(Press-News.org) Peking University, March 19, 2025: A research team led by Professor Sun Qing-Feng in colloboration with Professor He Lin’s research group from Beijing Normal University has achieved orbital hybridization in graphene-based artificial atoms for the first time. Their findings, entitled “Orbital hybridization in graphene-based artificial atoms” was published in Nature (DOI: 10.1038/s41586-025-08620-z). This work marks a significant milestone in the field of quantum physics and materials science, bridging the gap between artificial and real atomic behaviors.
Why it matters:
1. Quantum dots, often called artificial atoms, can mimic atomic orbitals but have not yet been used to simulate orbital hybridization, a crucial process in real atoms.
2. While quantum dots have successfully demonstrated artificial bonding and antibonding states, their ability to replicate orbital hybridization remained unexplored.
3. A fundamental understanding of how anisotropic confinement affects hybridization in quantum dots was lacking.
The Research:
The authors developed a theoretical framework and experimental approach to achieve orbital hybridization in graphene-based quantum dots.
1. They proposed that anisotropic potentials in artificial atoms could induce hybridization between confined states of different orbitals, such as the s orbital (orbital quantum number 0) and the d orbital (orbital quantum number 2).
2. By deforming the circular potential of graphene quantum dots into an elliptical potential, the team successfully induced orbital hybridization, resulting in two hybridized states with distinct shapes (θ shape and rotated θ shape).
3. The experimental results, obtained by probing confined states in various quantum dots, confirmed the theoretical predictions, demonstrating the recombination of atomic collapse states (a quantum electrodynamics phenomenon) and whispering gallery modes (an acoustic phenomenon).
Key Findings:
1. Orbital hybridization in artificial atoms was achieved for the first time, with hybridized states showing energy splitting as anisotropy increased.
2. This breakthrough provides a new platform for simulating real atomic processes, with potential applications in quantum computing and nanoelectronic
*This article is featured in PKU News' "Why It Matters" series. More from this series.
Click "here” to read the paper
Written by: Akaash Babar
Edited by: Zhang Jiang
Source: School of Physics, Peking University
END
Quantum leap: Graphene unlocks orbital hybridization
2025-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How black holes could nurture life
2025-03-21
At the center of most large galaxies, including our own Milky Way, sits a supermassive black hole. Interstellar gas periodically falls into the orbit of these bottomless pits, switching the black hole into active galactic nucleus (AGN)-mode, blasting high-energy radiation across the galaxy.
It's not an environment you'd expect a plant or animal to thrive in. But in a surprising new study in the Astrophysical Journal, researchers at Dartmouth and the University of Exeter show that AGN radiation can have a paradoxically nurturing effect on life. Rather ...
Dr. Amit Bar-Or, penn medicine neuroimmunologist, awarded the 2025 John Dystel prize for multiple sclerosis research
2025-03-21
Amit Bar-Or, MD, a distinguished researcher and neurologist at Penn Medicine, is the winner of the 2025 John Dystel Prize for Multiple Sclerosis Research, awarded jointly by the National Multiple Sclerosis Society and the American Academy of Neurology. He is being honored for advancing our knowledge of neuroimmunology, precision medicine, and biomarkers in MS. Dr. Bar-Or will deliver the Dystel Prize lecture and receive his award at the American Academy of Neurology 2025 Annual Meeting in San Diego, California on April 8, 2025.
“Dr. Bar-Or has been a key player in shaping the evolving conceptual framework of MS, including how the ...
Recent study in mice provides key insights on the impact of excessive sucrose consumption in specific organs
2025-03-21
Researchers at the Advanced Research Unit on Metabolism, Development & Aging (ARUMDA), in the Tata Institute of Fundamental Research (TIFR, Mumbai and TIFR Hyderabad), have unveiled a comprehensive understanding of the harmful effects of sugar-sweetened beverages (SSBs) on human health, using a preclinical mouse model that closely mimics human consumption patterns. The study, published in the Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry, sheds light on how chronic sucrose-water intake (10%) alters key physiological, molecular, and metabolic processes across various organs, driving ...
A less toxic way to manufacture daily goods
2025-03-21
Diisocyanates are used in the preparation of all polyurethanes, ranging from the foams used in shoe soles to the thermoplastics used in cell phone cases. Aromatic diisocyanates, which give polyurethane foams their structure, are commonly prepared on the megaton scale in highly secure facilities due to the use of phosgene, a highly reactive and toxic chemical reagent. Michael Burkart’s lab at UC San Diego recently reported the preparation of fully bio-based aromatic diisocyanates from a simple monosaccharide, D-galactose. This new route avoids the use of transition metals, gaseous reagents or any high-pressure/temperature reactions. As an application, the team demonstrates ...
Nearly half of depression diagnoses could be considered treatment-resistant
2025-03-21
Almost half of patients diagnosed with depression classify as being ‘treatment-resistant’ as new research suggests that many don’t respond to multiple antidepressant options.
The new study, published in the British Journal of Psychiatry was led by academics from the University of Birmingham and Birmingham and Solihull Mental Health NHS Foundation Trust. The study found that 48% of patients whose electronic healthcare records reported a diagnosis of depression had tried at least two antidepressants, and 37% had tried four or more different options.
Treatment-resistant depression (TRD) is ...
Deadly bacteria developed the ability to produce antimicrobials and wiped-out competitors
2025-03-21
A drug-resistant type of bacteria that has adapted to health care settings evolved in the past several years to weaponize an antimicrobial genetic tool, eliminating its cousins and replacing them as the dominate strain. University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine scientists made the discovery when combing through local hospital data – and then confirmed that it was a global phenomenon.
The finding, published today in Nature Microbiology, may be the impetus for new approaches in developing therapeutics against some of the world’s deadliest bacteria. It also validates a new use for a system developed at Pitt and UPMC that couples genomic sequencing ...
Device enables direct communication among multiple quantum processors
2025-03-21
Quantum computers have the potential to solve complex problems that would be impossible for the most powerful classical supercomputer to crack.
Just like a classical computer has separate, yet interconnected, components that must work together, such as a memory chip and a CPU on a motherboard, a quantum computer will need to communicate quantum information between multiple processors.
Current architectures used to interconnect superconducting quantum processors are “point-to-point” in connectivity, meaning they require a series of transfers between network nodes, with compounding error rates.
On the way ...
Nanotech-induced cooling improves crop yields in arid climates
2025-03-21
Scientists at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) have developed and combined a new nanoplastic and biodegradable mulch to passively cool greenhouses in hot, arid climates like those in the Middle East. Applying their technology, they lowered temperatures of miniature greenhouses by 25 degrees Celsius and increased crop yields of Chinese cabbage by nearly 200%. The study can be read in Nexus.
The nanoplastic consists of polyethylene, the most widely produced plastic in the world, infused with nanoparticles consisting of the molecule cesium tungsten oxide. These nanoparticles absorb ...
Home sweet home: some great hammerhead sharks stick to the perfect neighborhood in the Bahamas instead of migrating
2025-03-21
New research shows that some great hammerhead sharks are homebodies. Scientists studying great hammerheads around Andros in the Bahamas shark sanctuary have found that while some individuals migrate, others prefer to stay at home — potentially because their environment provides them with everything they need. This information could help protect the critically endangered species.
“The global population of great hammerheads is thought to have reduced by more than 80% over the last three generations, and genomic ...
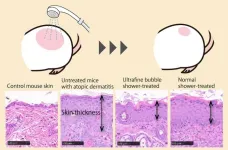
Bubbly idea: Ultrafine bubble showers suppress atopic dermatitis
2025-03-21
Bubble baths might be soothing soaks, but bubble showers could be the next thing in keeping the skin clean.
An Osaka Metropolitan University-led medical research team found that ultrafine bubble showers might help prevent atopic dermatitis.
Graduate School of Medicine student Ayaki Matsumoto and Associate Professor Hisayoshi Imanishi led the study into using ultrafine bubbles, often used to clean medical equipment, on mice with atopic dermatitis.
The scientists found that in mice with atopic dermatitis due to external factors, inflammation was markedly suppressed when the affected skin ...