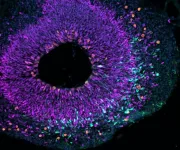
(Press-News.org) The results of the study show that the two genes act in a finely tuned interplay: one ensures that the progenitor cells of the brain multiply more, while the other causes these cells to transform into a different type of progenitor cell - the cells that later form the nerve cells of the brain. In the course of evolution, this interplay has led to the human brain being unique in its size and complexity.
The newly gained insights not only provide a deeper understanding of the evolutionary development of our brain but could also help to better comprehend how certain developmental disorders or diseases of the brain arise. ‘Our findings deepen the fundamental understanding of brain development and provide new insights into the evolutionary origins of our large brain. In the long term, they could contribute to the development of therapeutic approaches for malformations of the brain,’ says Nesil Eşiyok, first author of the study.
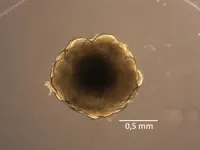
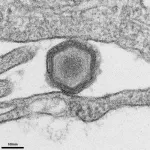
Various methods were combined for the study: In addition to animal experiments with mice, alternative methods such as chimpanzee brain organoids were also used. ‘The remarkable feature of our study is that the results from animal experiments and alternative methods complement each other well and mutually confirm their findings. . This not only emphasizes the high significance of our results, but could also help to reduce the need for animal experiments in the future by further developing, refining and confirming alternative methods,’ explains Michael Heide, the study’s lead researcher.
The German Primate Center (DPZ) - Leibniz Institute for Primate Research conducts biological and biomedical research on and with primates in the fields of infection research, neuroscience and primate biology. The DPZ also maintains five field stations in the tropics and is a reference and service center for all aspects of primate research. The DPZ is one of the 96 research and infrastructure facilities of the Leibniz Association.
END
How did the large brain evolve?
New insights into the development of the human brain
2025-03-26
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Rare disease drug nitisinone makes human blood deadly to mosquitoes
2025-03-26
In the fight against malaria, controlling the mosquito population is crucial.
Several methods are currently used to reduce mosquito numbers and malaria risk. One of these includes the antiparasitic medication ivermectin. When mosquitoes ingest blood containing ivermectin, it shortens the insect’s lifespan and helps decrease the spread of malaria.
However, ivermectin has its own issues. Not only is it environmentally toxic, but also, when it is overused to treat people and animals with worm ...
Mini rolling robot takes virtual biopsies
2025-03-26
Embargoed: Not for Release Until 2pm U.S. Eastern Time (6pm GMT) Wednesday, 26 March 2025
With images and videos
A tiny magnetic robot which can take 3D scans from deep within the body, that could revolutionise early cancer detection, has been developed by researchers.
The team, led by engineers from the University of Leeds, say this is the first time it has been possible to generate high-resolution three-dimensional ultrasound images taken from a probe deep inside the gastrointestinal ...
Researchers design tools to develop vaccines more efficiently for African swine fever virus (ASFV)
2025-03-26
Rockville, Maryland—March 26, 2024—Researchers from the J. Craig Venter Institute (JCVI), the Friedrich-Loeffler-Institut (FLI), and the International Livestock Research Institute (ILRI) have developed a reverse genetics system for African swine fever virus (ASFV). This new system will aid researchers in developing vaccines and in studying the pathogenesis and biology of ASFV, a highly contagious, deadly viral disease affecting domesticated and wild pigs, especially prevalent in Africa, Europe, Asia, and the Caribbean. A recent study estimates if ASFV reached the United States it could result ...
How survivors spanned the globe after Earth’s biggest mass extinction
2025-03-26
Scientists don’t call it the “Great Dying” for nothing. About 252 million years ago, upward of 80% of all marine species vanished during the end-Permian mass extinction – the most extreme event of its kind in Earth’s history.
What followed was a mysterious, multimillion-year span that could be called the “Great Dulling,” when marine animal communities looked remarkably alike all over the planet, from the equator to the poles. Researchers have long sought an explanation for this so-called taxonomic homogenization – a scene that played out after other mass extinctions over the past ...
Even in egalitarian Sweden, a "culture of silence" may prevent university staff and students from reporting sexual harassment
2025-03-26
Even in egalitarian Sweden, a "culture of silence" may prevent university staff and students from reporting sexual harassment, with just an 8.1% reporting rate for students who had experienced either rape or attempted rape.
####
Article URL: https://plos.io/4bW0elh
Article title: What determines the ‘culture of silence’? Disclosing and reporting sexual harassment among university employees and students at a large Swedish public university
Author countries: Sweden
Funding: This work was funded by the Swedish Research Council, ...
Data from the Healthy Minds Study of 140 college campuses in the US suggests that religiousness may be protective against symptoms of depression in students, although less so in sexual minorities
2025-03-26
Data from the Healthy Minds Study of 140 college campuses in the US suggests that religiousness may be protective against symptoms of depression in students, although less so in sexual minorities.
####
Article URL: https://plos.io/3XwiyM6
Article Title: Religiousness, sexual orientation, and depression among emerging adults in U.S. higher education: Findings from the Healthy Minds Study
Author Countries: Spain, United Kingdom, United States
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Idaho National Laboratory seeks sponsor for innovation incubator to support technology commercialization
2025-03-26
(IDAHO FALLS, Idaho) – The Idaho National Laboratory (INL) is seeking an industry sponsor to invest $5 million to $10 million in a privately funded innovation incubator. This program will combine the power of a national laboratory with private sector commercialization knowledge to unleash breakthrough innovations by finding and supporting promising startups in the areas of nuclear energy, integrated energy systems, cybersecurity and advanced materials.
The innovation incubator seeks to provide seed-stage startups aligned ...
Ochsner Health celebrates team members recognized as Louisiana State Nurses Association 40 Under 40 honorees
2025-03-26
NEW ORLEANS – Four outstanding Ochsner Health nurses have been named to the Louisiana State Nurses Association’s (LSNA) second annual 40 Under 40 list.
The LSNA 40 Under 40 list celebrates 40 future leaders of nursing in Louisiana who are 40 years of age and under, exemplify dedication to the nursing profession, and demonstrate exceptional leadership qualities.
“We are immensely proud of our Ochsner honorees. This recognition celebrates our nurses who fuel their purpose each day and use their voice to influence the growth of the nursing profession and how we deliver high-quality care to our patients and communities,” said Tiffany Murdock, senior ...
Study explores how time-restricted eating affects weight loss
2025-03-26
Time-restricted eating is the latest craze for people looking to lose weight, but whether it works is still the calorie-burning question.
A new study from the University of Mississippi shows that when healthy adults pair an eight-hour eating window with regular exercise, they lose more fat – without sacrificing lean muscle – compared to exercise alone, according to a study released in the International Journal of Obesity, which is published by the Nature Publishing Group.
“We saw that this did lead to more fat loss and reduced body fat percentage over time when healthy adults were following both exercise with time-restricting ...
Ochsner Health named 2025 Gallup Exceptional Workplace Award winner
2025-03-26
NEW ORLEANS – Ochsner Health, Louisiana’s largest non-profit, academic, multi-specialty, healthcare delivery system, has been awarded the 2025 Gallup Exceptional Workplace Award (GEWA) for employee engagement. This award recognizes the most engaged companies in the world and highlights Ochsner’s continued dedication to setting a standard of excellence in patient care and the workplace.
"Ochsner Health is honored to receive this recognition," said Pete November, chief executive officer, Ochsner Health. "Our commitment to fostering a supportive and dynamic workplace for our team members is directly ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
[Press-News.org] How did the large brain evolve?New insights into the development of the human brain