###
Please contact media@sfn.org for full-text PDF.
About JNeurosci
JNeurosci was launched in 1981 as a means to communicate the findings of the highest quality neuroscience research to the growing field. Today, the journal remains committed to publishing cutting-edge neuroscience that will have an immediate and lasting scientific impact, while responding to authors' changing publishing needs, representing breadth of the field and diversity in authorship.
About The Society for Neuroscience
The Society for Neuroscience is the world's largest organization of scientists and physicians devoted to understanding the brain and nervous system. The nonprofit organization, founded in 1969, now has nearly 35,000 members in more than 95 countries.
END
Exploring binge eating and binge drinking alcohol comorbidity
Mouse study suggests females are more sensitive to the cooccurrence of binge eating and drinking and identifies a protein that prevents this disease comorbidity in both sexes.
2025-03-31
(Press-News.org) The comorbidity of binge eating and alcohol binge drinking is prevalent and increases the risk of other neuropsychiatric and bodily conditions. However, the mechanisms linking these forms of binge consumption are unclear. To explore the link between binge eating and binge drinking alcohol, Karen Szumlinski, from the University of California, Santa Barbara, and colleagues developed a way to model the disease comorbidity in mice. As reported in their JNeurosci paper, this mouse model led to the discovery that females with a history of binge eating start binge drinking alcohol quicker than males. The researchers also found that females had increased levels of a protein previously associated with comorbid alcohol use disorder and eating disorders called phosphodiesterase 4B (PDE4B). Inhibiting the protein prevented cooccurrence of binging in both sexes of mice. According to the authors, this study supports previous work linking PDE4B to problematic alcohol use and eating disorders and may inform future work investigating whether the protein is an effective treatment target. The authors also emphasize that the behavioral paradigm they developed may be useful for preclinical researchers working to unveil more mechanisms linking binge eating and drinking.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The proportion of harmful substances in particulate matter is much higher than assumed
2025-03-31
People breathing contaminated air over the course of years are at greater risk of developing numerous diseases. This is thought to be due to highly reactive components in particulate matter, which affect biological processes in the body. However, researchers from the University of Basel, Switzerland, have now shown that precisely these components disappear within hours and that previous measurements therefore completely underestimate the quantities in which they are present.
From chronic respiratory problems to cardiovascular diseases, ...
Administration is weakening U.S. research capacity and endangering Americans, nation’s leading scientists warn
2025-03-31
The wellbeing of Americans and the country’s longstanding position as a world leader in science and technology are in jeopardy due to the actions of the Trump administration, approximately 1,900 leading figures in medicine, science, and engineering warn today in an open statement to the American public. The list of signatories includes Nobel Prize winners, deans of medical schools, and national leaders in science and technology.
“For over 80 years, wise investments by the US government have built up the nation’s research enterprise, making it the envy of ...
Trade Tariffs on Canadian Pharmaceuticals— Implications for US Drug Supply and Costs
2025-03-31
About The Study: Although Canada is not the largest supplier of medications to the U.S., tariffs could raise costs and strain supply chains. This study estimates that $3 billion in U.S. pharmaceuticals depend on Canadian manufacturing, with 25% tariffs adding $750 million in cost. Although the Inflation Reduction Act provisions limit cost pass-through to some payers (i.e., Medicare), manufacturers may still adjust production or alter distribution, increasing supply chain fragility.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Mina Tadrous, PharmD, PhD, email mina.tadrous@utoronto.ca.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
Cardiovascular Health Among Rural and Urban US Adults— Healthcare, Lifestyle, and Social Factors
2025-03-31
About The Study: This national cross-sectional study found substantial rural-urban disparities in cardiometabolic risk factors and cardiovascular diseases, which were largest among younger adults and almost entirely explained by social risk factors. These findings suggest that efforts to improve socioeconomic conditions in rural communities may be critical to address the rural-urban gap in cardiovascular health.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Rishi K. Wadhera, MD, MPP, MPhil, email rwadhera@bidmc.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2025.0538)
Editor’s ...
Study finds gap between heart disease outcomes in men and women has narrowed over past 20 years
2025-03-31
While the typical image of someone suffering a heart attack might be a man clutching his chest, heart disease is a major problem for women, too. In fact, it’s the leading cause of death among women in the United States, with nearly 45% of the nation’s women over age 20 living with some form of cardiovascular disease.
A new study from heart researchers at Intermountain Health in Salt Lake City shows that while rates of death and other cardiac-related events – like heart attack – are still high for women, the ...
New study links lower proportions of certain sleep stages to brain changes associated with Alzheimer’s disease
2025-03-31
DARIEN, IL — New research reveals that lower proportions of specific sleep stages are associated with reduced brain volume in regions vulnerable to the development of Alzheimer’s disease over time.
Results show that individuals with lower proportions of time spent in slow wave sleep and rapid eye movement sleep had smaller volumes in critical brain regions, particularly the inferior parietal region, which is known to undergo early structural changes in Alzheimer’s disease. The results were adjusted for potential confounders including demographic characteristics, smoking history, alcohol use, hypertension, and coronary heart disease.
“Our findings provide ...
Long-term practice of Transcendental Meditation may reduce both stress and aging
2025-03-31
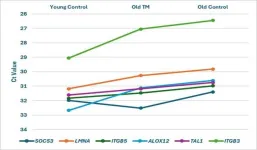
A collaborative study conducted by researchers at Maharishi International University (MIU), the University of Siegen, and the Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences reveals that individuals practicing Transcendental Meditation® (TM®) technologies long-term show favorable biological markers of aging and stress. The research compared gene expression, cognitive function (via EEG), and hair glucocorticoids (cortisol and cortisone) in 12-year and 40-year TM groups and non-meditator controls.
“This study provides evidence that long-term practice of TM technologies has a broad range of health benefits at the molecular ...
Delicate balancing act determines how many genome gateways form in cells
2025-03-31
EMBARGOED UNTIL MONDAY, MARCH 31 – 11:00 AM Eastern
The nuclei in our cells are miniature warehouses safeguarding the genetic blueprint for the body’s biologic machinery.
As warehouses go, nuclei are more like libraries than bank vaults. Too many cellular components need access to the genome to lock it down like Fort Knox. Instead, large groupings of more than 1,000 individual protein molecules called nuclear pore complexes (NPCs) pepper the dividing membrane, serving as gateways for materials and messages entering and exiting the nucleus.
While the basic need for this shuttle service is constant, ...
Postpartum hormonal contraceptive use and risk of depression
2025-03-31
About The Study: Hormonal contraceptive initiation postpartum was associated with an instantaneous increased risk of developing depression in this cohort study. The associated risk was higher the earlier it was initiated postpartum, at least for combined oral contraceptives. This finding raises the issue of whether the incidence of depression postpartum is increased by routine hormonal contraceptive initiation after childbirth.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Vibe Gedsø Frokjaer, PhD, email vibe.frokjaer@nru.dk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.2474)
Editor’s ...
CU research poised to change oxygen standards for trauma patients
2025-03-31
When a critically injured patient is admitted to the hospital, how much supplemental oxygen should they receive? New research published this week in JAMA Network Open led by investigators at the University of Colorado School of Medicine suggests it’s often less than the current standard.
“The idea has traditionally been that severe trauma causes stress to patients’ bodies, and we want to deliver as much oxygen as possible to the brain and to vital organs because they are losing blood,” says Adit Ginde, MD, MPH, professor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Engineered immune cells show promise against brain metastases in preclinical study
Improved EV battery technology will outmatch degradation from climate change
AI cancer tools risk “shortcut learning” rather than detecting true biology
Painless skin patch offers new way to monitor immune health
Children with poor oral health more often develop cardiovascular disease as adults
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
[Press-News.org] Exploring binge eating and binge drinking alcohol comorbidityMouse study suggests females are more sensitive to the cooccurrence of binge eating and drinking and identifies a protein that prevents this disease comorbidity in both sexes.