Statins, aspirin may impact muscle health in smokers
New study suggests statins protect chest muscles, while aspirin increases chest muscle loss
2025-03-13
(Press-News.org) Miami (March 13, 2025) – For current and former smokers, statins may reduce the amount of chest muscle loss, while aspirin may contribute to increased chest muscle loss, according to a new study. The study is published in the January 2025 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
Many people who are current or former smokers are prescribed statins to manage high cholesterol and aspirin to manage heart disease. Research has shown that current or former smokers experience increased skeletal muscle loss, especially in people with COPD.
COPD is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by genetics and irritants like smoke or pollution. The disease affects more than 30 million Americans and is the fourth leading cause of death worldwide.
This new study sought to determine if these common medications are associated with skeletal muscle loss. Researchers examined chest CT imaging data from the COPD Genetic Epidemiology (COPDGene®) study to determine loss in pectoralis muscle area and pectoralis muscle density. This study included 4,191 participants who had reported medication and chest CT scan data for both COPDGene phase 1 and phase 2 visits.
“Current and former smokers have a higher risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes and are commonly prescribed statins and aspirin to treat these conditions. By examining the impact of these medications on pectoralis muscle area and density, we found that statins can potentially reduce chest muscle loss, while aspirin may contribute to increased chest muscle loss,” said Toru Shirahata, M.D., a pulmonologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School and lead author of the study. “By further examining the impact of statins and aspirin on skeletal muscle mass, health care providers may be able to better personalize treatments to improve outcomes for these patients.”
To access current and past issues of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, visit journal.copdfoundation.org.
###
About the COPD Foundation
The COPD Foundation is a nonprofit organization whose mission is to help millions of people live longer and healthier lives by advancing research, advocacy, and awareness to stop COPD, bronchiectasis, and NTM lung disease. The Foundation does this through scientific research, education, advocacy, and awareness to prevent disease, slow progression, and find a cure. For more information, visit copdfoundation.org, or follow us on Twitter and LinkedIn.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-13
Many people dream of retiring to a warmer, less expensive country. But retirees who move abroad may be at greater risk of loneliness than those who stay in their home country, according to research published by the American Psychological Association.
“International retirement migration is increasingly popular in Europe and around the world. On social media you see all the people in Europe sunbathing in Spain, American retirees are moving to Mexico and Japanese retirees to Malaysia,” said study lead author Esma Betül Savaş, MSc, of the Netherlands Interdisciplinary Demographics Institute. “Although these retirement migrants generally ...
2025-03-13
Cambridge, MA, Mar 13 — Insilico Medicine(“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, announced today that it has successfully secured a $110 million Series E financing led by a private equity fund of Value Partners Group (HKG:0806), one of Asia’s largest independent asset management firms, with strong participation from industry- and technology-focused new investors, as well as continued support from global existing backers.
The funds raised in this round will be directed to advance Insilico's innovative drug pipeline ...
2025-03-13
CLEVELAND—Researchers at Case Western Reserve University have discovered molecules that present the potential to drive the development of gastric cancer—among the world’s deadliest forms of the disease.
Gastric, or stomach cancer, remains one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths, according to the American Cancer Society, because it’s difficult to diagnose at an early stage and treatments often fail once the disease has spread.
But a team of researchers led by Kishore Guda, associate professor at the Digestive ...
2025-03-13
WASHINGTON—Members of the media can now register to cover hormone health and science advances at ENDO 2025, the Endocrine Society’s annual meeting. The meeting will take place July 12-15, in San Francisco, Calif.
ENDO 2025 offers journalists the opportunity to discuss groundbreaking research with world-renowned experts in diverse fields, including obesity, diabetes, reproductive health, endocrine-disrupting chemicals, bone health and thyroid cancer. The meeting is the premier global conference in endocrinology research and clinical care. The event is expected to draw thousands of people from all over the world.
This year’s program will feature ...
2025-03-13
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — A nine-year study comparing a typical two-year corn and soybean rotation with a more intensive three-year rotation involving corn, cereal rye, soybean and winter wheat, found that the three-year system can dramatically reduce nitrogen — an important crop nutrient — in farm runoff without compromising yield.
The new findings are detailed in the journal Frontiers in Environmental Science.
“Subterranean drainage pipes called tiles transport nitrogen, in the form of nitrate, from fields to streams, impairing downstream surface waters,” the scientists wrote. ...
2025-03-13
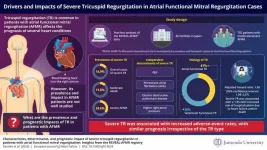
Atrial functional mitral regurgitation (AFMR) is a common type of MR linked to high rates of heart failure, highlighting the need to understand its prognostic factors. Tricuspid regurgitation (TR) is a known prognostic factor in heart diseases like heart failure and degenerative MR. It is also frequently observed in AFMR patients, making it crucial to understand its impact on AFMR outcomes.
To address this gap, a research team led by Dr. Tomohiro Kaneko and Dr. Nobuyuki Kagiyama from the Department of Cardiovascular Biology and Medicine at ...
2025-03-13
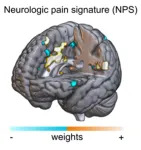
A new neuroimaging study has revealed that viewing nature can help ease how people experience pain, by reducing the brain activity linked to pain perception.
Published in the journal Nature Communications and led by a team from the University of Vienna and University of Exeter, the research offers a promising foundation for new types of non-pharmacological pain treatments.
Using an fMRI scanner, researchers monitored the brain activity of 49 participants in Austria, as they received pain delivered through a series of small electric shocks. When they were watching videos of a natural scene compared to ...
2025-03-13
A research group, led by Dr. Pavel Majer from IOCB Prague, in collaboration with the laboratories of Barbara Slusher and Louis Garza at Johns Hopkins University, have developed a compound that could potentially treat the autoimmune disorder alopecia areata, which causes hair loss leading to the formation of bald patches.The results of their study, recently published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, confirm the efficacy of a series of prodrugs based on derivatives of itaconic acid, simply referred to as itaconates. What is more, there is a good chance that the substances will be ...
2025-03-13
(BERGEN, Norway) – Today, the Holberg Prize—one of the largest international prizes awarded annually to an outstanding researcher in the humanities, social sciences, law or theology—named Indian scholar Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak as its 2025 Laureate.
Spivak is University Professor in the Humanities at Columbia University. She will receive the award of NOK 6,000,000 (approx. EUR 515,000) during a 5th June ceremony at the University of Bergen, Norway.
Spivak is considered one of the most influential global intellectuals of our time, and she has shaped literary criticism and philosophy since the ...
2025-03-13
Gut microbiota may be the key factor explaining why certain individuals do not respond well to the pneumococcal vaccine-a bacterium that can cause various diseases, such as pneumonia. This conclusion is drawn from a recent study led by the B Cell Biology Research Group at the Hospital del Mar Research Institute, published in Science Advances.
Researchers analyzed vaccine responses using genetically modified mouse models to study two types of pneumococcal vaccines-one commonly used in children and another in adults. Although these vaccines function through different mechanisms, both provide broad coverage. However, in individuals with a specific type of immunodeficiency, immunoglobulin ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Statins, aspirin may impact muscle health in smokers
New study suggests statins protect chest muscles, while aspirin increases chest muscle loss