(Press-News.org) Researchers at the Advanced Research Unit on Metabolism, Development & Aging (ARUMDA), in the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR, Mumbai and TIFR Hyderabad), have unveiled a comprehensive understanding of the harmful effects of sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs) on human health, using a preclinical mouse model that closely mimics human consumption patterns. The study, published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, sheds light on how chronic sucrose-water intake (10%) alters key physiological, molecular, and metabolic processes across various organs, driving the onset of diseases such as diabetes and obesity.
Significance of the study
This research provides critical insights into how chronic SSB consumption, even at human-relevant levels, disrupts physiological processes. The study uniquely integrates organ-specific molecular mechanisms, offering a systems-level understanding of how SSBs drive obesity, diabetes, and other metabolic disorders.
Findings from United Nations Public Division and Global Dietary Database, as well as population-level studies conducted by institutes like NHS, NIH and others have clearly indicated an alarming increase in the consumption of sugar sweetened beverages globally, including in India. This makes the findings of the study very relevant as it would contribute to the global efforts in combating the metabolic disorders associated with SSB overconsumption.
Research Methods
The study employed a physiologically relevant model in which mice were provided with 10% sucrose water, mimicking chronic human SSB consumption. Researchers conducted detailed analyses of molecular, cellular, and metabolic responses in multiple tissues, including the liver, muscles and small intestine, under fed and fasted conditions.
Key Findings
The Small Intestine’s Central Role in Metabolic Dysregulation
The study discovered that the small intestine is a major contributor to systemic glucose imbalances. Excessive sucrose consumption causes a "molecular addiction" in the intestinal lining, leading to disproportionate absorption of glucose (hexose sugars) over other essential nutrients such as amino acids and fats.
This nutrient uptake imbalance disrupts energy metabolism and amplifies the dysfunction of other organs like the liver and muscles.
Fed and Fasted State Differences
The impact of chronic dietary perturbation affecting physiology differently under fed and fasted states is under-appreciated. In this regard, the study demonstrated distinct anabolic and catabolic responses in fed versus fasted states due to chronic sucrose intake. This imbalance further underscores how nutrient allocation and resource mobilization contribute to systemic metabolic disorders.
Hepatic and Muscular Effects
Despite increased glucose absorption, the liver does not exhibit altered gene expression related to glucose metabolism. Instead, systemic insulin resistance is triggered, exacerbating gluconeogenesis (glucose production by the liver) that leads to metabolic imbalance.
In skeletal muscles, mitochondrial dysfunction and reduced efficiency in glucose utilization further contribute to the impaired metabolic state.
Implications for Public Health
The findings stress the urgent need for policies and awareness campaigns to reduce SSB consumption, particularly among vulnerable populations.
The identification of tissue-specific effects provides a roadmap for developing targeted therapies to combat the rising global burden of metabolic diseases linked to high sugar intake.
Potential Therapeutic Targets
By identifying these tissue-specific mechanisms, researchers propose targeting intestinal nutrient transport pathways and mitochondrial function across tissues as potential strategies to mitigate the metabolic effects of SSB consumption.
Publication: Ganguly, Saptarnab, et al. "Consumption of sucrose-water rewires macronutrient uptake and utilization mechanisms in a tissue specific manner." The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry (2025): 109850.
END
Recent study in mice provides key insights on the impact of excessive sucrose consumption in specific organs
2025-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A less toxic way to manufacture daily goods
2025-03-21
Diisocyanates are used in the preparation of all polyurethanes, ranging from the foams used in shoe soles to the thermoplastics used in cell phone cases. Aromatic diisocyanates, which give polyurethane foams their structure, are commonly prepared on the megaton scale in highly secure facilities due to the use of phosgene, a highly reactive and toxic chemical reagent. Michael Burkart’s lab at UC San Diego recently reported the preparation of fully bio-based aromatic diisocyanates from a simple monosaccharide, D-galactose. This new route avoids the use of transition metals, gaseous reagents or any high-pressure/temperature reactions. As an application, the team demonstrates ...
Nearly half of depression diagnoses could be considered treatment-resistant
2025-03-21
Almost half of patients diagnosed with depression classify as being ‘treatment-resistant’ as new research suggests that many don’t respond to multiple antidepressant options.
The new study, published in the British Journal of Psychiatry was led by academics from the University of Birmingham and Birmingham and Solihull Mental Health NHS Foundation Trust. The study found that 48% of patients whose electronic healthcare records reported a diagnosis of depression had tried at least two antidepressants, and 37% had tried four or more different options.
Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is ...
Deadly bacteria developed the ability to produce antimicrobials and wiped-out competitors
2025-03-21
A drug-resistant type of bacteria that has adapted to health care settings evolved in the past several years to weaponize an antimicrobial genetic tool, eliminating its cousins and replacing them as the dominate strain. University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine scientists made the discovery when combing through local hospital data – and then confirmed that it was a global phenomenon.
The finding, published today in Nature Microbiology, may be the impetus for new approaches in developing therapeutics against some of the world’s deadliest bacteria. It also validates a new use for a system developed at Pitt and UPMC that couples genomic sequencing ...
Device enables direct communication among multiple quantum processors
2025-03-21
Quantum computers have the potential to solve complex problems that would be impossible for the most powerful classical supercomputer to crack.
Just like a classical computer has separate, yet interconnected, components that must work together, such as a memory chip and a CPU on a motherboard, a quantum computer will need to communicate quantum information between multiple processors.
Current architectures used to interconnect superconducting quantum processors are “point-to-point” in connectivity, meaning they require a series of transfers between network nodes, with compounding error rates.
On the way ...
Nanotech-induced cooling improves crop yields in arid climates
2025-03-21
Scientists at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) have developed and combined a new nanoplastic and biodegradable mulch to passively cool greenhouses in hot, arid climates like those in the Middle East. Applying their technology, they lowered temperatures of miniature greenhouses by 25 degrees Celsius and increased crop yields of Chinese cabbage by nearly 200%. The study can be read in Nexus.
The nanoplastic consists of polyethylene, the most widely produced plastic in the world, infused with nanoparticles consisting of the molecule cesium tungsten oxide. These nanoparticles absorb ...
Home sweet home: some great hammerhead sharks stick to the perfect neighborhood in the Bahamas instead of migrating
2025-03-21
New research shows that some great hammerhead sharks are homebodies. Scientists studying great hammerheads around Andros in the Bahamas shark sanctuary have found that while some individuals migrate, others prefer to stay at home — potentially because their environment provides them with everything they need. This information could help protect the critically endangered species.
“The global population of great hammerheads is thought to have reduced by more than 80% over the last three generations, and genomic ...
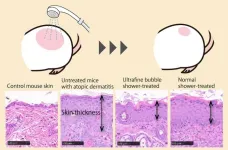
Bubbly idea: Ultrafine bubble showers suppress atopic dermatitis
2025-03-21
Bubble baths might be soothing soaks, but bubble showers could be the next thing in keeping the skin clean.
An Osaka Metropolitan University-led medical research team found that ultrafine bubble showers might help prevent atopic dermatitis.
Graduate School of Medicine student Ayaki Matsumoto and Associate Professor Hisayoshi Imanishi led the study into using ultrafine bubbles, often used to clean medical equipment, on mice with atopic dermatitis.
The scientists found that in mice with atopic dermatitis due to external factors, inflammation was markedly suppressed when the affected skin ...
Aotearoa once home to elephant seals
2025-03-21
Southern elephant seals are the “canary in the coal mine” for the Southern Ocean, offering insight into how the ecosystem may react to future climate change and human impact, new research shows.
Joint senior author Associate Professor Nic Rawlence, Director of the Otago Palaeogenetics Laboratory, says while elephant seals now only inhabit the subantarctic islands and South America, Aotearoa beaches used to be “heaving” with the colossal animals.
“At the time of human arrival in New Zealand, you would be hard pressed to find room on the beaches, with fur seals on the rocky headlands, prehistoric sealions and elephant seals ...
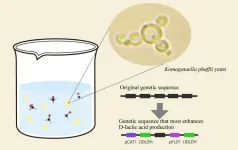
Green recipe: Engineered yeast boosts D-lactic acid production
2025-03-21
Great recipes require the perfect combination of ingredients — biotechnology recipes are no exception.
Researchers from Osaka Metropolitan University have discovered the ideal genetic “recipe” to turn yeast into a tiny yet powerful eco-friendly factory that converts methanol into D-lactic acid, a key compound used in biodegradable plastics and pharmaceuticals. This approach could help reduce reliance on petroleum-based processes and contribute to more sustainable chemical production.
Lactic acid is widely used in food, cosmetics, pharmaceuticals and bioplastics. It exists in two forms: L-lactic acid ...
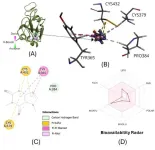
Computational drug discovery: Exploring natural products targeting SARS-CoV-2
2025-03-21
Ikoma, Japan—The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the urgent need for effective therapeutic agents against SARS-CoV-2. Although vaccines helped control the spread of the virus, the emergence of new variants continues to challenge global health efforts. Small-molecule inhibitors targeting viral proteins could serve as an effective alternative for controlling the spread of COVID-19 at both individual and community levels.
In this vein, a recent study led by Associate Professor Md. Altaf-Ul-Amin, along with Muhammad Alqaaf, Ahmad Kamal Nasution, Mohammad Bozlul Karim, Mahfujul Islam ...