(Press-News.org) A new study has discovered that birds in the Galápagos Islands are changing their behaviour due to traffic noise, with those frequently exposed to vehicles showing heightened levels of aggression.
Published in the journal Animal Behaviour and led by experts from Anglia Ruskin University (ARU) and the Konrad Lorenz Research Centre at the University of Vienna, the research examined the impact of vehicle noise pollution on Galápagos yellow warblers (Setophaga petechia aureola), a songbird widespread on the archipelago.
The Galápagos Islands, located over 500 miles off the coast of Ecuador, are considered a natural living laboratory due to the large number of unique, endemic species. The Galápagos yellow warbler is genetically distinct from other yellow warblers found in the Americas and is classified as a subspecies.
A visit to the Galápagos Islands in 1835 helped inspire Charles Darwin to develop the theory of evolution by natural selection. However, recent decades have seen significant human population growth. Alongside a rise in tourism, the permanent population is increasing by over 6% per year, leading to more vehicles on the islands’ roads.
The new study involved researchers playing bird songs from a speaker, simulating an intruder, accompanied by recorded traffic noise at 38 locations populated by Galápagos yellow warblers on the islands of Floreana and Santa Cruz – 20 sites were within 50 metres of the nearest road and 18 were over 100 metres away.
The researchers then measured song, typically used to ward off intruders, and physical, aggressive behaviours such as approaching the speaker closely and making repeated flights across it.
During trials with traffic noise, the researchers found that Galápagos yellow warblers living in roadside territories showed increased aggression, but those living away from the roads showed decreased aggression relative to trials without noise.
Importantly, the effect of living on a roadside territory was present even on Floreana Island, with only about 10 vehicles present on the island, suggesting even minimal experience of traffic affects responses to noise.
Additionally, Galápagos yellow warblers on the more populous island of Santa Cruz increased the duration of their song when confronted by traffic noise. These findings support the idea that long-term selection based on noise experience, or an individual bird’s previous experience of noise, allows them to adapt and adjust the features of their songs.
Finally, the birds increased the minimum frequencies of their songs during the noise experiments, regardless of their territory’s proximity to the road, helping to reduce any overlap of their songs with the low-frequency traffic noise.
Co-author Dr Caglar Akcay, Senior Lecturer in Behavioural Ecology at Anglia Ruskin University (ARU), said: “Birds use song during territorial defence as an aggressive signal. However, if external noise such as traffic interferes with the signalling, effectively blocking this communication channel, increasing physical aggression would be an appropriate response.
“Our results show that the change in aggressive responses in yellow warblers occurred mainly near roads. Birds occupying roadside territories on both islands, and therefore having regular experience of traffic noise, may have learned to increase physical aggression when the territorial intrusion was accompanied by traffic noise.
“We also found some evidence of birds trying to cope with noise by adjusting their song, with yellow warblers in all habitats increasing the minimum frequency of their songs to help them be heard above the traffic noise.
“Our study shows the importance of considering behavioural plasticity in conservation efforts and developing strategies to mitigate the effects of noise pollution on wildlife. It also highlights the significant impact of human activities on wildlife behaviour, even in relatively remote locations such as the Galápagos Islands.”
END
Galapagos birds exhibit ‘road rage’ due to noise
New study finds that aggressive behavior is linked to birds’ proximity to traffic
2025-03-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Groundbreaking study finds AI-driven interviews with children may boost accuracy in witness accounts
2025-03-20
Groundbreaking Study Finds AI-Driven Interviews with Children May Boost Accuracy in Witness Accounts
In a first-of-its-kind study published in the journal PLOS ONE, an international team of researchers led by scholars from New York University Shanghai and Åbo Akademi University in Turku, Finland explored the potential of artificial intelligence to assist in sensitive child investigative interviews. The study compared how effectively a Large Language Model (LLM), specifically ChatGPT, and untrained human interviewers were able to interview children about a mock event ...
New framework to measure economic well-being considers new and free goods and services; addition of digital goods boosts growth
2025-03-20
Welfare measurement is among the most fundamental questions in economics. Policymakers and others use gross domestic product (GDP) as a proxy for welfare, but this application does not reflect the benefits of introducing new and free goods and services, such as digital goods, and may result in misunderstanding the economy.
In a new study, researchers developed a framework to measure the welfare contributions of new and free goods and services and quantify their benefits. By applying the framework to several examples (e.g., Facebook, Smartphone cameras), the study found that these goods and services significantly increase welfare.
The study ...
Augmented reality guidance for placing intracranial drains now clinically validated
2025-03-20
March 20, 2025 — Placing an external ventricular drain (EVD) at bedside using augmented reality (AR) guidance is more precise than freehand placement and is associated with fewer reinterventions and complications, according to a clinical pilot study of a novel system. Frederick Van Gestel, MD, a neurosurgery resident at Universitair Ziekenhuis Brussel and PhD researcher at Vrije Universiteit Brussel in Brussels, Belgium, and colleagues report first-in-human results in Neurosurgery, the official publication of the Congress ...
How feathers develop in chickens
2025-03-20
Inhibiting the sonic hedgehog (Shh) pathway strongly perturbs feather development in chickens by restricting feather bud outgrowth, invagination and branching, according to a study published March 20th, in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Rory Cooper and Michel Milinkovitch from the University of Geneva, Switzerland.
Avian feathers are intricate appendages whose forms vary substantially across species and body areas, and between juvenile and adult stages. Understanding both the developmental and evolutionary mechanisms underpinning this morphological diversity has long fascinated biologists. The morphological intricacies ...
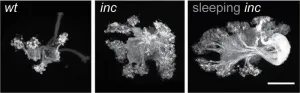
Insomniac fruit fly mutants show enhanced memory despite severe sleep loss
2025-03-20
Fruit fly mutants that have severe sleep deficits perform better at olfactory learning and memory tasks, according to a study published March 20th in the open-access journal PLOS Biology by Sheng Huang and Stephan Sigrist from Freie Universität Berlin, Germany, and colleagues. The paradox of enhanced memory despite sleep loss could be explained by protein kinase A (PKA) signaling in the mushroom body of the fly brain.
Sleep is a dynamic process conserved from invertebrates to mammals and humans. Although sleep is thought to serve many purposes, it is often studied for its restorative roles, which ...
Seals can sense their own circulating blood oxygen and it keeps them from drowning
2025-03-20
Marine mammals may have a secret weapon to survive long dives – an ability to directly sense their own circulating blood-oxygen levels that most mammals lack – allowing them to stay submerged longer and resurface before hypoxia leads to drowning, researchers report. Air-breathing marine mammals have developed a range of physiological adaptations to survive in aquatic environments, including thermoregulation to endure the pressures of the deep. However, one of the most critical evolutionary challenges for diving mammals is avoiding drowning. Despite adaptations for larger oxygen storage and tolerance to low oxygen levels, these animals still risk drowning if they ...
Infants encode short-lived hippocampal memories
2025-03-20
Challenging assumptions about infant memory, a novel functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study shows that babies as young as 12 months old can encode memories, researchers report. The findings suggest that infantile amnesia – the inability to remember our first few years of life – is more likely caused by memory retrieval failures rather than an inability to form memories in the first place. Despite infancy being a period of rapid learning, memories from this time do not persist into later childhood or adulthood. In ...
Mountain uplift and dynamic topography shapes biodiversity over deep time
2025-03-20
Rising mountains do more than reshape the landscape – they also drive evolutionary change, according to a new study. By simulating millions of years of tectonic uplift, researchers have uncovered a link between mountain building and biodiversity, shedding light on how Earth’s dynamic topography shapes biodiversity over deep time. Mountain ranges are widely recognized as global hotspots of terrestrial biodiversity yet only cover a relatively small proportion of the Earth’s surface, suggesting a strong connection between topographic evolution and species diversity. Mountainous terrain can promote speciation by isolating populations, ...
Majority of carbon sequestered on land is locked in nonliving carbon reservoirs
2025-03-20
Challenging long-held assumptions about global terrestrial carbon storage, a new study finds that the majority of carbon dioxide (CO2) absorbed by ecosystems has been locked away in dead plant material, soils, and sediments, rather than living biomass, researchers report. These new insights, which suggest that terrestrial carbon stocks are more resilient and stable than previously appreciated, are crucial for shaping future climate mitigation strategies and optimizing carbon sequestration efforts. Recent studies have shown that terrestrial carbon stocks are increasing, offsetting ...
From dinosaurs to birds: the origins of feather formation
2025-03-20
Feathers are among the most complex cutaneous appendages in the animal kingdom. While their evolutionary origin has been widely debated, paleontological discoveries and developmental biology studies suggest that feathers evolved from simple structures known as proto-feathers. These primitive structures, composed of a single tubular filament, emerged around 200 million years ago in certain dinosaurs. Paleontologists continue to discuss the possibility of their even earlier presence in the common ancestor of dinosaurs and pterosaurs (the first flying vertebrates with membranous wings) around 240 million years ago.
Proto-feathers are ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
[Press-News.org] Galapagos birds exhibit ‘road rage’ due to noiseNew study finds that aggressive behavior is linked to birds’ proximity to traffic