(Press-News.org) ● Records of more than 170,000 lung cancer patients combined with chest x-ray rates from 7,400 GP practices were analysed in the new research led by the University of Sheffield
● The study, published in the British Journal of General Practice, shows link between the frequency of chest x-rays and earlier diagnosis and improved survival
● Lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer deaths globally
A groundbreaking study has revealed a significant link between the frequency of chest x-ray referrals from GPs and earlier diagnosis and improved survival rates for lung cancer patients.
Research from the University of Sheffield analysed records from more than 170,000 lung cancer patients in England between 2014 and 2018, combined with chest x-ray rates from 7,400 GP practices.
The study, published in the British Journal of General Practice, found that patients attending practices with the highest chest x-ray usage were more likely to be diagnosed with lung cancer at an earlier, more treatable stage. The practices with the highest chest x-ray usage also saw patients less likely to be diagnosed at the later stages of cancer - stage three and four.
These patients were also shown to have better survival at both one and five years after diagnosis, compared with those with the lowest chest x-ray usage.
Lead author of the study, Dr Stephen Bradley from the University of Sheffield’s School of Medicine and Population Health, said: “Lung cancer remains the leading cause of cancer deaths both in the UK and globally. This is an important step forward in our understanding of how to improve lung cancer detection.
“Our research strongly suggests that increasing the use of chest x-rays for patients with relevant symptoms can lead to earlier diagnosis and, crucially, better chances of survival.”
Dr Bradley, who conducted the study whilst at the University of Leeds, added: “While advanced technologies like CT scanners play a vital role, this study highlights the potential for optimising the use of a simpler, cheaper tool like x-rays which are more easier for patients to access.
"By encouraging greater use of chest x-rays, we can potentially diagnose lung cancer earlier, when treatment is more likely to be successful."
Until now, it was not widely understood if GPs arranging more chest x-rays was beneficial. The uptake of chest x-rays varies a great deal between different GP practices - possibly in part because GPs may not have been convinced that there could be a benefit for patients with very common symptoms.
Co-author of the study, Willie Hamilton CBE, Professor of Primary Care Diagnostics at the University of Exeter, said: “This study matters. There’s few cancer tests available in general practice which are fairly accurate, fairly cheap and very acceptable to patients. Now we know that doing more chest X-rays finds more cancers, and identifies them earlier in their growth, which is crucial to the best outcomes for patients.”
This is the first study of its kind which links chest x-ray rates and the national cancer registry. The study was funded by Cancer Research UK.
Lyndsy Ambler, Senior Strategic Evidence Manager at Cancer Research UK, said: “This study highlights how the use of investigations in primary care can help diagnose cancer at an earlier stage to give people affected by cancer the best chance of a good outcome.
“Encouraging the use of chest x-ray for people with potential signs and symptoms of lung cancer by GPs and improving GP access to investigations is key.
“More research to understand the impact of other investigations used in primary care on patient outcomes is also needed to support efforts to diagnose cancer earlier.”
To view the full study after the embargo lifts, please visit:
https://doi.org/10.3399/BJGP.2024.0466
For more information please contact: Amy Huxtable, Senior Media Relations Officer, University of Sheffield, 07568116781, a.l.huxtable@sheffield.ac.uk
END
Increased use of chest x-rays linked to earlier lung cancer diagnosis and improved survival
2025-03-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
From economic struggles to culture wars: New study reveals how GDP influences polarization around the globe
2025-03-25
Polarisation in lower-income countries largely flows from economic and material issues, while social topics and identity-related debates are the most polarising subjects in richer nations, new research reveals.
The study from City St George’s, University of London analysed 40 years of global data to explore how modernisation influences ideological divides, shedding light on the factors driving ideological polarisation across different nations around the world.
As political divisions deepen in many countries, the study clarifies the complex, multifaceted implications ...
NYU Abu Dhabi researchers develop affordable sensing system to restore sense of touch in minimally invasive surgery
2025-03-24
Abu Dhabi, UAE, March 24, 2025: Researchers from NYU Abu Dhabi’s Advanced Microfluidics and Microdevices Laboratory (AMMLab) have developed an innovative sensing system that restores the missing tactile feedback in minimally invasive surgery (MIS), enhancing precision, ease of use, and safety. The new "off-the-jaw" system integrates force and angle sensors into the handle of laparoscopic tools, providing surgeons with real-time measurements of grasping forces and insights into tissue stiffness and thickness.
Minimally invasive surgery (MIS) involves small incisions, reducing ...
Rapid and accurate diagnosis of urinary tract infections using targeted next-generation sequencing: A multicenter comparative study with metagenomic sequencing and traditional culture methods
2025-03-24
BACKGROUND
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) rank among the most prevalent bacterial infections globally. Traditional urine culture methods have significant limitations in detection time and sensitivity, prompting the need to evaluate targeted next-generation sequencing (tNGS) as a potential diagnostic tool.
METHODS
The study included a discovery cohort of 400 suspected UTI patients (202 analyzed) and a validation cohort of 200 patients (110 analyzed). The study assessed detection time, concordance rates, ability to identify polymicrobial infections, and antibiotic resistance genes (ARGs). Both clear and turbid ...
Black infants and children consistently have double the risk for death compared to Whites
2025-03-24
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 24 March 2025
Follow @Annalsofim on X, Facebook, Instagram, threads, and Linkedin
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the ...
March/April Annals of Family Medicine Tip Sheet
2025-03-24
Original Research
Family-Based Lifestyle Intervention Improves Weight Management and Cardiovascular Health Among High-Risk Patients
Background and Goal: The PROgramme of Lifestyle Intervention in Families for Cardiovascular risk reduction (PROLIFIC) Study, conducted in India, aimed to assess whether a family-based approach to lifestyle interventions could improve weight management and obesity-related health outcomes among individuals with a family history of premature coronary heart disease.
Study Approach: In this cluster ...
Shared decision making among primary care clinic staff and family involvement improves follow-up for chronic patients
2025-03-24
Original Research
Background and Goal: Regular follow-up visits are critical for managing chronic conditions, yet some primary care clinics achieve higher visit regularity than others. This study aimed to identify specific strategies used by high-performing clinics to promote consistent follow-up visits for adults with chronic conditions.
Study Approach: This qualitative study used semi-structured interviews with 15 primary care physicians, 12 nurses, 15 administrative staff, and 4 pharmacists from 12 clinics—half with high temporal regularity (patients attending follow-ups consistently) and half with low temporal regularity, identifying strategies that helped high–temporal ...
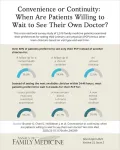
Over half of patients prefer their own doctor and will wait longer for an appointment
2025-03-24
Original Research
Background and Goal: This study focuses on how primary care patients balance the trade-off between continuity of care and access to timely appointments. It examines whether patients prefer to wait longer to see their own primary care physician (PCP) or prefer to see another clinician for faster care.
Study Approach: Researchers analyzed data from a cross-sectional online survey of adult primary care patients in Michigan. Patients were presented with scenarios in the survey for different visit types—annual checkups, chronic and mental health follow-ups, ...
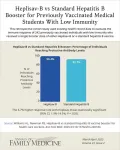
Newer hepatitis B vaccine shows promise as booster for health care workers
2025-03-24
Research Brief
Background and Goal: Health care workers are at higher risk of hepatitis B infection due to occupational exposure to blood and body fluids. They are considered protected if they have a hepatitis B surface antigen antibody (anti-HBs) titer of ≥10 mIU/mL after completing a full vaccination series. This study compared the effectiveness of Heplisav-B, a new hepatitis vaccine, vs. standard hepatitis B vaccines as a booster in previously vaccinated individuals.
Study Approach: Researchers ...
Family-based lifestyle intervention improves weight management and cardiovascular health among high-risk patients
2025-03-24
Original Research
Family-Based Lifestyle Intervention Improves Weight Management and Cardiovascular Health Among High-Risk Patients
Background and Goal: The PROgramme of Lifestyle Intervention in Families for Cardiovascular risk reduction (PROLIFIC) Study, conducted in India, aimed to assess whether a family-based approach to lifestyle interventions could improve weight management and obesity-related health outcomes among individuals with a family history of premature coronary heart disease.
Study ...
Long-term inhaled corticosteroid use for COPD linked to serious long-term health risks
2025-03-24
Background and Goal: Inhaled corticosteroids (ICS) are commonly prescribed for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), but not recommended as first-line treatment unless patients have asthma/COPD overlap or frequent exacerbations. This study examined whether long-term ICS use (more than two years) increases the risk of serious health conditions compared with short-term use (less than 4 months).
Study Approach: Researchers analyzed electronic health records from over 20 million patients, focusing on individuals aged 45 and ...