(Press-News.org) About The Study: Daily screen use was associated with later bedtimes and approximately 50 minutes less sleep each week in this study. Associations were greater among those with evening chronotypes, who are at risk for poor sleep due to social jetlag (i.e., misalignment between circadian rhythms and social commitments). These findings confirm disruptions to sleep from electronic screens are not limited to children and adolescents. Further work is needed to understand the best mechanisms for intervention.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Charlie Zhong, PhD, email charlie.zhong@cancer.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.2493)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.2493?guestAccessKey=c0957767-f5eb-4d6d-88a4-15c747418b57&utm_source=for_the_media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=032725
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Electronic Screen Use and Sleep Duration and Timing in Adults
JAMA Network Open
2025-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
State Minimum Wage and Food Insecurity Among US Households With Children
2025-03-27
About The Study: In this pooled cross-sectional study, findings suggest that state legislatures that elected to increase their state minimum wage may have also improved state food security rates among households with children at risk for economic hardship. The findings provide policymakers with actionable evidence to consider in setting minimum wages that could reduce the burden of food insecurity among U.S. children and families.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Megan R. Winkler, PhD, RN, email megan.winkler@emory.edu.
To ...
Novel adsorbent offers effective solution for perchlorate removal from water
2025-03-27
A study published in Engineering introduces an innovative approach to address the issue of perchlorate (ClO4−) contamination in water. Perchlorate is a harmful oxo-anion found in aquatic environments. It can enter the human body through drinking water and inhibit iodine absorption in the thyroid gland, potentially causing various thyroid-related diseases. Given the strict perchlorate limits in drinking water worldwide, such as 70 μg/L in China and 15 μg/L in the United States, developing efficient methods for its removal is crucial.
The research team, hailing from Hunan University and Shanghai Jiao Tong University, prepared an adsorbent ...
Terahertz imaging reveals new views of internal cochlear structure
2025-03-27
WASHINGTON — For the first time, researchers have shown that terahertz imaging can be used to visualize internal details of the mouse cochlea with micron-level spatial resolution. The non-invasive method could open new possibilities for diagnosing hearing loss and other ear-related conditions.
“Hearing relies on the cochlea, a spiral-shaped organ in the inner ear that converts sound waves into neural signals,” said research team leader Kazunori Serita from Waseda University in Japan. “Although conventional imaging methods often struggle to visualize this organ’s fine details, ...
Machine learning program enhances transplant risk assessment in myelofibrosis patients better than current models
2025-03-27
(WASHINGTON—March 27, 2025) — A machine learning model generated by a team from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation (EBMT) outperformed standard statistical models in identifying and stratifying transplant risk for patients with myelofibrosis, according to new research published today in Blood, the American Society of Hematology’s flagship journal.
“Although there are many models available to identify patients with high-risk myelofibrosis, we are still lacking ...
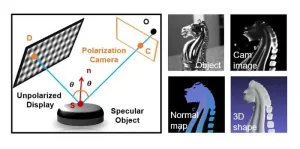
Beyond ambiguous reflections: Bridging optical 3D metrology and computer vision
2025-03-27
Accurate and robust 3D imaging of specular, or mirror-like, surfaces is crucial in fields such as industrial inspection, medical imaging, virtual reality and cultural heritage preservation. Yet anyone who has visited a house of mirrors at an amusement park knows how difficult it is to judge the shape and distance of reflective objects.
This challenge also persists in science and engineering, where the accurate 3D imaging of specular surfaces has long been a focus in both optical metrology and computer vision research. While specialized techniques ...
Baylor Anthropology scientist Julie Hoggarth, Ph.D., named AAAS Fellow
2025-03-27
Noted Maya archaeologist Julie Hoggarth, Ph.D., associate professor of anthropology at Baylor University, has been elected to the rank of AAAS Fellow, a lifetime honor announced today by the Council of the American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS), the world’s largest general scientific society and publisher of the Science family of journals.
Hoggarth is among the 471 scientists, engineers and innovators who have been elected 2024 Fellows for their scientifically and socially distinguished achievements throughout their careers. The new Fellow class hails from academic institutions, ...
Joint clinical commitment will advance integration of telehealth, value of patient care
2025-03-27
DALLAS, March 27, 2025 — Recent analysis by the National Health Institute indicates that telehealth now accounts for 23% of all health care encounters nationwide, with some clinical specialties reporting virtual visit rates now exceeding 50%.[1] To help ensure quality care in this rapidly expanding field, the American Heart Association Center for Telehealth and the National Institutes of Health-funded University of North Carolina Chapel Hill Center for Virtual Care Value and Excellence (UNC-Chapel Hill ViVE), are building ...
The Protein Society announces its 2025 Award Recipients
2025-03-27
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Contact:
Raluca Cadar
The Protein Society
Phone: (844) 377-6834
E-mail: rcadar@proteinsociety.org
LOS ANGELES, CA – The Protein Society, the premier international society dedicated to supporting protein research, announces the winners of the 2025 Protein Society Awards, which will be recognized at the 39th Annual Symposium, June 26 – 29, 2025, in San Francisco, USA. Plenary talks from award recipients will take place throughout the 3.5-day event. The winners’ scientific accomplishments, described by their nominators below, demonstrate their profound impact on protein science.
The Christian B. Anfinsen ...
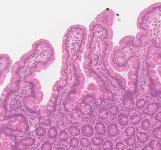
AI is as good as pathologists at diagnosing celiac disease, study finds
2025-03-27
A machine learning algorithm developed by Cambridge scientists was able to correctly identify in 97 cases out of 100 whether or not an individual had coeliac disease based on their biopsy, new research has shown.
The AI tool, which has been trained on almost 3,400 scanned biopsies from four NHS hospitals, could speed up diagnosis of the condition and take pressure off stretched healthcare resources, as well as improving diagnosis in developing nations, where shortages of pathologists are severe.
Digital ...
AI could help sonographers identify abnormalities in unborn babies more quickly
2025-03-27
Artificial intelligence (AI) could help sonographers identify any abnormalities at the 20-week pregnancy screening scan almost twice as quickly, without reducing the accuracy or reliability of diagnoses, a new study has shown.
This will help improve patient care by allowing sonographers to focus on other aspects of the scan, such as communicating with parents or spending more time looking at any areas of concern.
The trial is the first of its kind to use AI for the 20-week pregnancy scan on real patients, and is ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
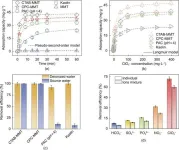
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
[Press-News.org] Electronic Screen Use and Sleep Duration and Timing in AdultsJAMA Network Open