New research reveals secrets about locust swarm movement
Study introduces a new theory that could improve locust control strategies
2025-03-24
(Press-News.org)
MEDIA INQUIRES
WRITTEN BY
Laura Muntean
Adam Russell
laura.muntean@ag.tamu.edu
601-248-1891
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
New research reveals secrets about locust swarm movement
Study introduces a new theory that could improve locust control strategies
- by Adam Russell
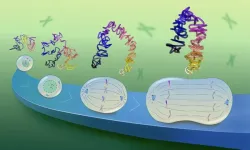
New research published in Science is reshaping our understanding of one of nature’s most stunning yet destructive phenomena — massive locust swarms moving together.
A team of researchers, including Greg Sword, Ph.D., Regents Professor and Charles R. Parencia Chair in Cotton Entomology in the Texas A&M College of Agriculture and Life Sciences Department of Entomology, is challenging the long-standing theories about how order emerges from disorder in animal collectives.
Sword, along with a team of researchers from the Max Planck Institute of Animal Behavior and Centre for the Advanced Study of Collective Behavior at the University of Konstanz, Germany, recently published “The behavioral mechanisms governing collective motion in swarming locusts.” This study proposes that locusts move in an uncoordinated version of follow-the-leader behavior rather than a synchronized collective motion, as previously believed.
Greg Sword, Ph.D., studies desert locusts and other swarming insects like crickets and is a researcher in the Behavioral Plasticity Research Institute at Texas A&M University. New research provides a new, science-based theory about how these pests move as a collective. (Sam Craft/Texas A&M AgriLife)
Finding patterns in locust swarm behavior
Environmental factors like topography or food availability may influence the direction of travel for locusts at the head of the swarm, Sword said. But the swarm movement is ultimately dictated by individual locusts reacting to their nearest neighbors.
Desert locusts, one of 20 locust species, undergo a dramatic transformation called locust phase polyphenism — a density dependent shift that alters their biology, morphology, color and behavior.
When populations are low, they remain solitary and avoid each other. But when densities increase, they become highly social, forming massive swarms that migrate. These swarms can cause billions of dollars in agricultural damage and lead to food insecurity that spans multiple continents.
“Patterns emerge at the group level as they interact with their neighbors,” Sword said. “They’re all acting in their own interest but are all following the same rules that create the pattern of movement. Knowing how these swarms move can help us predict where they are going, which could revolutionize the way we try to stop their devastating march.”
New theory could help mitigate locust damage
This study’s insights could improve locust monitoring and intervention strategies, helping minimize their agricultural production and habitat.
Sword, who is also a member of the Behavioral Plasticity Research Institute at Texas A&M, said the findings could help researchers in North America better understand Central American and South American locust species and other swarming insects like Mormon crickets.
“Do those species have the same behavioral mechanism?” he asked. “We’re uniquely positioned here at Texas A&M to start asking those questions. It’s crucial to find answers because, while the U.S. doesn’t currently face locust swarms, the Central American locust has swarmed within 150 miles of the Texas-Mexico border.”
-30-
Would you like more information from Texas A&M AgriLife?
Visit AgriLife Today, the news hub for Texas A&M AgriLife, which brings together a college and four state agencies focused on agriculture and life sciences within The Texas A&M University System, or sign up for our Texas A&M AgriLife E-Newsletter.
For more resources including photo repository, logo downloads and style guidelines, please visit the Resources for Press and Media.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-24
About The Study: This study found a disproportionate spike in firearm homicide among children and adults older than age 30 after the onset of the COVID-19 pandemic, indicating a change in the association between age and firearm victimization risk. This trend moved the peak victimization risk from age 21 to 19, and rates for children up to age 16 were markedly elevated. These age-specific patterns were most pronounced in later post-onset years.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jonathan ...
2025-03-24
About The Study: This study found that avoidable mortality (comprising both preventable deaths related to prevention and public health and treatable deaths related to timely and effective health care treatment) has worsened across all U.S. states, while other high-income countries show improvement. The results suggest poorer mortality is driven by broad factors across the entirety of the U.S. While other countries appear to make gains in health with increases in health care spending, such an association does not exist across U.S. states, raising questions regarding U.S. health spending efficiency.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Irene ...
2025-03-24
About The Study: Exclusive or longer duration of breastfeeding was associated with reduced odds of developmental delays and language or social neurodevelopmental conditions in this cohort study. These findings may guide parents, caregivers, and public health initiatives in promoting early child development.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Inbal Goldshtein, PhD, email inbal@kinstitute.org.il.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.1540)
Editor’s Note: Please see the ...
2025-03-24
Among the many marvels of life is the cell’s ability to divide and thus enable organisms to grow and renew themselves. For this, the cell must duplicate its DNA – its genome – and segregate it equally into two new daughter cells. To prepare the 46 chromosomes of a human cell for transport to the daughter cells during cell division, each chromosome forms a compact X-shaped structure with two rod-like copies. How the cell achieves this feat remains largely unknown.
Now, for the first time, EMBL scientists have directly observed this process in high resolution under the microscope ...
2025-03-24
After every meal, the intestines perform an action called peristalsis — moving food through their hollow interiors with coordinated contractions and relaxations of the smooth muscle.
For more than a century, scientists have known that nerve cells in the gut propel the colon to move, allowing the organ to perform its life-sustaining function. But exactly how these intestinal nerve cells do their job has remained elusive.
Now a new NIH-funded study led by researchers at Harvard Medical School and the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai has identified ...
2025-03-24
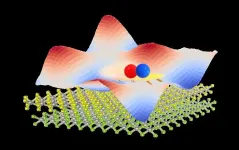
A moiré pattern appears when you stack and rotate two copies of an image with regularly repeating shapes, turning simple patterns of squares or triangles into a groovy wave pattern that moves across the combined image in an optical delight.
Similarly, stacking single layers of sub-nanometer-thick semiconductor materials known as transition metal dichalcogenides (TMDs) can generate a moiré potential, and novel electronic and optoelectronic properties may emerge between the layers.
A moiré potential is a “seascape” of potential energy with regularly repeating peaks and valleys. They were previously thought to be stationary. But a team of ...
2025-03-24
AI tools are transforming how we observe the world around us — and even the stars beyond. Recently, an international team proved that deep learning techniques and large language models can help astronomers classify stars with high accuracy and efficiency. Their study, “Deep Learning and Methods Based on Large Language Models Applied to Stellar Light Curve Classification,” was published Feb. 26 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal.
The team introduced the StarWhisper LightCurve series, a trio of AI models, and evaluated their performance ...
2025-03-24
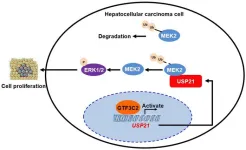
Background and Aims
General transcription factor IIIC subunit 2 (GTF3C2) is one of the polymerase III transcription-related factors. Previous studies have revealed that GTF3C2 is involved in regulating cell proliferation. However, the role of GTF3C2 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear. This study aimed to determine its expression, biological function, and mechanism in HCC.
Methods
The expression of GTF3C2 in HCC and non-tumor tissues, along with its clinical significance, was investigated using public databases and clinical samples. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase ...
2025-03-24
A recent article in BioScience, the journal of the American Institute of Biological Sciences, challenges conventional conservation wisdom, suggesting that protected areas such national parks and designated wilderness areas must embrace natural landscape dynamics rather than trying to preserve static conditions and landscape features.
Dr. Gavin M. Jones (USDA Forest Service) and colleagues contend that current conservation models often resist natural ecosystem processes such as wildfire, leading to a "backfire effect" that makes ecosystems more vulnerable ...
2025-03-24
WASHINGTON – A depression prevention program that has helped white youth wasn’t effective for Black youth, raising concerns about the need for more research to help racially diverse groups, according to new research published by the American Psychological Association.
“I was very surprised that we couldn’t help Black youth as much as white youth, and we don’t know why there was such a profound difference in the outcomes.” said lead researcher Patrick Pössel, Dr. rer. soc., a professor of counseling psychology ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] New research reveals secrets about locust swarm movement
Study introduces a new theory that could improve locust control strategies