(Press-News.org) Wheat is grown over more land area than any other food crop. Among pathogen-driven threats to wheat, fungi top the list, causing billions of dollars of losses each year and posing a serious challenge to food security worldwide.
In an effort to combat this problem, a research team led by Prof. LIU Zhiyong from the Institute of Genetics and Developmental Biology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, together with collaborators, has uncovered a novel immune mechanism by which tandem kinase proteins (TKPs) combat pathogen invasion in wheat.
TKPs are a recently discovered class of disease resistance proteins in wheat and barley. Characterized by two or more tandemly arranged kinase domains, these signaling proteins provide resistance against various fungal pathogens, including stripe rust, leaf rust, stem rust, powdery mildew, wheat blast, and smut. Their potential in breeding applications has garnered considerable attention.
The current study, which was published in Science on March 27, expands the understanding of TKP functionality. It establishes a new paradigm for cooperation between TKPs and nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat (NLR) proteins—a type of immune receptor protein—in disease resistance. Specifically, the researchers discovered that an atypical NLR protein, WTN1 (Wheat Tandem NBD 1), partners with the TKP WTK3 to detect pathogen effectors and initiate immune responses, thereby conferring resistance to multiple fungal diseases in wheat.
With this discovery, the study bridges a critical gap in understanding immune regulatory pathways and offers a foundation for engineering crop varieties with broad-spectrum pathogen resistance.
Previously, the research team successfully cloned the broad-spectrum powdery mildew resistance genes Pm24 (WTK3) and Pm36 (WTK7-TM), both of which encode novel TKPs derived from Chinese wheat landrace and wild emmer wheat, respectively. However, key questions remained regarding how these resistance proteins recognize pathogen effectors, what functional roles their kinase domains play, and which immune pathways they activate.
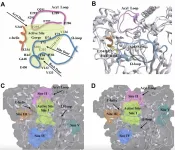
To address these questions, the researchers screened ethyl methanesulfonate (EMS)-induced susceptible mutants of Pm24 (WTK3) and identified WTN1 as a pivotal component of the WTK3-mediated disease resistance pathway. Genetic analyses and genome editing demonstrated that WTN1 is essential for WTK3-mediated immunity against wheat powdery mildew. The WTK3-WTN1 pair operates via a sensor-executor cooperative model, with WTK3 not only conferring resistance to powdery mildew but also recognizing the wheat blast effector PWT4, thus extending its resistance potential.
Using a multidisciplinary approach—including plant immunology, biochemical assays, electrophysiological experiments, and evolutionary analysis—the researchers uncovered a finely coordinated relationship between WTK3 and WTN1. Their findings indicate that WTK3 consists of two critical functional modules: the pseudo-kinase fragment (PKF) and the first kinase domain (Kin I), which recognize pathogen effectors, and the second kinase domain (Kin II), which interacts with WTN1 to form a robust "defense team." Upon pathogen detection, the WTK3-WTN1 complex activates an ion channel, facilitating calcium ion (Ca²⁺) influx and inducing hypersensitive responses and programmed cell death to curb infection.
Beyond its scientific impact, this study offers significant agricultural value. Pm24 (WTK3) originates from Chinese wheat landraces and has been successfully introduced into high-yield wheat varieties through backcrossing and marker-assisted breeding. These newly developed high-yielding disease-resistant germplasms have been freely distributed to domestic breeding institutions, addressing the scarcity of broad-spectrum powdery mildew resistance genes in China's key wheat-producing regions.
Moreover, this breakthrough paves the way for establishing genetic barriers against wheat blast and supports sustainable agricultural development and industry advancements.
END
Scientists uncover novel immune mechanism in wheat tandem kinase
2025-04-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Three University of Virginia Engineering faculty elected as AAAS Fellows
2025-04-01
Faculty representing three disciplines in the University of Virginia School of Engineering and Applied Science — computer science, mechanical and aerospace engineering, and civil and environmental engineering — have been elected to the rank of fellow by the American Association for the Advancement of Science.
The AAAS is one of the world’s largest general scientific societies and publisher of the Science family of journals. UVA Engineering’s faculty are among 471 scientists and engineers named in the class of 2024, according to the AAAS.
Fellows are selected ...
Unintentional drug overdoses take a toll across the U.S. unequally, study finds
2025-04-01
A recent study from Columbia University’s Mailman School of Public Health reveals significant racial and sex disparities in drug overdose mortality rates. The research found that both Black men and Black women have been disproportionately impacted by overdose deaths, with their mortality rates rising sharply compared to their White counterparts. This study expands scientific understanding of how race, sex, and regional factors intersect to affect overdose outcomes. The study's findings are published ...
A step toward plant-based gelatin
2025-04-01
WASHINGTON, April 1, 2025 – With increased awareness about food sources and their environmental impacts, replacing animal-derived products in food and drugs is a significant research area. One common — but often overlooked — animal protein is gelatin, found everywhere from candy to plastic-free packaging.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Ottawa present gum tragacanth as a plant-based alternative to gelatin for creating edible films.
“Gelatin has ...
ECMWF unveils groundbreaking ML tool for enhanced fire prediction
2025-04-01
The ability to predict wildfires - such as those that recently devastated Los Angeles and Canada - is advancing rapidly with the help of ML–driven high-quality data. A new paper, published today (Tuesday 1 April, 16:00 BST | https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-58097-7) in Nature Communications, highlights how the collection and integration of higher-quality data can significantly improve the accuracy and reliability of wildfire predictions.
The paper evaluates how ECMWF's new data-driven fire danger forecasting model, the Probability of Fire (PoF), performed in 2023 and in recent extreme events. ECMWF has been producing fire ...
The food and fuel that farms itself
2025-04-01
Under the right conditions, duckweed essentially farms itself. Wastewater, ponds, puddles, swamps—you name it. If there’s enough sunlight and carbon dioxide, the aquatic plant can grow freely. But that’s not all that makes it intriguing. Packed inside duckweed’s tiny fronds is enormous potential as a soil enricher, a fuel source, protein-rich foods, and more. New findings at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) could help bring all that potential to life.
CSHL Professor and HHMI Investigator Rob Martienssen and Computational Analyst Evan Ernst started working with duckweed over 15 years ago. They see their latest research as one of the most important ...
Patient- and Community-Level Characteristics Associated With RSV Vaccination
2025-04-01
About The Study: Knowledge of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease and RSV vaccine eligibility was low in this cross-sectional study of hospitalized adults. Older adults and those with certain medical conditions were more likely to have received vaccine, suggesting appropriate prioritization, but sociodemographic differences in vaccine uptake occurred.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Diya Surie, MD, email dsurie@cdc.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.2841)
Editor’s ...
Intersectional Racial and Sex Disparities in Unintentional Overdose Mortality
2025-04-01
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of overdose deaths, disparities in overdose mortality were evident, with Black men and Black women experiencing a pronounced and increasing burden of mortality compared with their white counterparts. Addressing these disparities will require a multipronged approach targeting the social, physical, economic, and policy risk environments.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kechna Cadet, PhD, MPH, email kc3010@cumc.columbia.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.2728)
Editor’s ...
PLOS announces new partnership in China
2025-04-01
San Francisco, California, United States - The Public Library of Science (PLOS) and the Society of China University Journals (CUJS) today announced a 3-year strategic partnership between the organizations to work together on topics and content related to open access, open science, scientific integrity and scientific evaluation.
CUJS is an academic, national and non-profit social organization with more than 1,200 journal members. The organization conducts academic research and training programs in the editing and publishing of STM journals and promotes the development of STM ...
New options for controlling type 2 diabetes
2025-04-01
Nearly 40% of patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes imperil their health by stopping their medication within the first year, UVA Health diabetes experts note in a new paper highlighting a growing array of treatment options.
The pragmatic new paper urges doctors to consider not just traditional diabetes medicines but emerging alternatives that patients may be more likely to stick with long-term. “Prescribing a medication or making lifestyle recommendations that a patient is not willing or able to follow for any reason is not likely to lead to improvements ...
Senolytics target Alzheimer’s-linked brain enzymes without harming healthy ones
2025-04-01
“This work provides new opportunities for the development of the next generation of ChE inhibitors that specifically target AChE and BChE associated with AD pathology.”
BUFFALO, NY — April 1, 2025 — A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on March 29, 2025, as the cover of Volume 17, Issue 3, titled “Differential senolytic inhibition of normal versus Aβ-associated cholinesterases: implications in aging and Alzheimer’s disease.”
In this study, a research team from Dalhousie University, led by Sultan Darvesh, discovered that certain anti-aging ...