EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4:00 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 26, 2025
MINNEAPOLIS — People living in more disadvantaged neighborhoods may be more likely to develop dementia than people living in neighborhoods with fewer disadvantages, according to a study published on March 26, 2025, online in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that neighborhood factors cause dementia; it only shows an association.
Neighborhood status was determined by factors such as income, employment, education and disability.
“Our findings show that the community in which you live influences your risk of developing dementia,” said study author Pankaja Desai, PhD, of Rush University in Chicago, Illinois. “Most studies of risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease focus on the individual level, not the community level. Of course, intervening at the community level is challenging, but prioritizing disadvantaged communities may be an effective way to mobilize resources for older adults and provide avenues for reducing the risk of dementia for the overall community.”
The study involved 6,781 people with an average age of 72 living in four communities in Chicago. Tests of thinking and memory skills were given at the beginning of the study and every three years for at least six years of follow-up. A group of 2,534 people were evaluated for dementia. A total of 66% of the study group were Black participants and the rest were white participants.
Researchers looked at U.S. Census tracts of the four neighborhoods based on amount of disadvantage. A U.S. Census tract is a small area within a county.
By the end of the study, 11% of the people in the tracts with the least disadvantage had developed Alzheimer’s disease, compared to 14% in the tracts with the next lowest disadvantage, 17% in the tracts with next-to-highest amount of disadvantage and 22% in the tracts with the highest amount of disadvantage.
Once researchers adjusted for other factors that could affect the risk of dementia, such as age, sex and education, they found that people in the tracts with the most disadvantage were more than twice as likely to develop dementia as those in the tracts with the least disadvantage.
“More Black participants lived in areas with greater disadvantage and more white participants lived in areas with lesser disadvantage. Once we took neighborhood disadvantage factors into account, there was no longer a significant difference between Black and white people in their risk of developing Alzheimer’s,” Desai said.
The study also looked at the annual rate of decline in scores on tests of thinking and memory skills. The scores of people in the tracts with the most disadvantage declined about 25% faster than those of people in the tracts with the least disadvantage.
A limitation of the study was that participants all lived in Chicago neighborhoods, so the results may not apply to other populations.
The study was funded by the National Institute on Aging.
Discover more about Alzheimer’s disease at BrainandLife.org, from the American Academy of Neurology. This resource also offers a magazine, podcast, and books that connect patients, caregivers and anyone interested in brain health with the most trusted information, straight from the world’s leading experts in brain health. Follow Brain & Life® on Facebook, X, and Instagram.
The American Academy of Neurology is the leading voice in brain health. As the world’s largest association of neurologists and neuroscience professionals with more than 40,000 members, the AAN provides access to the latest news, science and research affecting neurology for patients, caregivers, physicians and professionals alike. The AAN’s mission is to enhance member career fulfillment and promote brain health for all. A neurologist is a doctor who specializes in the diagnosis, care and treatment of brain, spinal cord and nervous system diseases such as Alzheimer's disease, stroke, concussion, epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, headache and migraine.
Explore the latest in neurological disease and brain health, from the minds at the AAN at AAN.com or find us on Facebook, X, Instagram, LinkedIn, and YouTube.
END
Your neighborhood may affect your risk of dementia
2025-03-26
(Press-News.org)
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Early signs of heart problems linked to smaller brain volumes
2025-03-26
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4:00 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 26, 2025
MINNEAPOLIS — People who have early signs of heart problems may also have changes in brain health that can be early signs of dementia, such as loss of brain volume, according to a meta-analysis published on March 26, 2025, online in Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The meta-analysis does not prove that early heart problems cause loss of brain cells; it only shows an association.
“This review shows that better ...
Research finds potential “molecular mimics” behind COVID-induced autoimmune disease
2025-03-26
COVID infection has been linked to higher risk of autoimmune disorders, including rheumatoid arthritis and type 1 diabetes. But why the virus might cause the body’s immune system to go haywire remains unknown, making it difficult to develop therapies to avoid autoimmunity. One hypothesis is that viral “molecular mimics” that resemble the body’s own proteins trigger an immune response against the virus—and healthy tissues get caught in the crossfire.
Now, with advanced data analysis and machine learning, scientists have identified a set of COVID-derived ...
Pennington Biomedical researchers identify neurons in brain that regulate energy levels and body temperature
2025-03-26
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
March 26, 2025
BATON ROUGE – Scientists at Pennington Biomedical Research Center have gained greater clarity in the brain regions and neurons that control metabolism, body temperature and energy use. Featured in the February edition of the journal Metabolism, Dr. Heike Münzberg-Gruening and a team of researchers discovered which chemicals influence the signals that control how much energy the body uses. In “Leptin Receptor Neurons in the dorsomedial hypothalamus require distinct neuronal subsets for thermogenesis and weight loss,” researchers laid out the pathways, chemicals, neurons ...
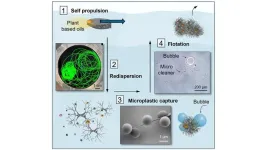
Cleaning microplastics
2025-03-26
In a new paper, researchers at North Carolina State University show proof of concept for a system that, in a single cycle, actively removes microplastics from water.
The findings, described in the journal Advanced Functional Materials, hold the potential for advances in cleansing oceans and other bodies of water of tiny plastics that may harm human health and the environment.
“The idea behind this work is: Can we make the cleaning materials in the form of soft particles that self-disperse in water, capture microplastics as they sink, and then return to the surface with the captured microplastic contaminants?” said Orlin Velev, the S. Frank and Doris Culberson Distinguished ...
MD Anderson names Jeffrey E. Lee, M.D., Chief Medical Executive
2025-03-26
HOUSTON ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center today announced that Jeffrey E. Lee, M.D., an internationally regarded leader in the field of oncology, has been appointed chief medical executive (CME) effective April 1.
Prior to his appointment, Lee served as CME ad interim, demonstrating strength as a leader committed to advancing the institution’s efforts in research, patient care, prevention and education. Assuming the role of CME is the culmination of Lee’s 34-year tenure at the institution, where he has made substantial contributions in the field ...
Sensor technology uses nature’s blueprint and machinery to monitor metabolism in body
2025-03-26
Life’s essential functions are powered by a set of compounds called metabolites, which are involved in every natural process including producing energy, regulating cell activity and keeping the body’s systems in balance. Tracking these molecules offers a window into the onset and status of many diseases, overall health, response to treatment and the intricate workings of biological systems.
However, today’s metabolite sensing methods fall short. Most rely on resource-intensive lab tests that give only brief snapshots from isolated samples. The few sensors that can track metabolites continuously are largely limited to detecting blood sugar.
An interdisciplinary ...
Chan Zuckerberg Initiative announces new biohub to develop breakthrough imaging technologies to observe cells in action
2025-03-26
REDWOOD CITY, Calif. (March 26, 2025) — The Chan Zuckerberg Initiative (CZI) announced a new grand challenge to develop groundbreaking imaging technologies to transform how scientists observe, measure and understand living cells and organisms. CZI’s two powerhouse institutes, CZ Biohub San Francisco and CZ Institute for Advanced Biological Imaging, will leverage their complementary expertise to form a new Biohub unmatched in the field of life science imaging research. They will combine their teams at a new science campus in Redwood City, Calif., adjacent to CZI ...
Encryption breakthrough lays groundwork for privacy-preserving AI models
2025-03-26
In an era where data privacy concerns loom large, a new approach in artificial intelligence (AI) could reshape how sensitive information is processed.
Researchers Austin Ebel and Karthik Garimella, Ph.D students, and Assistant Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering Brandon Reagen have introduced Orion, a novel framework that brings fully homomorphic encryption (FHE) to deep learning — allowing AI models to practically and efficiently operate directly on encrypted data without needing to decrypt it first.
The implications of this advancement, ...
Top global award for young technologists goes to researcher who advanced AI with high-performance computers
2025-03-26
ACM, the Association for Computing Machinery, today named Torsten Hoefler, a Professor at ETH Zurich, the recipient of the 2024 ACM Prize in Computing for fundamental contributions to high-performance computing and the ongoing AI revolution. Hoefler developed many of the core capabilities of modern supercomputers and defined key aspects of the algorithms for distributing AI models on them.
The ACM Prize in Computing recognizes early-to-mid-career computer scientists whose research contributions have fundamental impact and broad implications. ...
How did the large brain evolve?
2025-03-26
The results of the study show that the two genes act in a finely tuned interplay: one ensures that the progenitor cells of the brain multiply more, while the other causes these cells to transform into a different type of progenitor cell - the cells that later form the nerve cells of the brain. In the course of evolution, this interplay has led to the human brain being unique in its size and complexity.
The newly gained insights not only provide a deeper understanding of the evolutionary development of our brain but could also help to better comprehend how certain developmental disorders or diseases of the brain arise. ‘Our findings deepen the fundamental ...