(Press-News.org) Miami (March 12, 2025) – The Bronchiectasis and NTM Association has accepted 27 Care Center and six Clinical Associate Center sites in 23 states and the District of Columbia into the new Bronchiectasis and NTM Care Center Network (CCN).
The CCN aims to facilitate access to specialized care and support for the hundreds of thousands of people with bronchiectasis and nontuberculous mycobacterial (NTM) lung disease.
“As the prevalence of bronchiectasis and NTM lung disease grows, it is even more important for us to create this Care Center Network to improve access to high-quality, specialty care and resources patients need,” said Doreen Addrizzo-Harris, M.D., Chair of the CCN Steering Committee. “The CCN’s innovative, nationwide network will help us achieve our goals of improving care and quality of life for those with these conditions, as well as advancing toward a cure.”
Centers accepted into the CCN receive a designation of either a Bronchiectasis and NTM Care Center or a Bronchiectasis and NTM Clinical Associate Center, based on institutional resources and infrastructure. The requirements are established by the CCN’s Steering Committee, comprised of leading experts in the field.
The new Bronchiectasis and NTM Care Center sites are:
Cleveland Clinic Florida, Weston, Fla.
Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York
Emory University Center for Bronchiectasis and Nontuberculous Mycobacterial Lung Disease Care, Atlanta
Georgetown University Medical Center/MedStar Georgetown University Hospital Center for Bronchiectasis and NTM Disease, Washington
Johns Hopkins Center for Nontuberculous Mycobacteria and Bronchiectasis, Baltimore
LSU Health New Orleans, New Orleans
Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston
Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, S.C.
National Jewish Health, Denver
Northwell Health Bronchiectasis and NTM Care Center at Long Island Jewish Medical Center, New Hyde Park, New York
Northwestern University, Chicago
NYU Langone Health Bronchiectasis and NTM Program, New York
Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, Ore.
Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia
Stanford University, Stanford, Calif.
University of Alabama at Birmingham, Birmingham, Ala.
University of California, San Francisco
University of Kansas Medical Center, Kansas City, Kan.
University of Michigan Health, Ann Arbor, Mich.
University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha, Neb.
University of North Carolina Bronchiectasis/NTM Care and Research Center, Chapel Hill, N.C.
The University of Texas Health Science Center at Tyler, Tyler, Texas
The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio, San Antonio
UVA Health, Charlottesville, Va.
Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn.
Washington University School of Medicine/Barnes-Jewish Hospital, St. Louis
The new Bronchiectasis and NTM Clinical Associate Center sites are:
Cleveland Clinic Foundation, Cleveland
Norton Thoracic Institute at St. Joseph’s Hospital & Medical Center, Phoenix
NYC Health + Hospitals/Bellevue, New York
UC San Diego Health, San Diego
University of Miami Health System, Miami
University of Rochester Medical Center, Rochester, N.Y.
The network will span 150 medical centers in diverse geographical locations nationwide over the next three years. The Bronchiectasis and NTM Care Center Network is generously supported by Insmed Incorporated as a Founding Sponsor and Boehringer Ingelheim.
For more information about the Bronchiectasis and NTM Care Center Network, visit www.bronchandntm.org.
###
About Bronchiectasis and NTM Lung Disease
Bronchiectasis is a chronic lung disease characterized by enlarged airways that are thickened and/or scarred. These permanently widened airways lead to a buildup of mucus and impaired clearance of bacteria from the lungs. Between 340,000 and 522,000 adults are receiving treatment in the U.S.
Nontuberculous mycobacterial (NTM) lung disease is a chronic respiratory condition caused by certain types of mycobacteria commonly found in the environment, such as in soil and water. NTM lung disease predominantly affects individuals with compromised immune systems or pre-existing lung conditions, such as bronchiectasis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). NTM lung disease affects tens of thousands of individuals in the U.S. with rates of infection on the rise.
About the Bronchiectasis and NTM Association
The Bronchiectasis and NTM Association is a nonprofit organization whose mission is to improve the lives of people with bronchiectasis, nontuberculous mycobacterial lung (NTM) disease, or both conditions. The Association accomplishes this by providing education, supporting advocacy, furthering research, and advancing high-quality, specialized care. For more information, visit www.bronchandntm.org.
END
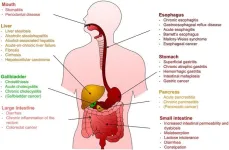
Excessive alcohol consumption is a significant public health concern, responsible for approximately 6% of all deaths and contributing to 5.1% of the global disease burden. Alcohol use is a major risk factor for over 200 diseases, including liver cirrhosis, pancreatitis, and esophageal cancer, with a particularly high incidence of gastrointestinal diseases. More than 50% of alcohol-related deaths are caused by gastrointestinal diseases, highlighting the importance of understanding how ethanol affects the digestive system. This review aims to provide an overview of ethanol ...
Dr. Joungho Park and his research team from the Energy AI and Computational Science Laboratory at the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) have conducted an economic analysis of water electrolysis, a key technology for future eco-friendly hydrogen production, and presented optimal operation strategies to maximize efficiency and reduce costs.
Green hydrogen, considered a key eco-friendly fuel of the future, is primarily produced using two technologies: alkaline water electrolysis and proton exchange membrane (PEM) water electrolysis. Among ...
Skin cancer is the most common cancer in the United States and a significant health issue, with millions of non-melanoma cases and tens of thousands of melanomas diagnosed annually. Furthermore, treating skin cancer costs the U.S. approximately $8.9 billion annually.
Those with fair skin, a history of sun exposure or tanning bed use, and a genetic predisposition, are at higher risk. Key barriers to prevention include a lack of awareness, cultural preferences for tanned skin, and limited access to sun protection.
A study by researchers at Florida Atlantic University’s Charles ...
A new report by the Bankwest Curtin Economics Centre has revealed that young Australians are feeling the squeeze from financial pressures, worsening mental health and declining trust in political institutions, with concerns about the cost of living now topping their list of priorities.
Released today, the Youth in Focus: Navigating Wellbeing in a Changing World report draws on insights from young Australians aged 14 to 25, highlighting their biggest challenges and what they want to see change. While cost of living, education and mental health were identified as key concerns, the report also ...
Researchers have conducted the first national survey on public awareness and perceptions of food, health, and Food is Medicine programs. A team at the Food is Medicine Institute at the Gerald J. and Dorothy R. Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University found that nearly 90 percent of Americans surveyed agreed that eating healthy foods is important for preventing conditions like obesity, high blood pressure, and type-2 diabetes.
The results, published March 12 in the journal Health ...
"UNCG philosopher of biology Dr. Derek Skillings is the lead investigator on a new, three-year, $600,000 grant from the John Templeton Foundation for a study of the emergence and evolution of goal-directed behavior in collective entities.
“A holobiont is a term for a host organism and all of the things that live inside of it and on it,” says Skillings, who is an assistant professor of philosophy at UNCG with adjunct positions in biology and geography, environment, and sustainability.
Examples of collective entities include simple biofilms and massive coral reefs.
“We used to think these weird things like corals, ...
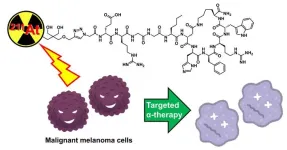
Metastatic melanoma, also known as stage IV melanoma, is a type of skin cancer that spreads to other parts of the body. It is one of the most aggressive forms of skin cancer, with current therapies—including immunotherapy and targeted drugs—showing limited effectiveness. Radiotherapy is an emerging treatment for melanoma, but conventional beta-emitting radionuclide therapies have limitations due to their low energy transfer and long-range radiation, which can cause unintended damage to healthy tissues.
To enhance the efficacy of radiotherapy, a research team from Japan, led by Assistant Professor Hiroyuki Suzuki ...
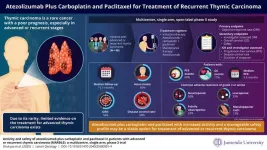
Thymic epithelial tumors are a rare group of malignancies originating in the thymus gland, that includes thymoma and thymic carcinoma. Among these, thymic carcinoma is the more aggressive subtype, characterized by high invasiveness, metastatic potential, and poor prognosis. With an incidence of just 0.15 cases per 100,000 person-years, its rarity poses significant challenges for treatment development. While platinum-based chemotherapy remains the current standard of care, its efficacy is limited. Immune checkpoint inhibitors have shown promise in pretreated cases, but durable ...
The skin consists of two primary layers. The epidermis, the outermost layer, is predominantly made up of keratinocytes, while the deeper dermis contains blood vessels, nerves, and structural proteins such as collagen, which give the skin its strength and texture. Traditionally, fibroblasts—specialized supporting cells within the dermis—have been believed to play a key role in producing collagen.
In humans, collagen is formed before and after birth. It has been believed that fibroblasts play an exclusive role in collagen production in the skin, and no keratinocytes contribute to collagen production. The statement “Collagen production in the human skin is achieved by fibroblasts” ...
New Delhi's air pollution is more severe than previously estimated with particles absorbing atmospheric water vapour leading to particulate matter levels across the city being underestimated by up to 20%, a new study reveals.
Hygroscopic growth causes fine particulate matter (PM1) to swell, reducing sampling devices efficiency and leading to underestimation, with greatest underestimation in estimated concentrations happening during winter morning rush hours, when humidity is highest and pollution is most severe.
In contrast, research shows that the monsoon ...