a severe condition that affects the central nervous system, often leading to permanent loss of sensation and motor function. Current treatments, such as surgical decompression and drug therapy, can only alleviate symptoms to a certain extent, making it crucial to explore new therapeutic approaches. Tissue engineering, an interdisciplinary field integrating life science, material science, engineering technology, and clinical medicine, offers new possibilities.
The researchers first focused on biomaterials. SCI can cause an inflammatory storm and the formation of scar tissue, which hinders axon regeneration. Biomaterials play a vital role in SCI treatment by creating a new microenvironment at the injury site. For example, biodegradable materials like hydrogels have shown great potential. Cai et al. fabricated a GelMA-MXene hydrogel with a grooved configuration, which enhanced hind-limb motor function recovery in rats with SCI. Wang et al. designed an anisotropic Fe3S4 ferromagnetic fluid hydrogel that promoted axon regeneration and functional recovery.
Cells also play a significant role in SCI repair. Stem cells, such as bone-marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), umbilical cord-derived MSCs, and adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs), have been widely studied. They can differentiate into various cell types and secrete cytokines to promote nerve regeneration. For instance, Liu et al. used 3D printing technology to create a neural scaffold for the survival and differentiation of neural stem cells (NSCs) into neurons, improving the hind-limb motor function of rats with SCI.
In addition, the decellularized extracellular matrix (dECM) and exosomes have emerged as promising candidates. dECM can provide a conducive environment for nerve regeneration, while exosomes have therapeutic potential. Zhu et al. developed an HA hydrogel patch that can release exosomes and methylprednisolone, enhancing functional and electrophysiological performance in rats with SCI.
The study also explored other active factors, small molecules, and RNA. Delivering neurotrophic factors, such as NT3, can facilitate the restoration of structure and function. Wang et al. found that NT3-chitosan promoted neuron regeneration and reconstructed the damaged neural network.
Creating a regenerative microenvironment is crucial for SCI repair. Combining biomaterials with cells or active factors can enhance nerve regeneration. Yuan et al. designed a DNA hydrogel to carry NSCs, restoring hind-limb function in rats. Song et al. fabricated an IGF-1 bioactive supramolecular nanofiber hydrogel that promoted the survival and differentiation of NSCs.
Although significant progress has been made, the researchers noted that further research is needed to validate the safety and efficacy of these treatment strategies. They emphasized the importance of coordinated efforts from experts in various disciplines and global collaborative innovation to translate these findings into clinical applications. This research provides valuable insights into the future treatment of SCI, offering new hope for patients suffering from this debilitating condition.
The paper “Tissue Engineering and Spinal Cord Injury Repair,” authored by Lai Xu, Songlin Zhou, Xiu Dai, Xiaosong Gu, Zhaolian Ouyang. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.12.027. For more information about the Engineering, follow us on X (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) & like us on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringJrnl).
END
A preclinical study by HSS investigators found that earlier anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) reconstruction led to lower immune cell activity, less inflammation and fewer joint changes associated with knee osteoarthritis compared to delayed surgery. The research team shared their study results today in a poster presentation at the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons 2025 Annual Meeting.
After a knee injury, such as an ACL tear or rupture, immune cells travel to lymph nodes, where they interact with ...
INDIANAPOLIS – As many as half of nursing home residents are cognitively impaired and may be unable to communicate symptoms such as pain or anxiety to the staff and clinicians caring for them. Therefore, information needed for the evaluation of symptoms and subsequent treatment decisions typically does not reliably exist in nursing home electronic health records (EHRs).
A new paper reports on the novel adaptation of a commonly used symptom assessment instrument to more comprehensively acquire this difficult-to-obtain data with the ultimate goal of enabling knowledge-based expansion of palliative care services in nursing homes ...
Miami (March 12, 2025) – The Bronchiectasis and NTM Association has accepted 27 Care Center and six Clinical Associate Center sites in 23 states and the District of Columbia into the new Bronchiectasis and NTM Care Center Network (CCN).
The CCN aims to facilitate access to specialized care and support for the hundreds of thousands of people with bronchiectasis and nontuberculous mycobacterial (NTM) lung disease.
“As the prevalence of bronchiectasis and NTM lung disease grows, it is even more important for us to create this Care Center Network to improve ...
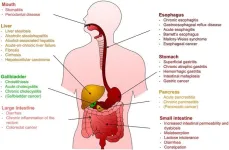
Excessive alcohol consumption is a significant public health concern, responsible for approximately 6% of all deaths and contributing to 5.1% of the global disease burden. Alcohol use is a major risk factor for over 200 diseases, including liver cirrhosis, pancreatitis, and esophageal cancer, with a particularly high incidence of gastrointestinal diseases. More than 50% of alcohol-related deaths are caused by gastrointestinal diseases, highlighting the importance of understanding how ethanol affects the digestive system. This review aims to provide an overview of ethanol ...
Dr. Joungho Park and his research team from the Energy AI and Computational Science Laboratory at the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) have conducted an economic analysis of water electrolysis, a key technology for future eco-friendly hydrogen production, and presented optimal operation strategies to maximize efficiency and reduce costs.
Green hydrogen, considered a key eco-friendly fuel of the future, is primarily produced using two technologies: alkaline water electrolysis and proton exchange membrane (PEM) water electrolysis. Among ...
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States and a significant health issue, with millions of non-melanoma cases and tens of thousands of melanomas diagnosed annually. Furthermore, treating skin cancer costs the U.S. approximately $8.9 billion annually.
Those with fair skin, a history of sun exposure or tanning bed use, and a genetic predisposition, are at higher risk. Key barriers to prevention include a lack of awareness, cultural preferences for tanned skin, and limited access to sun protection.
A study by researchers at Florida Atlantic University’s Charles ...
A new report by the Bankwest Curtin Economics Centre has revealed that young Australians are feeling the squeeze from financial pressures, worsening mental health and declining trust in political institutions, with concerns about the cost of living now topping their list of priorities.
Released today, the Youth in Focus: Navigating Wellbeing in a Changing World report draws on insights from young Australians aged 14 to 25, highlighting their biggest challenges and what they want to see change. While cost of living, education and mental health were identified as key concerns, the report also ...
Researchers have conducted the first national survey on public awareness and perceptions of food, health, and Food is Medicine programs. A team at the Food is Medicine Institute at the Gerald J. and Dorothy R. Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University found that nearly 90 percent of Americans surveyed agreed that eating healthy foods is important for preventing conditions like obesity, high blood pressure, and type-2 diabetes.
The results, published March 12 in the journal Health ...
"UNCG philosopher of biology Dr. Derek Skillings is the lead investigator on a new, three-year, $600,000 grant from the John Templeton Foundation for a study of the emergence and evolution of goal-directed behavior in collective entities.
“A holobiont is a term for a host organism and all of the things that live inside of it and on it,” says Skillings, who is an assistant professor of philosophy at UNCG with adjunct positions in biology and geography, environment, and sustainability.
Examples of collective entities include simple biofilms and massive coral reefs.
“We used to think these weird things like corals, ...
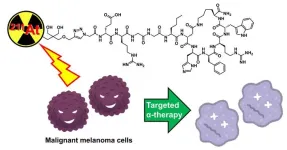
Metastatic melanoma, also known as stage IV melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that spreads to other parts of the body. It is one of the most aggressive forms of skin cancer, with current therapies—including immunotherapy and targeted drugs—showing limited effectiveness. Radiotherapy is an emerging treatment for melanoma, but conventional beta-emitting radionuclide therapies have limitations due to their low energy transfer and long-range radiation, which can cause unintended damage to healthy tissues.
To enhance the efficacy of radiotherapy, a research team from Japan, led by Assistant Professor Hiroyuki Suzuki ...