(Press-News.org) Prostate cancer is the second-leading cause of cancer deaths in American men. Further, non-Hispanic Blacks have a higher incidence of prostate cancer and are more likely to die from it than are non-Hispanic whites. A biopsy is recommended if a patient has certain risk factors like age, family history, symptoms and screening test results. When the biopsy sample is taken, physicians use either ultrasound or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to guide the procedure.
In a new study, researchers at Thomas Jefferson University combed through one of the largest cancer databases to assess the use of MRI in diagnosing prostate cancer from 2012 - 2019 and whether this choice contributes to disparities in cancer care.
“According to clinical guidelines, MRI is better at identifying cancers and has been increasingly used over the past decade,” says Christiane El Khoury, PharmD, assistant director of cancer research administration at Jefferson and first author of the study. Studies have found that MRI-guided biopsies reduce the number of future biopsies a patient may undergo. However, the technology is more costly and may incur more out-of-pocket expenses.
Dr. El Khoury and her colleagues at the Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center - Jefferson Health found that there continues to be a gap in MRI use between Black and white patients. The good news is that the gap was halved in 2019 when it was about 20% compared to 2012, when it was 43%.
However, other disparities persist. Rural patients are 35% less likely than urban patients to have used MRI diagnostics, and that gap was relatively stable over the study period. In addition, the study identified regional differences, with far less MRI use in South and Central U.S. compared to the West. The research team, led by Grace Lu-Yao, PhD, population science researcher and professor at Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center - Jefferson Health – Jefferson Health, plans to dig more deeply into geographic disparities to look for clusters of high or low utilization.
“We’re passionate about this research: finding drivers of disparities,” Dr. El Khoury says, adding that the hope is to enhance access to MRI and potentially improve prostate cancer outcomes.
By Jill Adams
END
Disparities in use of MRI to detect prostate cancer
A patient’s race and location may influence diagnostic testing for prostate tumors
2025-03-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Biology Open smashes the peer review mold
2025-03-25
Academic peer review is notoriously cumbersome. The process assesses the quality of scientific research prior to publication in an academic journal, sometimes delaying publication by many months. The system depends on members of the academic community providing their time and expertise for free. However, finding reviewers can be lengthy and there are no consequences when reviewers produce poor-quality reports lacking constructive feedback. Daniel Gorelick, Editor-in-Chief of the journal Biology Open believed that there could an alternative. ‘My vision is a ...
Scientists unlock frogs’ antibacterial secrets to combat superbugs
2025-03-25
Frogs have thrived for hundreds of millions of years, spreading across virtually every corner of the earth, from tropical jungles to subarctic forests. Throughout their evolution, they have developed remarkable defenses — including previously unreported antibiotics — against the hordes of bacteria that thrive in their moist environments. Variants of these compounds may one day protect humans from drug-resistant pathogens.
In a new paper in Trends in Biotechnology (Cell Press), Cesar de la Fuente, Presidential Associate Professor in Bioengineering and in Chemical and Biomolecular ...
Making foie gras without force-feeding
2025-03-25
WASHINGTON, March 25, 2025 — Foie gras is a unique delicacy made from the liver of a duck or goose. While it can be an acquired taste, the buttery, fatty dish is an indulgent cuisine prized in many parts of the world.
Foie gras is distinct from regular fowl liver thanks to its high fat content, which is traditionally achieved by force-feeding the ducks and geese beyond their normal diets. Researcher Thomas Vilgis is a lover of foie gras, but he wondered if there was a more ethical way to enjoy the dish.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, Vilgis, as well as researchers from Max Planck Institute for Polymer Research and the University of Southern Denmark, created a process to ...
The best butter for a vegan shortbread
2025-03-25
WASHINGTON, March 25, 2025 – Butter is a key ingredient in many baked goods, but for those who are lactose intolerant, finding a good alternative can be a challenge. Vegan butters can sometimes have the wrong consistency, or produce bakes that are not quite right, leaving bakers frustrated or unwilling to try dairy-free alternatives.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Strathclyde examined the properties of several vegan or dairy-free butter alternatives inside one of the region’s most well-known snacks: Scottish shortbread.
“We have a Ph.D. student in the group who is a vegan, and he turns all of our baking habits upside down,” ...
Recovery potential in patients after cardiac arrest who die after limitations or withdrawal of life support.
2025-03-25
About The Study: In this cohort study of comatose patients resuscitated from cardiac arrest, most who died after withdrawal of life-sustaining therapy were considered by experts to have had recovery potential. These findings suggest that novel solutions to avoiding deaths based on biased prognostication or incomplete information are needed.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jonathan Elmer, MD, MS, email elmerjp@upmc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.1714)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
LGBTQ+ inclusive policies, nurse job outcomes, and quality of care in hospitals.
2025-03-25
About The Study: Nurses in hospitals with high lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, queer or questioning, and other sexual and gender minority (LGBTQ+) inclusion reported more favorable job outcomes and care quality in this cross-sectional study. Hospitals should understand that implementing LGBTQ+ inclusive policies goes beyond compliance or diversity; it is essential for improving the work climate, enhancing staff well-being, and optimizing care delivery.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hyunmin Yu, PhD, email hyuy@nursing.upenn.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media ...
C. diff uses toxic compound to fuel growth advantage
2025-03-25
The pathogen C. diff — the most common cause of health care-associated infectious diarrhea — can use a compound that kills the human gut’s resident microbes to survive and grow, giving it a competitive advantage in the infected gut.
A team led by investigators at Vanderbilt University Medical Center has discovered how C. diff (Clostridioides difficile) converts the poisonous compound 4-thiouracil, which could come from foods like broccoli, into a usable nutrient. Their findings, published March 25 in the journal Cell Host & Microbe, increase ...
Nation of Lifesavers™ takes CPR education to Japan
2025-03-25
DALLAS, March 25, 2025 — Understanding how to properly respond in a cardiac emergency when seconds matter is critical to everyone, everywhere. That is why the American Heart Association, devoted to changing the future to a world of healthier lives for all, and its Nation of Lifesavers™ national ambassador and Buffalo Bills safety, Damar Hamlin, are expanding the Chasing M’s Foundation cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) tour to Tokyo during March 27-30. This work is supporting the American Heart Association’s impact goal to improve survival rates of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest[1].
“Our national Nation ...
ACS study finds nearly four million pre-mature lung cancer deaths in U.S. averted and 76 million years of lives gained due to tobacco control
2025-03-25
New research led by American Cancer Society (ACS) researchers estimates more than 3.8 million lung cancer deaths were averted and a little over 76 million years of life gained in the United States during 1970-2022 due to substantial reductions in smoking prevalence driven by tobacco control. The study is published today in CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians.
“The substantial estimated numbers of averted lung cancer deaths and person-years of life gained highlight the remarkable effect of progress ...
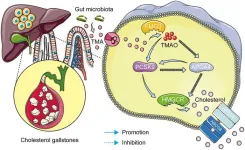
PCSK9 and APOA4: the dynamic duo in TMAO-induced cholesterol metabolism and cholelithiasis
2025-03-25
Background and Aims
Cholesterol synthesis and gallstone formation are promoted by trimethylamine-N-oxide (TMAO), a derivative of trimethylamine, which is a metabolite of gut microbiota. However, the underlying mechanisms of TMAO-induced lithogenesis remain incompletely understood. This study aimed to explore the specific molecular mechanisms through which TMAO promotes gallstone formation.
Methods
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays were used to compare serum concentrations of TMAO, apolipoprotein A4 (APOA4), and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tundra tongue: The science behind a very cold mistake
Targeting a dangerous gut infection
Scientists successfully harvest chickpeas from “moon dirt”
Teen aggression a warning sign for faster aging later in life
Study confirms food fortification is highly cost-effective in fighting hidden hunger across 63 countries
Special issue elevates disease ecology in marine management
A kaleidoscope of cosmic collisions: the new catalogue of gravitational signals from LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA
New catalog more than doubles the number of gravitational-wave detections made by LIGO, Virgo, and KAGRA observatories
Antifibrotic drug shows promise for premature ovarian insufficiency
Altered copper metabolism is a crucial factor in inflammatory bone diseases
Real-time imaging of microplastics in the body improves understanding of health risks
Reconstructing the world’s ant diversity in 3D
UMD entomologist helps bring the world’s ant diversity to life in 3D imagery
ESA’s Mars orbiters watch solar superstorm hit the Red Planet
The secret lives of catalysts: How microscopic networks power reactions
Molecular ‘catapult’ fires electrons at the limits of physics
Researcher finds evidence supporting sucrose can help manage painful procedures in infants
New study identifies key factors supporting indigenous well-being
Bureaucracy Index 2026: Business sector hit hardest
ECMWF’s portable global forecasting model OpenIFS now available for all
Yale study challenges notion that aging means decline, finds many older adults improve over time
Korean researchers enable early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva!
Swipe right, but safer
Duke-NUS scientists identify more effective way to detect poultry viruses in live markets
Low-intensity treadmill exercise preconditioning mitigates post-stroke injury in mouse models
How moss helped solve a grave-robbing mystery
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
[Press-News.org] Disparities in use of MRI to detect prostate cancerA patient’s race and location may influence diagnostic testing for prostate tumors