(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON—Members of the media can now register to cover hormone health and science advances at ENDO 2025, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting. The meeting will take place July 12-15, in San Francisco, Calif.
ENDO 2025 offers journalists the opportunity to discuss groundbreaking research with world-renowned experts in diverse fields, including obesity, diabetes, reproductive health, endocrine-disrupting chemicals, bone health and thyroid cancer. The meeting is the premier global conference in endocrinology research and clinical care. The event is expected to draw thousands of people from all over the world.
This year’s program will feature nearly 2,500 abstracts and over 200 other sessions. The Society will distribute news releases and offer one-on-one interviews with our experts on scientific findings being released at ENDO 2025.
News Media Registration Information
To register as media for ENDO 2025, please complete the online registration form. Eligible members of the news media will receive complimentary access to meeting sessions. The meeting program will be available to in-person media attendees only.
Media registrations are approved at the discretion of the Endocrine Society. Eligibility requirements are listed in our online newsroom. Media approved for attendance will receive official notification via email from Endocrine Society staff.
You can find the program and more information about the meeting at endocrine.org/meetings-and-events/endo-2025.
# # #
Endocrinologists are at the core of solving the most pressing health problems of our time, from diabetes and obesity to infertility, bone health, and hormone-related cancers. The Endocrine Society is the world’s oldest and largest organization of scientists devoted to hormone research and physicians who care for people with hormone-related conditions.
The Society has more than 18,000 members, including scientists, physicians, educators, nurses and students in 122 countries. To learn more about the Society and the field of endocrinology, visit our site at www.endocrine.org. Follow us on X @TheEndoSociety and @EndoMedia.
END
ENDO 2025 opens media registration
Meeting offers latest research on obesity, diabetes, chemicals and more hormone science
2025-03-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study: ‘Sustainable intensification’ on the farm reduces soil nitrate losses, maintains crop yields
2025-03-13
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A nine-year study comparing a typical two-year corn and soybean rotation with a more intensive three-year rotation involving corn, cereal rye, soybean and winter wheat, found that the three-year system can dramatically reduce nitrogen — an important crop nutrient — in farm runoff without compromising yield.
The new findings are detailed in the journal Frontiers in Environmental Science.
“Subterranean drainage pipes called tiles transport nitrogen, in the form of nitrate, from fields to streams, impairing downstream surface waters,” the scientists wrote. ...
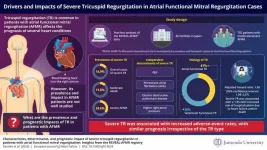
A closer look at severe tricuspid regurgitation in AFMR patients
2025-03-13
Atrial functional mitral regurgitation (AFMR) is a common type of MR linked to high rates of heart failure, highlighting the need to understand its prognostic factors. Tricuspid regurgitation (TR) is a known prognostic factor in heart diseases like heart failure and degenerative MR. It is also frequently observed in AFMR patients, making it crucial to understand its impact on AFMR outcomes.
To address this gap, a research team led by Dr. Tomohiro Kaneko and Dr. Nobuyuki Kagiyama from the Department of Cardiovascular Biology and Medicine at ...
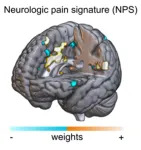
Watching nature scenes can reduce pain, new study shows
2025-03-13
A new neuroimaging study has revealed that viewing nature can help ease how people experience pain, by reducing the brain activity linked to pain perception.
Published in the journal Nature Communications and led by a team from the University of Vienna and University of Exeter, the research offers a promising foundation for new types of non-pharmacological pain treatments.
Using an fMRI scanner, researchers monitored the brain activity of 49 participants in Austria, as they received pain delivered through a series of small electric shocks. When they were watching videos of a natural scene compared to ...
Scientists from IOCB Prague are on track of finding a treatment for autoimmune hair loss
2025-03-13
A research group, led by Dr. Pavel Majer from IOCB Prague, in collaboration with the laboratories of Barbara Slusher and Louis Garza at Johns Hopkins University, have developed a compound that could potentially treat the autoimmune disorder alopecia areata, which causes hair loss leading to the formation of bald patches.The results of their study, recently published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, confirm the efficacy of a series of prodrugs based on derivatives of itaconic acid, simply referred to as itaconates. What is more, there is a good chance that the substances will be ...
Literary theorist Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak named 2025 Holberg Prize Laureate
2025-03-13
(BERGEN, Norway) – Today, the Holberg Prize—one of the largest international prizes awarded annually to an outstanding researcher in the humanities, social sciences, law or theology—named Indian scholar Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak as its 2025 Laureate.
Spivak is University Professor in the Humanities at Columbia University. She will receive the award of NOK 6,000,000 (approx. EUR 515,000) during a 5th June ceremony at the University of Bergen, Norway.
Spivak is considered one of the most influential global intellectuals of our time, and she has shaped literary criticism and philosophy since the ...
The relationship between gut microbiota, immunoglobulin A, and vaccine efficacy
2025-03-13
Gut microbiota may be the key factor explaining why certain individuals do not respond well to the pneumococcal vaccine-a bacterium that can cause various diseases, such as pneumonia. This conclusion is drawn from a recent study led by the B Cell Biology Research Group at the Hospital del Mar Research Institute, published in Science Advances.
Researchers analyzed vaccine responses using genetically modified mouse models to study two types of pneumococcal vaccines-one commonly used in children and another in adults. Although these vaccines function through different mechanisms, both provide broad coverage. However, in individuals with a specific type of immunodeficiency, immunoglobulin ...
Advancing sorghum science: drought-resilient crop for Spain's agricultural future
2025-03-13
Press release
Information embargoed until March 13, 2025, at 09:00 am (time in Barcelona, Spain)
Sorghum is an increasingly important crop for animal and human nutrition, especially in arid and semi-arid regions, due to its natural resistance to drought and high temperatures.
CRAG researchers have identified the molecular mechanisms responsible for drought resistance in sorghum and developed tools that could be used in biotechnological applications.
These advances could combat the effects of climate change, reduce dependence on imports and improve food security for human consumption.
Bellaterra (Barcelona), 13 March ...
Round up, just below, or precise amount? Choosing the final price of a product may be just a cultural thing
2025-03-13
It is well known that culture influences consumer behavior, but the impact of culture on pricing is less studied. One way culture might reflect in price tags is through price endings, which can be round (eg $10.00), just below (eg £9.99), or precise (eg €9.87). While all these price endings are common, little is known about why sellers in certain markets prefer one over the others.
Now, researchers in Germany have examined whether cultural dimensions – individualism, uncertainty avoidance, and long-term orientation – impact how often consumers see certain types of price endings.
“Given that culture significantly influences behavior, cognition, ...
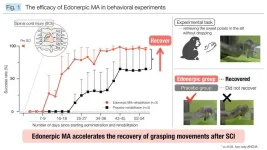
Improving rehabilitation after spinal cord injury using a small compound oral drug
2025-03-13
Spinal cord injury (SCI)—a condition that leads to partial or complete paralysis—has a profound impact on millions of individuals globally. Despite recent advances in SCI treatment, restoring lost motor functions, such as hand movement, remains a significant challenge.
Now, in a new study published online in Brain Communications on March 13, 2025, a team led by Professor Takuya Takahashi from the Department of Physiology, Graduate School of Medicine at Yokohama City University, Japan, along with Dr. Yukio Nishimura, ...
The long wait for bees to return to restored grasslands
2025-03-13
Recovered grasslands need more than 75 years of continuous management to regain their biodiversity because specialized pollinators are slow to return. Kobe University's finding underscores the importance of preserving old grasslands as reservoirs of biodiversity, even if it is just as ski slopes.
Grasslands worldwide are rapidly disappearing due to land-use conversion and abandonment, leading to a well-documented loss of grassland biodiversity. Restoring abandoned grasslands by removing woody vegetation and resuming traditional land management practices has positive effects ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
UCSB researcher bridges the worlds of general relativity and supernova astrophysics
Global exchange of knowledge and technology to significantly advance reef restoration efforts
Vision sensing for intelligent driving: technical challenges and innovative solutions
To attempt world record, researchers will use their finding that prep phase is most vital to accurate three-point shooting
AI is homogenizing human expression and thought, computer scientists and psychologists say
Severe COVID-19, flu facilitate lung cancer months or years later, new research shows
Housing displacement, employment disruption, and mental health after the 2023 Maui wildfires
GLP-1 receptor agonist use and survival among patients with type 2 diabetes and brain metastases
Solid but fluid: New materials reconfigure their entire crystal structure in response to humidity
New research reveals how development and sex shape the brain
New discovery may improve kidney disease diagnosis in black patients
What changes happen in the aging brain?
Pew awards fellowships to seven scientists advancing marine conservation
Turning cancer’s protein machinery against itself to boost immunity
Current Pharmaceutical Analysis releases Volume 22, Issue 2 with open access research
Researchers capture thermal fluctuations in polymer segments for the first time
16-year study finds major health burden in single‑ventricle heart
Disposable vapes ban could lead young adults to switch to cigarettes, study finds
[Press-News.org] ENDO 2025 opens media registrationMeeting offers latest research on obesity, diabetes, chemicals and more hormone science