(Press-News.org) Interferometers, devices that can modulate aspects of light, play the important role of modulating and switching light signals in fiber-optic communications networks and are frequently used for gas sensing and optical computing.
Now, applied physicists at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have invented a new type of interferometer that allows precise control of light’s frequency, intensity and mode in one compact package.
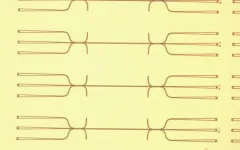
Called a cascaded-mode interferometer, it is a single waveguide on a silicon-on-insulator platform that can create multiple signal paths to control the amplitude and phase of light simultaneously, a process known as optical spectral shaping. By combining mechanisms to manipulate different aspects of light into a single waveguide, the device could be used in advanced nanophotonic sensors or on-chip quantum computing.
Published in Science Advances, the research was led by postdoctoral fellow Jinsheng Lu, who works in the lab of Federico Capasso, the Robert L. Wallace Professor of Applied Physics and Vinton Hayes Senior Research Fellow in Electrical Engineering. Federal support for the work included award No. FA9550-23-1-0699 from the Air Force Office of Scientific Research under. Devices were made at Harvard’s Center for Nanoscale Systems, supported by the National Science Foundation under award No. ECCS-2025158.
“Conceptually, this is a very big step forward compared to the state of the art for commercial high-speed modulators that are particularly used for communications,” Capasso said.
The most widely used such devices, known as Mach-Zehnder interferometers, work by splitting a beam of light down two paths to toggle its output. Despite their widespread use, Mach-Zehnder interferometers have their limitations – they are not very good at simultaneously controlling different aspects of light. Today, multiple interferometers are needed in succession to make up for these limitations, taking up space and restricting the amount of signal that can travel through.
The new cascaded-mode interferometer is a reimagining of a Mach-Zehnder device integrated into a single-chip waveguide. Rather than the traditional split beam, the new interferometer has a unique, nanoscale pattern of gratings etched into the waveguide that control the energy exchange between different modes of light.
This makes the new interferometer able to control the spectrum of light passing through by finely adjusting the intensity and characteristics of different colors. Light can move through in different patterns, or transverse modes. And the device allows for precise, sharp lines of color, or light waves with distinct features.
In the paper, the team not only demonstrates the capabilities of their new interferometer but also lays out the theoretical framework for extending the physics of the device to many different modes of light.
END
A multimodal light manipulator
New interferometer could replace beam-splitting waveguides for fiber optics
2025-03-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
OU researcher leverages technology for alcohol disorder interventions in primary care
2025-03-25
OKLAHOMA CITY – According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 1 in 7 adults in the United States will experience a substance use disorder during their lifetime. University of Oklahoma College of Medicine faculty member Brandi Fink, Ph.D., is working with primary care clinics and health care systems to identify people with an alcohol use disorder and intervene early before the problem worsens.
Fink, an associate professor in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Sciences, created an assessment for patients to fill out on an iPad while waiting for an appointment ...
Automated lead nurturing boosts sales—but only under the right conditions
2025-03-25
Businesses invest billions in marketing automation, and many assume that Automated Lead Nurturing (ALN) is a proven driver of sales. However, a new Journal of Marketing study reveals that ALN is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The research finds that while ALN improves engagement and enhances salesperson–lead interactions, its impact on sales conversions varies significantly across industries and customer segments.
Authored by Johannes Habel (University of Houston), Nathaniel Hartmann (University of South Florida), Phillip Wiseman (Texas Tech University), Michael Ahearne (University of ...
Lessons from Venezuela’s democratic collapse: How opposition movements can defy autocratic leaders
2025-03-25
Until the 1990s, Venezuela was home to one of the most established democracies in Latin America. Today, however, it stands as one of the region’s most firmly entrenched authoritarian regimes.
How did this shift occur, and what can other countries learn from Venezuela’s transformation?
A new paper from political scientist Laura Gamboa at the University of Notre Dame chronicles the country’s 25-year evolution, during which Hugo Chávez and his successor, Nicolás Maduro, destroyed ...
USU ecologists document Utah's bee species and say beehive state is rich in bee diversity
2025-03-25
TOOELE, UTAH, USA -- Wildlife conservation is critical to sustaining the planet’s biodiversity and health. But putting together a conservation plan is a tall order. First of all, you need to determine what species you’re conserving, along with their numbers, habitat needs, threats and how they fit into a complex ecosystem.
As pollinators for native plants and food crops, bees play a pivotal role in our ecosystem, according to Utah State University ecologist Joseph Wilson. He and undergraduate researcher Anthony Hunsaker took on the herculean task of documenting Utah’s bee species using online occurrence records from the Symbiota Collection of Arthropods ...
A hit of dopamine tells baby birds when their song practice is paying off
2025-03-25
DURHAM, N.C. -- In his home office in Durham, Duke neuroscientist Richard Mooney shows a series of images of a bird’s brain on song.
In one, what looks like a pointillist painting illustrates a young zebra finch’s myriad attempts to sound more like an adult, capable of wooing a mate. In another, squiggly lines trace the ebb and flow of chemical signals in the reward circuit of the bird’s brain.
“Their songs don’t sound like much at first,” said Mooney, who has studied birdsong for four decades.
That’s because some things take considerable practice to master. Nobody walks onto a tennis court for the first time and plays ...
Basketball analytics investment is key to NBA wins and other successes
2025-03-25
If you filled out a March Madness bracket this month, you probably faced the same question with each college match-up: What gives one team an edge over another? Is it a team’s record through the regular season? Or the chemistry among its players? Maybe it’s the experience of its coaching staff or the buzz around a top scorer.
All of these factors play some role in a team’s chance to advance. But according to a new study by MIT researchers, there’s one member who consistently ...
Scientific cooperation is strategic for Brazil to strengthen relations with Europe
2025-03-25
Relations between Europe and South America – and especially with Brazil - are at a favorable moment, due to factors such as the free trade agreement between Mercosur and the European Union, signed in December 2024 and currently being approved. However, in order to take advantage of this window of opportunity and be competitive, Brazil must continue to expand scientific and technological cooperation with European partners.
This assessment was made by the Brazilian Ambassador to Germany, Roberto Jaguaribe, ...
Engineering antibodies with a novel fusion protein
2025-03-25
The Food and Drug Administration has approved more than 100 monoclonal antibodies to treat a range of diseases. Other antibodies are used by physicians to diagnose conditions or by scientists to advance research projects.
Even with significant expansion in the global market for antibodies used in clinical care and research, scientists recognize that there is still untapped potential for finding new antibodies. Many proteins group together in what are called protein complexes to carry out biological functions. The traditional method of generating antibodies by immunizing animals struggles to make antibodies related to these protein complexes.
The conventional ...
Transforming cardiovascular care through upfront combination therapy
2025-03-25
NEW ORLEANS - Ochsner Health Medical Director for Cardiac Rehabilitation and Preventive Cardiology, Carl J. “Chip” Lavie, Jr., MD, recently co-authored a groundbreaking research study featured in the prestigious Mayo Clinic Proceedings highlighting the comparative efficacy of lipid-lowering therapies for reducing cardiovascular risks and led by Maciej Banach, MD,PhD from Poland and leader of the International Lipid Expert Panel ( ILEP). Impact of Lipid-Lowering Combination Therapy With Statins ...
URI to host international XV Progress in Motor Control Conference
2025-03-25
Scientists from around the world specializing in motor control and neuroscience will travel to the University of Rhode Island this summer as the university hosts the international XV Progress in Motor Control Conference.
The university’s Department of Physical Therapy, its George & Anne Ryan Institute for Neuroscience, and the Interdisciplinary Neuroscience Program at URI, will host the biennial meeting of the International Society of Motor Control (ISMC) June 30 to July 2. This year’s conference will be held in the Center for ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
New study clarifies how temperature shapes sex development in leopard gecko
[Press-News.org] A multimodal light manipulatorNew interferometer could replace beam-splitting waveguides for fiber optics