(Press-News.org) Quantum annealing processors outperform classical supercomputers in solving real-world scientific simulations of quantum spin dynamics, researchers report in a new study, achieving results far beyond the capacity of conventional computational methods, which may require impossible time and energy to match. The results provide a challenge to classical computing, where method improvement has in the past tempered claims of quantum advantage. Only in recent years have quantum computers begun to live up to their lofty promises, with quantum processing units (QPUs) with diverse architectures – such as photonic, neutral-atom, and superconducting systems – beginning to surpass even the most powerful supercomputers in solving complex problems. However, while it is now widely accepted that current QPU technologies outperform classical methods in certain tasks, such as random-number generation, hardware imperfections have limited the advantage of quantum processors over classical computation in practical scientific applications, making it difficult to demonstrate clear cases of quantum superiority. Here, Andrew King and colleagues evaluate the performance of superconducting quantum annealing (QA) processors in simulating a more complex problem – the continuous-time quantum dynamics of the transverse-field Ising model (TFIM). To benchmark the QPUs performance, King et al. compared the results to high-precision matrix product state (MPS) simulations run on powerful classical supercomputers and used advanced classical techniques, such as tensor networks and neural networks, to estimate the cost of approximating quantum dynamics to match QPU accuracy. According to the findings, the quantum processor outperformed classical MPS simulations across a range of Ising model topologies. Moreover, resource requirement estimates for classical simulation reveal severe limitations. To match QPU performance, the authors estimate that MPS methods would require computational resources far beyond practical feasibility, including millions of years of supercomputing time and electricity requirements that exceed annual global consumption. “This impracticability of classical simulation opens the door to quantum advantage in optimization and AI, addressing scientific questions that may otherwise remain unanswered, and applications that may be classically impossible,” write King et al.
END
Quantum annealing processors achieve computational advantage in simulating problems on quantum entanglement
Summary author: Walter Beckwith
2025-03-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How UV radiation triggers a cellular rescue mission
2025-03-12
How UV Radiation Triggers a Cellular Rescue Mission
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun is a well-known cause of DNA damage, which can lead to diseases like skin cancer. But how do our cells repair this damage to protect us? Researchers from Sabanci University, Veysel Oğulcan Kaya and Ogün Adebali, have uncovered a fascinating answer: when DNA is damaged by UV light, our cells reorganize their genetic material in 3D space to prioritize repair, in what might be called a “cellular rescue mission.”
A New Look at DNA Repair
DNA, the blueprint of ...
Hepatic stellate cells control liver function and regeneration
2025-03-12
Until now, doctors knew hepatic stellate cells mainly as drivers of liver fibrosis. The actual functions of this cell type have hardly been studied to date. Researchers from the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), the Mannheim Medical Faculty and Columbia University in New York have now published in the journal Nature that hepatic stellate cells control liver metabolism as well as liver regeneration and size. The results of the study could contribute to new therapeutic approaches for liver diseases.
The liver is a central organ for carbohydrate and protein metabolism as well as for the detoxification ...
The secret DNA circles fueling pancreatic cancer’s aggression
2025-03-12
Pancreatic cancer is one of the deadliest cancers worldwide, with a five-year survival rate of 13%. This poor prognosis stems from both late detection and the cancer’s notorious capacity to adapt and resist therapy. Now, a study led by researchers at the University of Verona, University of Glasgow, and the Botton-Champalimaud Pancreatic Cancer Centre uncovers a hidden driver of this adaptability: extrachromosomal DNA (ecDNA).
A New Player in Pancreatic Cancer
The team found that some pancreatic cancer cells gain a major survival edge by carrying copies of critical cancer genes—such as ...
2D metals: Chinese scientists achieve breakthrough in atomic manufacturing
2025-03-12
Since the groundbreaking discovery of graphene in 2004, the dizzying pace of progress in two-dimensional (2D) materials has ushered in a new era of fundamental research and technological innovation. Although nearly 2,000 2D materials have been theoretically predicted and hundreds have been created in laboratory settings, most of these 2D materials are limited to van der Waals (vdW) layered crystals.
Scientists have long been keen to develop atomically thin 2D metals, thereby expanding ...
Cause of post-COVID inflammatory shock in children identified
2025-03-12
MIS-C is a serious inflammatory shock that affects children. It can occur several weeks after a COVID infection and can be life-threatening. Until now, however, the precise cause of the condition was unknown. Researchers at Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin and the German Rheumatology Research Center (DRFZ), an institute of the Leibniz Association, have identified that reactivation of a pre-existing, dormant infection with the Epstein-Barr virus triggers an excessive inflammatory response. The researchers have detailed their findings in an article in Nature.* These insights open the door to new treatment methods, potentially not limited to MIS-C.
The majority of children ...
QIA researchers create first Operating System for Quantum Networks
2025-03-12
Delft, The Netherlands: Quantum Internet Alliance (QIA) researchers at TU Delft, QuTech, University of Innsbruck, INRIA and CNRS recently announced the creation of the first operating system designed for quantum networks: QNodeOS. The research, published in Nature, marks a major step forward in transforming quantum networking from a theoretical concept to a practical technology that could revolutionize the future of the internet.
“The goal of our research is to bring quantum network technology to all. With QNodeOS we're taking a big step forward. We're making it possible – ...
How the brain uses ‘building blocks’ to navigate social interactions
2025-03-12
Our brains use basic ‘building blocks’ of information to keep track of how people interact, enabling us to navigate complex social interactions, finds a new study led by University College London (UCL) researchers.
For the study, published in Nature, the researchers scanned the brains of participants who were playing a simple game involving a teammate and two opponents, to see how their brains were able to keep track of information about the group of players.
The scientists found that rather ...
Want to preserve biodiversity? Go big, U-M researchers say
2025-03-12
ANN ARBOR—Large, undisturbed forests are better for harboring biodiversity than fragmented landscapes, according to University of Michigan research.
Ecologists agree that habitat loss and the fragmentation of forests reduces biodiversity in the remaining fragments. But ecologists don't agree whether it's better to focus on preserving many smaller, fragmented tracts of land or larger, continuous landscapes. The study, published in Nature and led by U-M ecologist Thiago Gonçalves-Souza, comes to a conclusion on the decades-long debate.
"Fragmentation is bad," said study author Nate Sanders, U-M professor of ecology and evolutionary biology. ...
Ultra-broadband photonic chip boosts optical signals
2025-03-12
Modern communication networks rely on optical signals to transfer vast amounts of data. But just like a weak radio signal, these optical signals need to be amplified to travel long distances without losing information. The most common amplifiers, erbium-doped fiber amplifiers (EDFAs), have served this purpose for decades, enabling longer transmission distances without the need for frequent signal regeneration. However, they operate within a limited spectral bandwidth, restricting the expansion of optical networks.
To meet the growing demand for high-speed data transmission, researchers have been seeking ways to develop more powerful, flexible, ...
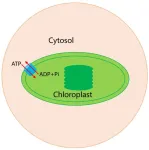
Chinese scientists explain energy transfer mechanism in chloroplasts and its evolution
2025-03-12
A recent study by Chinese scientists has revealed the intricate molecular machinery driving energy exchange within chloroplasts, shedding light on a key event in the evolution of plant life. Led by FAN Minrui from the Center for Excellence in Molecular Plant Sciences of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the research elucidates the structure and function of the ATP/ADP translocator—a crucial member of the nucleotide transporter (NTT) family of proteins—which facilitates the transfer of energy across chloroplast membranes.
Their findings were published online in ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Fossil amber reveals the secret lives of Cretaceous ants
Predicting extreme rainfall through novel spatial modeling
The Lancet: First-ever in-utero stem cell therapy for fetal spina bifida repair is safe, study finds
Nanoplastics can interact with Salmonella to affect food safety, study shows
Eric Moore, M.D., elected to Mayo Clinic Board of Trustees
NYU named “research powerhouse” in new analysis
New polymer materials may offer breakthrough solution for hard-to-remove PFAS in water
Biochar can either curb or boost greenhouse gas emissions depending on soil conditions, new study finds
Nanobiochar emerges as a next generation solution for cleaner water, healthier soils, and resilient ecosystems
Study finds more parents saying ‘No’ to vitamin K, putting babies’ brains at risk
Scientists develop new gut health measure that tracks disease
Rice gene discovery could cut fertiliser use while protecting yields
Jumping ‘DNA parasites’ linked to early stages of tumour formation
Ultra-sensitive CAR T cells provide potential strategy to treat solid tumors
Early Neanderthal-Human interbreeding was strongly sex biased
North American bird declines are widespread and accelerating in agricultural hotspots
Researchers recommend strategies for improved genetic privacy legislation
How birds achieve sweet success
More sensitive cell therapy may be a HIT against solid cancers
Scientists map how aging reshapes cells across the entire mammalian body
Hotspots of accelerated bird decline linked to agricultural activity
How ancient attraction shaped the human genome
NJIT faculty named Senior Members of the National Academy of Inventors
App aids substance use recovery in vulnerable populations
College students nationwide received lifesaving education on sudden cardiac death
Oak Ridge National Laboratory launches the Next-Generation Data Centers Institute
Improved short-term sea level change predictions with better AI training
UAlbany researchers develop new laser technique to test mRNA-based therapeutics
New water-treatment system removes nitrogen, phosphorus from farm tile drainage
Major Canadian study finds strong link between cannabis, anxiety and depression
[Press-News.org] Quantum annealing processors achieve computational advantage in simulating problems on quantum entanglementSummary author: Walter Beckwith