(Press-News.org) Patients who have been treated for heart failure and experience an improvement of their pump function, are still at higher risk of heart-related death or hospitalisation if they stop taking heart failure medications. This is according to a new study from Karolinska Institutet published in the top-ranked journal Circulation.
“Our finding raises awareness about the importance of implementing and not withdrawing medical treatments in daily clinical practice even if patients with heart failure experience an improvement in symptoms and pump function,” says the study’s last author Gianluigi Savarese, docent and senior lecturer at the Department of Clinical Science and Education, Södersjukhuset, Karolinska Institutet and senior cardiologist at Södersjukhuset.
Using data from the Swedish Heart Failure Registry, RiksSvikt, the researchers have analysed more than 8,700 patients with heart failure whose heart pump function, the ejection fraction, was initially impaired (below 40 percent) but later improved to 40 percent or more.
By linking RiksSvikt with other national registers, the researchers from Karolinska Institutet and Linköping University, Sweden, and the University of Naples, Italy, among others, were able to track hospitalisations and deaths in patients who stopped or continued various heart failure treatments.
Increased morbidity and mortality
The observational study shows that patients who stopped taking medication of the type RASi (renin-angiotensin system inhibitors), ARNi (angiotensin receptor-neprilysin inhibitors) or MRA (mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists) had between 36 and 38 percent higher risk of heart-related death or hospitalisation within one year of medication discontinuation.
However, stopping beta-blocker medication was only associated with a higher risk in patients whose heart function had only moderately improved.
“Our results show that heart failure medications continue to provide important benefits even when heart function has improved,” says Gianluigi Savarese. “This supports the current recommendation to continue with RASi/ARNi and MRA treatment, but also opens up the possibility of reconsidering whether beta-blockers can be discontinued in certain patients whose heart function has recovered well.”
More tailored treatment strategies
Since it was an observational study, no firm conclusions can be drawn about causality. It cannot be ruled out that the results were influenced by residual confounding. The researchers are now planning further studies to confirm the results.
“Our goal is to understand how heart failure medications affect patients with improved heart function and to develop guidelines for when/if it is safe to discontinue certain treatments. This can lead to more tailored and effective treatment strategies for heart failure patients,” says Christian Basile, the study’s first author and PhD student in Gianluigi Savarese’s research group.
The study was funded by the Swedish Heart-Lung Foundation and the EU Horizon project MORE-Europa. The researchers report no conflicts of interest.
Publication: "Withdrawal of Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy in Patients with Heart Failure and Improved Ejection Fraction", Christian Basile, Felix Lindberg, Lina Benson, Federica Guidetti, Ulf Dahlström, Massimo Piepoli, Peter Mol, Raffaele Scorza, Aldo Pietro Maggioni, Lars H Lund, Gianluigi Savarese. Circulation, online 17 March 2025, doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.124.072855.
END
Continued medication important for heart failure patients
2025-03-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Tools to succeed: Learning support for new nurses
2025-03-17
First-year nurses often have difficulties while bridging the gap between educational theory and required workplace practice. In the fast-paced medical field, sufficient guidance is hard to come by, so new nurses must actively learn on their feet through modeling senior nurses’ actions and techniques. There are several studies on learning from role models, but no specific tools that focus on new nurses’ learning progress through this practice.
A new tool, called the Modeling Scale for Novice Nurses, has been developed by Dr. Yayoi Nagano and Professor Yasuko Hosoda at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Nursing. They conducted a questionnaire on ...
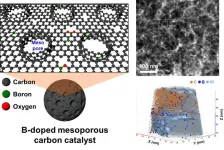
A breakthrough in green hydrogen peroxide production: KIST develops carbon catalyst utilizing airborne oxygen
2025-03-17
Hydrogen peroxide is one of the world's top 100 industrial chemicals with a wide range of applications in the chemical, medical, and semiconductor industries. Currently, hydrogen peroxide is mainly produced through the anthraquinone process, but this process has several problems, including high energy consumption, the use of expensive palladium catalysts, and environmental pollution due to by-products. In recent years, an environmentally friendly method of producing hydrogen peroxide by electrochemical reduction of oxygen using inexpensive carbon catalysts has gained attention. However, this method has been limited by the high cost of injecting high-purity oxygen gas and ...
Travellers: beware of Oropouche virus. Is it the next Zika?
2025-03-17
Heading south for the winter? Oropouche virus, a new infectious disease, has been reported in travellers from Canada and the United States who visited Bolivia, Brazil, Peru, and Cuba. An article published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241440 provides an overview of this emerging virus.
Similar to viruses like dengue and Zika, Oropouche virus symptoms include fever, chills, headache, and muscle aches. The incubation period is 3–10 days, and symptoms last 2–7 days and may recur weeks later in some ...
No increased death rates, admission differences for people experiencing homelessness with severe COVID-19
2025-03-17
Did people experiencing homelessness (PEH) have worse in-hospital outcomes from COVID-19 than housed people? New research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241282 found no differences in in-hospital deaths or hospital admission rates for PEH who visited hospital for acute COVID-19 symptoms.
“In our study, we sought to answer the question of whether experiencing homelessness is a risk factor for worse prognosis from COVID-19 illness independent of important clinical variables including age, comorbidities, vaccination status, and substance use — i.e., whether clinicians should have ...
Optimizing public placement of naloxone kits to save lives
2025-03-17
Making it easy to access naloxone kits to reverse the effects of opioid poisoning will help save lives, according to research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.241228 that looks at the best placements for these kits.
Researchers wanted to understand the best placement for public-access naloxone kits in Vancouver, British Columbia, to help prevent deaths from opioid poisoning. They compared public access strategies for more than 14 000 opioid poisonings over 6 years. They looked at placement at existing locations of take-home naloxone, at public locations like chain businesses, and at public transit ...
Burden of cardiovascular disease caused by extreme heat in Australia to more than double by 2050
2025-03-17
Hot weather is responsible for an average of almost 50,000 years of healthy life lost to cardiovascular disease every year among people in Australia, according to research published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Monday). This equates to around 7.3% of the total burden due to illness and death from cardiovascular disease.
The study also suggests that this figure could double, or even triple, by the middle of the century, if we continue with the current trend of greenhouse gas ...
Who does Darth Vader vote for? Not the same party as Harry Potter
2025-03-17
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 00:01AM UK TIME ON MONDAY 17 MARCH 2025
People think that Harry Potter, Spiderman and Gandalf would vote the same way they do, whereas Darth Vader, Cruella de Vill and Joffrey Baratheon would vote for the rival party.
New research from the University of Southampton, published today [17 March] in the journal Political Science Research & Method, shows how people in the UK and USA believe that fictional characters they admire would share their voting preferences, while those they dislike would vote the other way.
The researchers also found that around one in six people recalled ...
Ground breaking advances in construction robotics in extreme environments unveiled in review
2025-03-16
As the new wave of technological revolution and industrial transformation progresses, scientific research is expanding towards the macroscopic, delving into the microscopic, and advancing into extreme conditions, which becoming the developmental trends at the forefront of global science and technology. With the implementation of national strategies such as the high-quality development of green and low-carbon, China faces a series of new scientific and technological challenges in the field of construction under extreme environments. Among these, construction robotics in extreme environments, which meets the needs for high-risk operations, highly repetitive ...
New strategies to enhance chiral optical signals unveiled
2025-03-15
A recent review article published in Engineering delves into the latest research on enhancing chiral optical signals, a topic with significant implications for various scientific fields. Chirality, a property found in many molecules, plays a crucial role in areas such as chemistry, biology, and pharmacology. However, the measurement of chiral optical signals can be challenging because they are often weak.
The review, led by researchers from the University of Shanghai for Science and Technology, covers a range of methods to boost these signals. One approach involves tailoring optical fields. For instance, ...
Cambridge research uncovers powerful virtual reality treatment for speech anxiety
2025-03-15
As discussed in the paper, the fear of public speaking is widely cited as being the most common fear. Furthermore, there is evidence to suggest that the prevalence of social anxiety and a fear of public speaking are both on the rise. This is concerning when one considers the range of known subsequent negative impacts on mental health, physical health, academic attainment, and career progression.
To address this, Dr Chris Macdonald created an online platform where users transform into skilled and confident public speakers. On the platform, tailored course ...