(Press-News.org) Life may not have begun with a dramatic lightning strike into the ocean but from many smaller “microlightning” exchanges among water droplets from crashing waterfalls or breaking waves.
New research from Stanford University shows that water sprayed into a mixture of gases thought to be present in Earth’s early atmosphere can lead to the formation of organic molecules with carbon-nitrogen bonds, including uracil, one of the components of DNA and RNA.
The study, published in the journal Science Advances, adds evidence – and a new angle – to the much-disputed Miller-Urey hypothesis, which argues that life on the planet started from a lightning strike. That theory is based on a 1952 experiment showing that organic compounds could form with application of electricity to a mixture of water and inorganic gases.
In the current study, the researchers found that water spray, which produces small electrical charges, could do that work all by itself, no added electricity necessary.
“Microelectric discharges between oppositely charged water microdroplets make all the organic molecules observed previously in the Miller-Urey experiment, and we propose that this is a new mechanism for the prebiotic synthesis of molecules that constitute the building blocks of life,” said senior author Richard Zare, the Marguerite Blake Wilbur Professor of Natural Science and professor of chemistry in Stanford’s School of Humanities and Sciences.
Microlightning’s power and potential
For a couple billion years after its formation, Earth is believed to have had a swirl of chemicals but almost no organic molecules with carbon-nitrogen bonds, which are essential for proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids, chlorophyll, and other compounds that make up living things today.
How these biological components came about has long puzzled scientists, and the Miller-Urey experiment provided one possible explanation: that lightning striking into the ocean and interacting with early planet gases like methane, ammonia, and hydrogen could create these organic molecules. Critics of that theory have pointed out that lightning is too infrequent and the ocean too large and dispersed for this to be a realistic cause.
Zare, along with postdoctoral scholars Yifan Meng and Yu Xia, and graduate student Jinheng Xu, propose another possibility with this research. The team first investigated how droplets of water developed different charges when divided by a spray or splash. They found that larger droplets often carried positive charges, while smaller ones were negative. When the oppositely charged droplets came close to each other, sparks jumped between them. Zare calls this “microlightning,” since the process is related to the way energy is built up and discharged as lightning in clouds. The researchers used high-speed cameras to document the flashes of light, which are hard to detect with the human eye.
Even though the tiny flashes of microlightning may be hard to see, they still carry a lot of energy. The researchers demonstrated that power by sending sprays of room temperature water into a gas mixture containing nitrogen, methane, carbon dioxide, and ammonia gases, which are all thought to be present on early Earth. This resulted in the formation of organic molecules with carbon-nitrogen bonds including hydrogen cyanide, the amino acid glycine, and uracil.
The researchers argue that these findings indicate that it was not necessarily lightning strikes, but the tiny sparks made by crashing waves or waterfalls that jump-started life on this planet.
“On early Earth, there were water sprays all over the place – into crevices or against rocks, and they can accumulate and create this chemical reaction,” Zare said. “I think this overcomes many of the problems people have with the Miller-Urey hypothesis.”
Zare’s research team focuses on investigating the potential power of small bits of water, including how water vapor may help produce ammonia, a key ingredient in fertilizer, and how water droplets spontaneously produce hydrogen peroxide.
“We usually think of water as so benign, but when it’s divided in the form of little droplets, water is highly reactive,” he said.
Acknowledgements
Zare is also a member of Stanford Bio-X, the Cardiovascular Institute, Stanford Cancer Institute, and the Wu Tsai Neurosciences Institute as well as an affiliate of the Stanford Woods Institute for the Environment.
This research received support from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
END
‘Microlightning’ in water droplets may have sparked life on Earth
2025-03-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Smoke from wildland-urban interface fires more deadly than remote wildfires
2025-03-14
EMBARGOED until Friday, March 14 at 2:00 p.m. Eastern Time (12 noon MT)
Contacts:
David Hosansky, NSF NCAR and UCAR Manager of Media Relations
hosansky@ucar.edu
303-497-8611
Audrey Merket, NSF NCAR and UCAR Science Writer and Public Information Officer
amerket@ucar.edu
303-497-8293
The smoke from fires that blaze through the wildland-urban interface (WUI) has far greater health impacts than smoke from wildfires in remote areas, new research finds.
The study, published this week in Science Advances, estimates that emissions from WUI fires are proportionately about three times more likely to lead ...
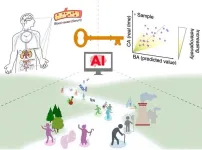
What’s your body really worth? New AI model reveals your true biological age from 5 drops of blood
2025-03-14
Osaka-Japan - We all know someone who seems to defy aging—people who look younger than their peers despite being the same age. What’s their secret? Scientists at Osaka University (Japan) may have found a way to quantify this difference. By incorporating hormone (steroid) metabolism pathways into an AI-driven model, they have developed a new system to estimate a person’s biological age a measure of how well their body has aged, rather than just counting the years since birth.
Using just five drops of ...
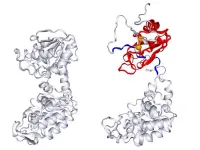
Protein accidentally lassos itself, helping explain unusual refolding behavior
2025-03-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Proteins are long molecules that must fold into complex three-dimensional structures to perform their cellular functions. This folding process occasionally goes awry, resulting in misfolded proteins that, if not corrected, can potentially lead to disease. Now, a new study has described a potential mechanism that could help explain why some proteins refold in a different pattern than expected. The researchers, led by chemists at Penn State, found that a type of misfolding, in which the ...
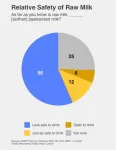
With bird flu in raw milk, many in U.S. still do not know risks of consuming it
2025-03-14
PHILADELPHIA – Although the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) located H5N1 bird flu virus in samples of raw, or unpasteurized, milk in tests in four states in April 2024, and bird flu has been detected in commercially sold raw milk, many Americans do not know that consuming raw milk and its products poses greater health risks than consuming pasteurized milk and its products, especially for children. Consuming raw milk can expose one to Salmonella, E. coli, Campylobacter, Cryptosporidium, Listeria, and Brucella – and, potentially, H5N1 bird flu.
A majority of U.S. adults (56%) knows that drinking raw milk from cows, sheep, or goats is less safe than drinking pasteurized milk. ...
University of Minnesota research team awarded $3.8 million grant to develop cell therapy to combat Alzheimer’s disease
2025-03-14
MINNEAPOLIS/ST. PAUL (03/14/2025) — A University of Minnesota research team was recently awarded a five-year, $3.8 million grant from the U.S. National Institutes of Health to develop a new cell therapy to combat Alzheimer’s disease. More than 55 million people worldwide live with dementia, which includes Alzheimer's disease and other related conditions.
The project aims to adapt advanced techniques developed for cancer treatment to create specialized macrophages — immune cells that can surround and remove proteins from their environment — to seek out and clear harmful proteins in the brain.
"Engineered ...
UConn uncovers new clue on what is leading to neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and ALS
2025-03-14
In Nature Neuroscience, UConn School of Medicine researchers have revealed a new scientific clue that could unlock the key cellular pathway leading to devastating neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease, and the progressive damage to the brain’s frontal and temporal lobes in frontotemporal degeneration (FTD) and the associated disease amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
The study, “Endothelial TDP-43 Depletion Disrupts Core Blood-Brain Barrier Pathways in Neurodegeneration,” was published on March 14, 2025. The lead author, Omar Moustafa Fathy, an MD/Ph.D. candidate at the Center for Vascular Biology at UConn School of ...
Resuscitation in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest – it’s how quickly it is done, rather than who does it
2025-03-14
Key takeaways:
The proportion of bystanders (as opposed to emergency medical services) performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) on individuals experiencing out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) has steadily increased over the past decades.
The study emphasises that the speed of CPR initiation, rather than who performs it, is crucial to survival and better outcomes.
Each 5-minute delay in return of spontaneous circulation in patients experiencing OCHA is associated with a 38% increased risk of death.
Based on these findings, the authors emphasise that increasing the number of individuals trained in proper CPR ...
A closer look at biomolecular ‘silly putty’
2025-03-14
Biomolecular condensates are shifting blobs in our cells that organize cellular matter. They are distinct molecular communities made of DNA, RNA and proteins that “condense” molecules to key locations, yet they frequently defy description. Partly this is because they are so small, they cannot be measured using traditional microscopes.
“These blobs were once described as being ‘liquid-like’ because some of them were observed to kiss, fuse, drip and flow like raindrops on windshields,” said Rohit Pappu, Gene K. Beare Distinguished Professor of biomedical engineering ...
Oxytocin system of breastfeeding affected in mothers with postnatal depression
2025-03-14
The oxytocin system – which helps release breast milk and strengthens the bond between mother and baby – may be affected during breastfeeding in mothers experiencing postnatal depression, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
The new research, published in Psychoneuroendocrinology, investigated the link between maternal mood and the oxytocin pathway during breastfeeding, in mothers with and without symptoms of postnatal depression.
Oxytocin is a hormone that is released in both the brain and body. It plays a central role in childbirth and breastfeeding, ...
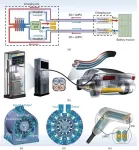
Liquid metal-enabled synergetic cooling and charging: a leap forward for electric vehicles
2025-03-14
A recent study published in Engineering presents a novel approach to address the challenges of high-power direct current fast charging (DC-HPC) in electric vehicles (EVs). The research, led by a team from China Agricultural University, focuses on developing a synergetic cooling and charging strategy using a gallium-based liquid metal flexible charging connector (LMFCC).
As the demand for EVs grows, DC-HPC technology, especially for megawatt-level charging currents (≥1000 A), is crucial for reducing charging time. However, it brings the ...