(Press-News.org) A recent study from Columbia University’s Mailman School of Public Health reveals significant racial and sex disparities in drug overdose mortality rates. The research found that both Black men and Black women have been disproportionately impacted by overdose deaths, with their mortality rates rising sharply compared to their White counterparts. This study expands scientific understanding of how race, sex, and regional factors intersect to affect overdose outcomes. The study's findings are published in JAMA Network Open.
“Efforts to reduce drug-related mortality must address the specific needs of marginalized communities, especially Black men,” said Kechna Cadet, PhD, postdoctoral researcher in the Department of Epidemiology. “Addressing these disparities requires a comprehensive, multifaceted approach that targets social, economic, physical, and policy risk factors.”
The study examined trends in drug poisoning mortality between Black men, Black women, White men, and White women across all 50 states from 2010 to 2020. Data on unintentional drug poisoning deaths was sourced from the CDC’s Injury Statistics Query and Reporting System. The analysis included 518,724 fatal drug poisoning cases, broken down as follows: 46,776 Black men, 20,087 Black women, 150,405 White women, and 301,456 White men. The study accounted for 11,820,781 years of potential life lost during the 10-year period.
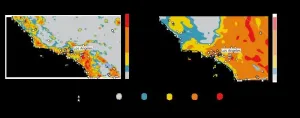
For the entire time period, findings show Black men had the highest mean age-adjusted mortality rate at 23 deaths per 100,000, followed by White men at 22 per 100,000, with lower rates for White women (12 per 100,000) and Black women (9 per 100,000). The study revealed that Black men mortality rates saw the most dramatic increases, particularly in Maryland (+485 percent) and the District of Columbia (+360 percent). In contrast, White women mortality rates declined in states like Alaska (-23 percent) and Wyoming (-20 percent) and Oklahoma (-19 percent).
“Our goal was to identify the specific sociodemographic groups and regions that have faced the highest levels of inequality and are in urgent need of intervention,” said Dr. Cadet.
The study found that in 2016, Black men overdose mortality rates surpassed those of White men, with Black men rates nearly 60 percent higher by 2020. Similarly, Black women saw a steady increase in mortality rates, surpassing those of White women by 2019.
The opioid overdose epidemic, which has caused nearly one million deaths in the U.S. since its onset, remains a leading contributor to the country’s declining life expectancy. In 2021 alone, roughly 107,000 lives were lost to overdoses involving fentanyl, heroin, and cocaine. Historically, the majority of opioid-related deaths have been among White individuals. However, overdose rates involving opioids and cocaine have plateaued among non-Hispanic White populations while rising among Black and Hispanic groups. In addition, men have experienced consistently higher overdose rates than women.
“Our analysis of intersectional race and sex disparities over the past decade offers crucial insights for directing much needed resources such as harm reduction services and tailored treatment programs to the populations most in need of urgent targeted interventions to decrease unintentional drug overdoses.” said Silvia Martins, MD, professor of Epidemiology at Columbia Mailman School, and senior author of the study.
Dr. Bianca Smith, a co-author of the study from Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, also contributed to the research.
The study reported in this press release was supported by the National Institute of Drug Abuse of the National Institutes of Health, under grant numbers T32DA031099, T32DA007292, and R01DA059376. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health
Founded in 1922, the Columbia University Mailman School of Public Health pursues an agenda of research, education, and service to address the critical and complex public health issues affecting New Yorkers, the nation and the world. The Columbia Mailman School is the fourth largest recipient of NIH grants among schools of public health. Its nearly 300 multi-disciplinary faculty members work in more than 100 countries around the world, addressing such issues as preventing infectious and chronic diseases, environmental health, maternal and child health, health policy, climate change and health, and public health preparedness. It is a leader in public health education with more than 1,300 graduate students from 55 nations pursuing a variety of master’s and doctoral degree programs. The Columbia Mailman School is also home to numerous world-renowned research centers, including ICAP and the Center for Infection and Immunity. For more information, please visit www.mailman.columbia.edu.
END
Unintentional drug overdoses take a toll across the U.S. unequally, study finds
New research highlights intersectional racial and sex disparities
2025-04-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A step toward plant-based gelatin
2025-04-01
WASHINGTON, April 1, 2025 – With increased awareness about food sources and their environmental impacts, replacing animal-derived products in food and drugs is a significant research area. One common — but often overlooked — animal protein is gelatin, found everywhere from candy to plastic-free packaging.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from the University of Ottawa present gum tragacanth as a plant-based alternative to gelatin for creating edible films.
“Gelatin has ...
ECMWF unveils groundbreaking ML tool for enhanced fire prediction
2025-04-01
The ability to predict wildfires - such as those that recently devastated Los Angeles and Canada - is advancing rapidly with the help of ML–driven high-quality data. A new paper, published today (Tuesday 1 April, 16:00 BST | https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-58097-7) in Nature Communications, highlights how the collection and integration of higher-quality data can significantly improve the accuracy and reliability of wildfire predictions.
The paper evaluates how ECMWF's new data-driven fire danger forecasting model, the Probability of Fire (PoF), performed in 2023 and in recent extreme events. ECMWF has been producing fire ...
The food and fuel that farms itself
2025-04-01
Under the right conditions, duckweed essentially farms itself. Wastewater, ponds, puddles, swamps—you name it. If there’s enough sunlight and carbon dioxide, the aquatic plant can grow freely. But that’s not all that makes it intriguing. Packed inside duckweed’s tiny fronds is enormous potential as a soil enricher, a fuel source, protein-rich foods, and more. New findings at Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) could help bring all that potential to life.
CSHL Professor and HHMI Investigator Rob Martienssen and Computational Analyst Evan Ernst started working with duckweed over 15 years ago. They see their latest research as one of the most important ...
Patient- and Community-Level Characteristics Associated With RSV Vaccination
2025-04-01
About The Study: Knowledge of respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) disease and RSV vaccine eligibility was low in this cross-sectional study of hospitalized adults. Older adults and those with certain medical conditions were more likely to have received vaccine, suggesting appropriate prioritization, but sociodemographic differences in vaccine uptake occurred.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Diya Surie, MD, email dsurie@cdc.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.2841)
Editor’s ...
Intersectional Racial and Sex Disparities in Unintentional Overdose Mortality
2025-04-01
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study of overdose deaths, disparities in overdose mortality were evident, with Black men and Black women experiencing a pronounced and increasing burden of mortality compared with their white counterparts. Addressing these disparities will require a multipronged approach targeting the social, physical, economic, and policy risk environments.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Kechna Cadet, PhD, MPH, email kc3010@cumc.columbia.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.2728)
Editor’s ...
PLOS announces new partnership in China
2025-04-01
San Francisco, California, United States - The Public Library of Science (PLOS) and the Society of China University Journals (CUJS) today announced a 3-year strategic partnership between the organizations to work together on topics and content related to open access, open science, scientific integrity and scientific evaluation.
CUJS is an academic, national and non-profit social organization with more than 1,200 journal members. The organization conducts academic research and training programs in the editing and publishing of STM journals and promotes the development of STM ...
New options for controlling type 2 diabetes
2025-04-01
Nearly 40% of patients diagnosed with type 2 diabetes imperil their health by stopping their medication within the first year, UVA Health diabetes experts note in a new paper highlighting a growing array of treatment options.
The pragmatic new paper urges doctors to consider not just traditional diabetes medicines but emerging alternatives that patients may be more likely to stick with long-term. “Prescribing a medication or making lifestyle recommendations that a patient is not willing or able to follow for any reason is not likely to lead to improvements ...
Senolytics target Alzheimer’s-linked brain enzymes without harming healthy ones
2025-04-01
“This work provides new opportunities for the development of the next generation of ChE inhibitors that specifically target AChE and BChE associated with AD pathology.”
BUFFALO, NY — April 1, 2025 — A new research paper was published in Aging (Aging-US) on March 29, 2025, as the cover of Volume 17, Issue 3, titled “Differential senolytic inhibition of normal versus Aβ-associated cholinesterases: implications in aging and Alzheimer’s disease.”
In this study, a research team from Dalhousie University, led by Sultan Darvesh, discovered that certain anti-aging ...
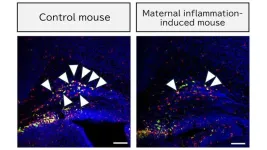
An immune cell may explain how maternal inflammation causes neurodevelopmental disorder
2025-04-01
A research group led by Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine in Japan has uncovered a potential mechanism linking maternal inflammation to delayed neurodevelopment in infants. The research suggests the role of CD11c-positive microglia—immune cells in the brain crucial for myelination—during infant brain development. The results, published in Communications Biology, suggest new strategies to mitigate the long-term neurodevelopmental effects of maternal inflammation.
Inflammation during pregnancy occurs when the mother’s immune system becomes activated during pregnancy, typically due to an infection, autoimmune response, or environmental factors. ...
New study refocuses research on mysterious falcon decline
2025-04-01
North America’s smallest falcon, the American Kestrel (Falco sparverius), has declined across the continent since the 1970s, yet the causes continue to stump raptor biologists. A new study published in the Journal of Raptor Research adds a piece to the puzzle with the discovery that in the Northeast, where declines are most alarming, fledglings demonstrate a relatively high survival rate. This paper, titled “Juvenile and Adult Survival Estimates of American Kestrels Throughout the Full Annual Cycle in Eastern North America,” is the first of its kind. No other study has assessed winter survival ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] Unintentional drug overdoses take a toll across the U.S. unequally, study findsNew research highlights intersectional racial and sex disparities