(Press-News.org) Those who start work earlier express more discomfort with the seasonal time change. This is the main conclusion of a study that the lecturers at the University of Santiago de Compostela (USC) and the University of Seville (US), Jorge Mira Pérez and José María Martín Olalla, have just published in the journal Chronobiology International, in which they analyse in detail the results of the public consultation organised by the European Commission in 2018 in the then 28 member states, which obtained 4 million responses.
The study shows that the rate of responses against the current regulation was higher as the latitude of the country was higher. To explain this result, Martín Olalla and Mira, who have just published a review study in Royal Society Open Science, which has been referenced by Science magazine, compare the rates against the time change with the time of the start of work activity and show that earlier activity starts resulted in a higher rate of people against the current regulation. “The public consultation was treated as if it were a survey, highlighting the balance of responses for and against changing the clocks. We treated it as a natural experiment and studied how those who said ‘no’ (or ‘yes’) were distributed,” stresses Jorge Mira. “On average, 0.5% of the country’s population responded to the public consultation; it is too small a rate to predict the outcome of a hypothetical referendum on changing the clocks, but it is more than enough to carry out an observational study and analyse what stimuli influenced people to vote for or against the current mechanism,” stresses Martín Olalla.
The authors explain that the regulation covering the changing of the clocks aims to align the start of work with the sunrise. That is why in their calculations they use the distance between the start of work and the winter sunrise, which gives an idea of the light conditions at that time. “Nuance is key. When we use the time at which work begins we do not find significant correlations with the public consultation, but when we analyse the distance from the start time to the winter sunrise, then we do see that countries with earlier start times have higher rates against,” says Martín Olalla. “This result cannot be explained if, as usual, changing the clocks is related to time zone or geographical longitude; it only makes sense when changing the clocks is seen as a response that is physiologically modulated,” stresses Mira.
The study suggests that the current regulation acts as a compromise between those who start earlier, and therefore are more uncomfortable and would be more disadvantaged by a permanent summer time, and those who start later, who are more comfortable with the current situation but would be more disadvantaged by a permanent winter time.
END
Study shows link between the start of the working day and time preferences
2025-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
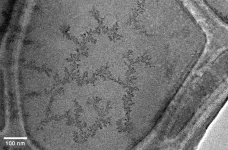
Scientists discovered chemical oscillations in palladium nanoparticles, paving the way for recycling precious metal catalysts
2025-03-26
Scientists have for the first time filmed the real-time growth and contraction of Palladium nanoparticles, opening new avenues for utilising and recycling precious metal catalysts.
Researchers at the University of Nottingham’s School of Chemistry used transmission electron microscopy (TEM) to observe the complete lifecycle of palladium nanoparticles in a liquid environment, from nucleation through growth to dissolution, with the entire cycle repeating multiple times. This study has been published today in Nanoscale.
One of the most important applications of metal nanoparticles is in catalysis, which forms a backbone of chemical industries. Dr Jesum Alves ...
Tadpoles try to flee dangerous virus in their pond by growing much faster than normal
2025-03-26
The world’s amphibians are in trouble. Because of their sensitivity to climate change, habitat loss, and pollution, they may be the canary in the coalmine for the nascent anthropogenic mass extinction. Approximately 200 amphibian species have become extinct since the 1970s, and the International Union for the Conservation of Nature estimates that 34% of the 7,296 known remaining species are likewise at risk.
Another reason why amphibians are vulnerable is their susceptibility to disease. An emerging, potentially deadly disease of frogs and salamanders is ranavirus, a genus of at least seven species within the family Iridoviridae. Ranavirus can rapidly jump ...
Build it and they shall come
2025-03-26
Designing walkable neighborhoods has gained attention as a method to increase physical activity among urban populations. Moreover, highly walkable areas stimulate increased neighborhood retail sales, higher property values, and greater urban sustainability. However, only limited methods are available for improving walkability in the urban centers of highly motorized suburban cities. In the urban areas of suburban cities, increasing land-use diversity by opening a multifunctional facility is considered one of the most effective strategies for an architecture-scale intervention.
Dr. Haruka Kato, ...
How elephants plan their journeys: New study reveals energy-saving strategies
2025-03-26
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL 05:01 GMT / 01:01 ET WEDNESDAY 26 MARCH 2025
How elephants plan their journeys: New study reveals energy-saving strategies
A new study has revealed that African Elephants have an extraordinary ability to meet their colossal food requirements as efficiently as possible. Data from over 150 elephants demonstrated that these giants plan their journeys based on energy costs and resource availability. The findings – published today (26 March) in the Journal of Animal Ecology– could provide crucial information to help protect these iconic animals and their habitats.
Being an elephant is no easy task. As massive herbivores weighing several ...
New study challenges the ‘monogamy-superiority myth’, as non-monogamous people report just as happy relationships and sex lives
2025-03-26
Monogamous and non-monogamous individuals report similar levels of satisfaction in both their relationships and sex lives, according to a comprehensive new meta-analysis.
Published today in The Journal of Sex Research, the peer-reviewed study debunks the prevailing belief that monogamous relationships – defined as exclusive romantic and sexual commitment to one partner – are inherently superior in fostering fulfilling relationships compared to alternative structures.
While monogamy has been the predominant type of relationship in much of recent Western history, many individuals choose alternative structures. Non-monogamy includes various ...
Government of Guyana, Mount Sinai Health System and Hess Corporation announce five-year extension of national healthcare initiative.
2025-03-26
His Excellency Dr. Irfaan Ali, President of the Co-operative Republic of Guyana, today announced a five-year extension of the national healthcare initiative to transform Guyana’s public health system with world-class healthcare services accessible to every Guyanese citizen. This next phase of the initiative, launched in 2022 by the Government of Guyana in collaboration with the Mount Sinai Health System and Hess Corporation, will include establishment of a national cancer center, continued modernization of national health facilities including Georgetown Public Hospital Corporation, and the implementation of one ...
Preclinical study: after heart attack, a boost in anti-inflammatory cells promoted healing
2025-03-26
A scientific technique that rapidly increases the body’s production of anti-inflammatory cells promoted healing from heart attacks in mice, according to a new study by investigators from the Smidt Heart Institute at Cedars-Sinai. Once adapted to treat humans, the technique could potentially be used to repair heart muscle damage after a heart attack and be applied to a variety of inflammatory disorders.
The investigators’ findings were published in the peer-reviewed Journal of Clinical Investigation.
Heart attacks occur when the heart muscle is damaged by reduced blood flow from one or more arteries. They strike more than ...
Glucose revealed as a master regulator of tissue regeneration in Stanford Medicine study
2025-03-26
The sugar glucose, which is the main source of energy in almost every living cell, has been revealed in a Stanford Medicine study to also be a master regulator of tissue differentiation — the process by which stem cells give rise to specialized cells that make up all the body’s tissues.
It does so not by being catabolized, or broken down, to release the energy sequestered in its chemical bonds, but instead by binding in its intact form to proteins that control which genes in the genome are made into proteins and when.
The discovery of glucose’s undercover double life was so surprising the researchers ...
Open-label placebo appears to reduce premenstrual symptoms, study suggests
2025-03-25
Women affected by premenstrual syndrome (PMS) appear to experience less intense and debilitating symptoms after taking placebo pills even when told they do not contain any active medication, suggests a study published in the open-access journal BMJ Evidence-Based Medicine.
PMS can result in significant distress for women of reproductive age and cause psychological symptoms such as irritability, depressed mood, and mood swings as well as physical symptoms including breast tenderness, bloating, and joint pain.
Women ...
New mums advised to do two hours of moderate to vigorous exercise a week
2025-03-25
New mums should be strongly encouraged to begin clocking up at least two hours of moderate to vigorous intensity physical activity such as brisk walking and muscle strengthening exercises each week in the first three months after birth, when physically able, to improve health and well-being, say experts in a new guideline published by the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
They also strongly recommend daily pelvic floor muscle training to reduce the risk of urinary incontinence, and taking steps to improve sleep ...