Novel adsorbent offers effective solution for perchlorate removal from water
2025-03-27
(Press-News.org)
A study published in Engineering introduces an innovative approach to address the issue of perchlorate (ClO4−) contamination in water. Perchlorate is a harmful oxo-anion found in aquatic environments. It can enter the human body through drinking water and inhibit iodine absorption in the thyroid gland, potentially causing various thyroid-related diseases. Given the strict perchlorate limits in drinking water worldwide, such as 70 μg/L in China and 15 μg/L in the United States, developing efficient methods for its removal is crucial.
The research team, hailing from Hunan University and Shanghai Jiao Tong University, prepared an adsorbent by anchoring N⁺–C–H hydrogen bond donors in hydrophobic cavities. This was achieved through the interaction of cationic surfactants, like cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) and cetylpyridinium chloride (CPC), with montmorillonite (MMT).
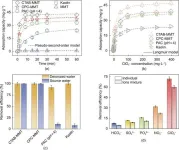
Batch experiments demonstrated the excellent performance of the cationic surfactant-modified MMT. It showed high selectivity for perchlorate over common competing anions, including SO42–, NO3–, PO43–, HCO3–, and halide anions. The adsorption kinetics were fast, and the adsorption capacity was relatively high compared to traditional adsorbents such as activated carbon, clay, or zeolite. For instance, the pseudo-second-order adsorption rate constants for CTAB-MMT and CPC-MMT were 0.0306 and 0.0153 per minute respectively, much higher than those of some traditional counterparts.
The researchers delved into the adsorption mechanisms. Electrostatic attraction was ruled out as the main driving force because the adsorbent could effectively remove perchlorate even at pH values higher than its isoelectric point. Instead, density functional theory (DFT) calculations indicated that unconventional CH···O hydrogen bonding was the primary mechanism. The C–H bonds adjacent to the quaternary ammonium in the cationic surfactants could act as hydrogen bond donors, forming strong bonds with perchlorate. The hydrophobic cavities formed by the long-chain tail groups of the cationic surfactants also played a role. They sheltered the C–H bonds, allowing only anions with low hydration energy, like perchlorate, to interact with the hydrogen bond donors.
To assess its practicality, cyclic adsorption experiments and fixed-bed column tests were carried out. The adsorbent exhibited good cyclic stability, maintaining a removal efficiency of over 80% after 20 cycles. In the fixed-bed column test, it could treat a large volume of water with an initial perchlorate concentration of 500 μg/L to below the drinking water limit of 70 μg/L, with an enrichment factor of 10.3.
This new adsorbent provides a practical and potentially cost-effective solution for perchlorate removal from water. It holds promise for applications in drinking water treatment plants, potentially improving the quality of drinking water and safeguarding public health.
The paper “Highly Selective Removal of Perchlorate from Water: Roles of Unconventional Hydrogen Bond and Hydrophobic Cavity,” authored by Jian Ao, Lingjun Bu, Yangtao Wu, Jinming Luo, Shiqing Zhou. Full text of the open access paper: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eng.2024.12.029. For more information about the Engineering, follow us on X (https://twitter.com/EngineeringJrnl) & like us on Facebook (https://www.facebook.com/EngineeringJrnl).
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-03-27
WASHINGTON — For the first time, researchers have shown that terahertz imaging can be used to visualize internal details of the mouse cochlea with micron-level spatial resolution. The non-invasive method could open new possibilities for diagnosing hearing loss and other ear-related conditions.
“Hearing relies on the cochlea, a spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear that converts sound waves into neural signals,” said research team leader Kazunori Serita from Waseda University in Japan. “Although conventional imaging methods often struggle to visualize this organ’s fine details, ...
2025-03-27
(WASHINGTON—March 27, 2025) — A machine learning model generated by a team from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) outperformed standard statistical models in identifying and stratifying transplant risk for patients with myelofibrosis, according to new research published today in Blood, the American Society of Hematology’s flagship journal.
“Although there are many models available to identify patients with high-risk myelofibrosis, we are still lacking ...
2025-03-27
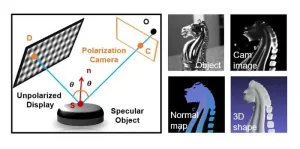
Accurate and robust 3D imaging of specular, or mirror-like, surfaces is crucial in fields such as industrial inspection, medical imaging, virtual reality and cultural heritage preservation. Yet anyone who has visited a house of mirrors at an amusement park knows how difficult it is to judge the shape and distance of reflective objects.
This challenge also persists in science and engineering, where the accurate 3D imaging of specular surfaces has long been a focus in both optical metrology and computer vision research. While specialized techniques ...
2025-03-27
Noted Maya archaeologist Julie Hoggarth, Ph.D., associate professor of anthropology at Baylor University, has been elected to the rank of AAAS Fellow, a lifetime honor announced today by the Council of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), the world’s largest general scientific society and publisher of the Science family of journals.
Hoggarth is among the 471 scientists, engineers and innovators who have been elected 2024 Fellows for their scientifically and socially distinguished achievements throughout their careers. The new Fellow class hails from academic institutions, ...
2025-03-27
DALLAS, March 27, 2025 — Recent analysis by the National Health Institute indicates that telehealth now accounts for 23% of all health care encounters nationwide, with some clinical specialties reporting virtual visit rates now exceeding 50%.[1] To help ensure quality care in this rapidly expanding field, the American Heart Association Center for Telehealth and the National Institutes of Health-funded University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Center for Virtual Care Value and Excellence (UNC-Chapel Hill ViVE), are building ...
2025-03-27
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Contact:
Raluca Cadar
The Protein Society
Phone: (844) 377-6834
E-mail: rcadar@proteinsociety.org
LOS ANGELES, CA – The Protein Society, the premier international society dedicated to supporting protein research, announces the winners of the 2025 Protein Society Awards, which will be recognized at the 39th Annual Symposium, June 26 – 29, 2025, in San Francisco, USA. Plenary talks from award recipients will take place throughout the 3.5-day event. The winners’ scientific accomplishments, described by their nominators below, demonstrate their profound impact on protein science.
The Christian B. Anfinsen ...
2025-03-27
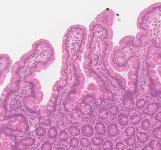
A machine learning algorithm developed by Cambridge scientists was able to correctly identify in 97 cases out of 100 whether or not an individual had coeliac disease based on their biopsy, new research has shown.
The AI tool, which has been trained on almost 3,400 scanned biopsies from four NHS hospitals, could speed up diagnosis of the condition and take pressure off stretched healthcare resources, as well as improving diagnosis in developing nations, where shortages of pathologists are severe.
Digital ...
2025-03-27
Artificial intelligence (AI) could help sonographers identify any abnormalities at the 20-week pregnancy screening scan almost twice as quickly, without reducing the accuracy or reliability of diagnoses, a new study has shown.
This will help improve patient care by allowing sonographers to focus on other aspects of the scan, such as communicating with parents or spending more time looking at any areas of concern.
The trial is the first of its kind to use AI for the 20-week pregnancy scan on real patients, and is ...
2025-03-27
Dartmouth researchers conducted the first clinical trial of a therapy chatbot powered by generative AI and found that the software resulted in significant improvements in participants' symptoms, according to results published March 27 in the New England Journal of Medicine AI.
People in the study also reported they could trust and communicate with the system, known as Therabot, to a degree that is comparable to working with a mental-health professional.
The trial consisted of 106 people from across the United States diagnosed with major depressive disorder, generalized anxiety disorder, or an eating disorder. ...
2025-03-27
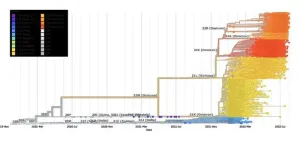
It’s been five years since COVID-19 was declared a global pandemic. As SARS-CoV-2 shifts to endemic status, questions about its future evolution remain. New variants of the virus will likely emerge, driven by positive selection for traits such as increased transmissibility, longer infection duration and the ability to evade immune defenses. These changes could allow the virus to spread among previously immunized populations, potentially triggering new waves of infection.
Predicting new mutations in viruses is crucial for advancing life science research, particularly when trying to understand how viruses evolve, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Novel adsorbent offers effective solution for perchlorate removal from water