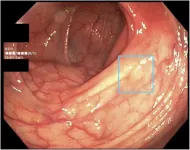
(Press-News.org) The American Gastroenterological Association (AGA) released a new clinical guideline making no recommendation — for or against — the use of computer-aided detection systems (CADe) in colonoscopy. A rigorous review of evidence showed that artificial intelligence-assisted technology helps identify colorectal polyps. However, its impact on preventing colorectal cancer — the third most common cancer worldwide — remains unclear.
Colonoscopy, performed more than 15 million times annually in the U.S., is an effective tool for detecting and preventing colorectal cancer. CADe systems have been shown to improve polyp detection rates, but whether that translates to reduced cancer cases is as yet unknown.
“We are confident that using AI will lead to more polyps removed and more colonoscopies,” said guideline author Benjamin Lebwohl, MD, AGAF, who said he encouraged his institution to adopt the technology. “We’re less sure about the extent to which it will lead to less colon cancer. AI-assisted colonoscopy technology is promising and exciting. It’s reasonable for practitioners to use the tech now, but we’re not yet at a point where we can recommend universal adoption.”
With a growing number of studies evaluating the impact of AI-driven polyp detection, AGA is the first gastroenterological society in the U.S. to tackle an AI guideline for polyp detection. Data were evaluated using the rigorous GRADE process, and the final recommendation reflects significant input from GIs in community and academic practices. The guideline highlights key knowledge gaps that future studies need to address.
Currently, CADe systems predominantly drive up the detection of low-risk polyps, which may result in more frequent and costly follow-up colonoscopies with uncertain benefits in preventing cancer, guideline authors said. Widespread adoption could also strain resources, limiting access for high-risk patients who need colonoscopies most.
“If AI is going to be impactful, it needs to be better than the human eye,” said guideline author Shahnaz Sultan, MD, MHSc, AGAF. "Right now, AI is detecting easy-to-detect lesions. This is version 1.0. Before we can recommend everyone use AI, we need version 4.0, where it helps detect polyps that are truly difficult to find.”
Next steps: Key knowledge gaps and future research
AGA plans to update the guideline in one to two years as more data linking the use of CADe in colonoscopy to improve patient outcomes becomes available. Key areas for future research include:
Practitioner guidance: Clinicians should not feel obligated to use CADe but are encouraged to start as AI systems improve over time.
Quality over quantity: The focus should be on patient outcomes, such as post-colonoscopy colorectal cancer rates, rather than just polyp detection.
Rethinking surveillance: As CADe increases polyp detection, guidance on follow-up colonoscopy intervals should be reassessed.
Transparency in AI research: More publicly available data is needed to ensure AI models are rigorously compared and improved.
Understanding colorectal cancer:
Colorectal cancer (also known as colon cancer) is cancer of the colon and/or rectum and occurs when a growth in the lining of the colon or rectum becomes cancerous. It is the third most common cancer worldwide and ranks as the third most common cause of cancer-related death in the United States. Most colorectal cancers come from precancerous polyps — adenomatous polyps or serrated polyps — that form over years (10 years on average) to become a cancer. A polyp is a mushroom-like or flat growth on the inside wall of the colon or rectum. Polyps grow slowly over many years. Not all colon polyps have the same risk of turning into colon cancer. Precancerous polyps could become cancerous; other types of polyps (hyperplastic, inflammatory) do not. Learn more at the AGA GI Patient Center.
###
AGA Media Contact: Annie Mehl, Communications and Media Relations Manager, media@gastro.org, 301-327-0013
About the AGA Institute
The American Gastroenterological Association is the trusted voice of the GI community. Founded in 1897, the AGA has grown to more than 16,000 members from around the globe who are involved in all aspects of the science, practice, and advancement of gastroenterology. The AGA Institute administers the practice, research and educational programs of the organization. www.gastro.org
AGA is on Instagram.
Like AGA on Facebook.
Follow us on X @AmerGastroAssn and Bluesky @amergastroassn.bsky.social.
Check out our videos on YouTube.
Join AGA on LinkedIn.
About Gastroenterology
Gastroenterology is the most prominent journal in the field of gastrointestinal disease. As the official journal of the AGA Institute, Gastroenterology delivers up-to-date and authoritative coverage of both basic and clinical gastroenterology. Regular features include articles by leading authorities and reports on the latest treatments for diseases. Original research is organized by clinical and basic-translational content, as well as by alimentary tract, liver, pancreas, and biliary content. www.gastrojournal.org/
END
AI technology for colon cancer detection shows promise for widespread use – in the future
American Gastroenterological Association guideline concludes that it is not clear whether computer-aided detection systems (CADe) for colonoscopy should be recommended for routine widespread use
2025-03-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Researchers identify promising drug candidates for previously “undruggable” cancer target
2025-03-20
For the first time scientists have identified promising drug candidates that bind irreversibly with a notoriously “undruggable” cancer protein target, permanently blocking it.
Transcription factors are proteins that act as ‘master switches’ of gene activity and play a key role in cancer development. Attempts over the years to design “small molecule” drugs that block them have been largely unsuccessful, so in recent years scientists have explored using peptides – small protein fragments – to block these “undruggable” targets.
Now researchers from the University of Bath have for ...
Smartwatch data: Study finds early health differences in long COVID patients
2025-03-20
[Vienna, 19.03.2025]—Between April 2020 and December 2022, over 535,000 people in Germany downloaded and activated the Corona Data Donation App (CDA). Of these, more than 120,000 voluntarily shared daily data from their smartwatches and fitness trackers with researchers, providing insights into vital functions such as resting heart rate and step count.
“These high-resolution data served as the starting point for our study,” explains CSH researcher Katharina Ledebur. “We were able to compare vital signs in 15-minute intervals before, during, and after a SARS-CoV-2 infection.”
Higher Resting Heart Rate ...
Mere whiff of penguin poo pushes krill to take frantic evasive action
2025-03-20
Imagine looking at the world through the stalked compound eyes of krill in the Southern Ocean. All of a sudden, a penguin appears like a voracious giant, streamlined like a torpedo, chasing and consuming thousands of krill at rapid speed.
Now, researchers have shown that the water-borne smell of the poo of these flightless birds is enough to cause the krill to show escape behaviors.
“Here we show for the first time that a small amount of penguin guano causes a sudden change in the feeding and swimming behaviors of Antarctic krill,” said Dr Nicole ...
Deep in the Mediterranean, in search of quantum gravity
2025-03-20
Quantum gravity is the missing link between general relativity and quantum mechanics, the yet-to-be-discovered key to a unified theory capable of explaining both the infinitely large and the infinitely small. The solution to this puzzle might lie in the humble neutrino, an elementary particle with no electric charge and almost invisible, as it rarely interacts with matter, passing through everything on our planet without consequences.
For this very reason, neutrinos are difficult to detect. However, in rare cases, ...
Parts of the brain that are needed to remember words identified
2025-03-20
The parts of the brain that are needed to remember words, and how these are affected by a common form of epilepsy, have been identified by a team of neurologists and neurosurgeons at UCL.
The new study, published in Brain Communications, found that shrinkage in the front and side of the brain (prefrontal, temporal and cingulate cortices, and the hippocampus) was linked to difficulty remembering words.
The new discovery highlights how the network that is involved in creating and storing word memories is dispersed throughout the brain.
This is particularly crucial for helping to understand conditions such as epilepsy, in which patients may have difficulty with remembering words. ...
Anti-amyloid drug shows signs of preventing Alzheimer’s dementia
2025-03-20
An experimental drug appears to reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s-related dementia in people destined to develop the disease in their 30s, 40s or 50s, according to the results of a study led by the Knight Family Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer Network-Trials Unit (DIAN-TU), which is based at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis. The findings suggest – for the first time in a clinical trial – that early treatment to remove amyloid plaques from the brain many years before symptoms arise can delay the onset of Alzheimer’s dementia.
The study is published March 19 in The Lancet Neurology.
The international study ...
Sharing mealtimes with others linked to better wellbeing
2025-03-20
UCL Press Release
Under embargo until Thursday 20th March, 00:01 UK time / Wednesday 19th March, 20:01 Eastern US time
Not peer reviewed | Literature review & data analysis | People
People who share more mealtimes with others are more likely to report higher levels of life satisfaction and wellbeing, finds research led by a UCL academic for the World Happiness Report.
In chapter three of the report, Sharing Meals with Others, the researchers from UCL, University of Oxford, Harvard University and Gallup found that meal sharing as an indicator ...
New DESI results: Evidence mounts for evolving dark energy
2025-03-19
A new analysis of data collected over three years by the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) collaboration provides even stronger evidence than the group’s previous datasets that dark energy, long thought to be a “cosmological constant,” might be evolving over time in unexpected ways.
Dr. Mustapha Ishak-Boushaki, professor of physics at The University of Texas at Dallas, is co-chair of the DESI working group that interprets cosmological survey data gathered by the international collaboration, which includes more than 900 researchers ...
New DESI results strengthen hints that dark energy may evolve
2025-03-19
The fate of the universe hinges on the balance between matter and dark energy: the fundamental ingredient that drives its accelerating expansion. New results from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) collaboration use the largest 3D map of our universe ever made to track dark energy’s influence over the past 11 billion years. Researchers see hints that dark energy, widely thought to be a “cosmological constant,” might be evolving over time in unexpected ways.
DESI is an international experiment with more than 900 researchers from over 70 institutions around the world and is managed by the U.S. Department of Energy’s Lawrence Berkeley ...
DESI opens access to the largest 3D map of the universe yet
2025-03-19
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) is mapping millions of celestial objects to better understand dark energy: the mysterious driver of our universe’s accelerating expansion. Today, the DESI collaboration released a new collection of data for anyone in the world to investigate. The dataset is the largest of its kind, with information on 18.7 million objects: roughly 4 million stars, 13.1 million galaxies, and 1.6 million quasars (extremely bright but distant objects powered by supermassive black holes at their cores).
While the experiment’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] AI technology for colon cancer detection shows promise for widespread use – in the futureAmerican Gastroenterological Association guideline concludes that it is not clear whether computer-aided detection systems (CADe) for colonoscopy should be recommended for routine widespread use