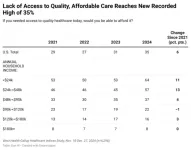
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, D.C. – April 2, 2025 – The inability to pay for healthcare in the U.S. has reached a new high, with more than one-third of Americans (35%), or an estimated 91 million people, reporting that they could not access quality healthcare if they needed it today, according to the latest West Health-Gallup Healthcare Affordability Index. The Index has been tracking healthcare affordability and access in the U.S. since 2021.
Rates were higher among Black and Hispanic Americans, with 46% and 52%, respectively, reporting that they would be unable to afford quality healthcare. Americans in higher-income households remained relatively stable in their ability to access affordable care, but the rate of unaffordability increased significantly among lower-income households. About two-thirds (64%) of people earning less than $24,000 and 57% of households with annual incomes between $24,000 and $48,000 reported difficulties with affordability, an 11- and 12-point increase from 2023, respectively.
“The rising trajectory in the inability to pay for healthcare is a disturbing trend that is likely to continue and even accelerate,” said Tim Lash, president of West Health Policy Center, part of a group of nonprofit organizations focused on healthcare and aging. “Policy action at both the state and federal level is urgently needed, or even more Americans will have to go without treatment or be forced to make painful tradeoffs between paying for medical care or paying for other necessities. The human and economic costs are enormous.”
The West Health-Gallup Healthcare Affordability Index categorizes Americans into one of three groups:
Cost Secure: faced no recent difficulty accessing or affording care or paying for prescription medicine
Cost Insecure: recently unable to access care or afford either care or prescription medicine
Cost Desperate: recently unable to access care and afford care and prescription medicine
Based on these criteria, just over half of Americans (51%) are considered Cost Secure, the lowest level since 2021. Hispanic adults saw the greatest declines in security over the four-year period, dropping 17 points to 34%, followed by Black adults, who dropped 13 points to 41%. Overall, about 29 million Americans, or 11% of U.S. adults, are classified as Cost Desperate, a record high.
The healthcare affordability gap has widened since 2021, particularly among Hispanic adults (up eight points to 18%), Black adults (up five points to 14%) and lower-income households earning under $24,000 per year (up 11 points to 25%), while there was little to no change in status among White adults or Americans in middle- to high-income households. The percentage of Americans age 65 and above who moved into the Cost Desperate category edged up just one point to 4%, while rising three points to 11% among those aged 50-64, and four points for people 50 and under (now 14%).
“Healthcare affordability and access continue to erode nationally, and this issue is especially acute among Black, Hispanic, and lower-income adults. White adults and those in higher-income households, in contrast, remain largely insulated from these worsening trends," said Dan Witters, senior researcher at Gallup. "Among these groups, this is the widest gap in access to care we have recorded thus far, with many Americans experiencing increased hardship year over year.”
Methodology
The West Health-Gallup Healthcare Indices Survey was conducted by web and mail Nov. 18-Dec. 27, 2024, with 6,296 adults aged 18 and older living in all 50 U.S. states and the District of Columbia as a part of the Gallup Panel™. For results based on the full sample, the margin of sampling error at the 95% confidence level is ±1.6 percentage points for response percentages around 50% and ±1.0 percentage points for response percentages around 10% or 90%, design effect included. Reported sub-groups will have a larger margin of error, typically ±3 to 5 percentage points.
About West Health
Solely funded by philanthropists Gary and Mary West, West Health is a family of nonprofit and nonpartisan organizations including the Gary and Mary West Foundation and Gary and Mary West Health Institute in San Diego, and the Gary and Mary West Health Policy Center in Washington, D.C. West Health is dedicated to lowering healthcare costs to enable seniors to successfully age in place with access to high-quality, affordable health and support services that preserve and protect their dignity, quality of life and independence. Learn more at westhealth.org and follow @westhealth.
About Gallup
Gallup delivers analytics and advice to help leaders and organizations solve their most pressing problems. Combining more than 80 years of experience with its global reach, Gallup knows more about the attitudes and behaviors of employees, customers, students and citizens than any other organization in the world.
END
Inability to pay for healthcare reaches record high in U.S.
Affordability gap widens for low-income households, Black and Hispanic Americans
2025-04-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Science ‘storytelling’ urgently needed amid climate and biodiversity crisis
2025-04-02
Scientists should experiment with creative ways of communicating their work to inspire action to protect the natural world, researchers say.
Scientists primarily publish their work in academic journals, where writing is expected to be technical, objective and dispassionate – making it unlikely to appeal to, or be easily understood by non-experts.
The researchers – from the University of Exeter – argue for science “translated into stories”, with benefits both for science and wider society.
They suggest ways that scientists can tell powerful, passionate stories without compromising the objectivity of science.
“As ...
KAIST Develops Retinal Therapy to Restore Lost Vision
2025-04-02
Vision is one of the most crucial human senses, yet over 300 million people worldwide are at risk of vision loss due to various retinal diseases. While recent advancements in retinal disease treatments have successfully slowed disease progression, no effective therapy has been developed to restore already lost vision—until now. KAIST researchers have successfully developed a novel drug to restore vision.
< Photo 1. (From left) Ph.D. candidate Museong Kim, Professor ...
Adipocyte-hepatocyte signaling mechanism uncovered in endoplasmic reticulum stress response
2025-04-02
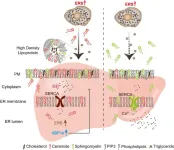
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the portion of the cell responsible for manufacturing and folding proteins. Proteins are essential for a wide range of cellular functions—as enzymes, transporters, hormones, antibodies, receptors, and more. They must be folded into the correct three-dimensional shape to function properly. If the ER is unable to manufacture or fold proteins correctly, the cell develops ER stress, which activates the unfolded protein response (UPR)—a protective mechanism aimed at restoring cellular function.
While UPR begins ...
Mammals were adapting from life in the trees to living on the ground before dinosaur-killing asteroid
2025-04-02
More mammals were living on the ground several million years before the mass extinction event that wiped out the dinosaurs, new research led by the University of Bristol has revealed.
The study, published today in the journal Palaeontology, provides fresh evidence that many mammals were already shifting toward a more ground-based lifestyle leading up to the asteroid’s impact.
By analysing small-fossilised bone fragments, specifically end of limb bones, from marsupial and placental mammals found in Western North America - the only place with a well-preserved terrestrial fossil record from this time – the team discovered signs that ...
Low LDL cholesterol levels linked to reduced risk of dementia
2025-04-01
People with low levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) in their blood have a lower risk of dementia, including lower risk of Alzheimer’s disease related dementia, shows a study published online today in the Journal of Neurology Neurosurgery & Psychiatry.
Use of statins conveyed an additional protective effect for people with low LDL-C, specifically those with blood levels less than 1.8 mmol/L (<70 mg/dL), reducing their risk of dementia even further.
However, reducing LDL-C ...
Thickening of the eye’s retina associated with greater risk and severity of postoperative delirium in older patients
2025-04-01
Thickening of the macular layer of the eye’s retina is associated with a greater risk of postoperative delirium for older patients undergoing surgery under general anaesthetic, reveals a study published online in the open access journal General Psychiatry.
Postoperative delirium is one of the most common complications for older patients after surgery and can have profound implications for long-term health and wellbeing.
Patients with postoperative delirium require longer hospital stays and are more likely to require support at home to help with daily tasks such as washing, dressing, and eating or be discharged ...
Almost one in ten people surveyed report having been harmed by the NHS in the last three years
2025-04-01
Almost one in ten people in Great Britain experienced healthcare-related harm due to care or treatment they received from the National Health Service (NHS) or difficulties accessing care in the last three years, show the findings of a large population survey published in the journal BMJ Quality & Safety.
In more than eight out of ten cases, the harm had a moderate or severe impact on the respondent. Disadvantaged groups, including people with disabilities, long term conditions and those in lower socioeconomic groups, were ...
Enhancing light control with complex frequency excitations
2025-04-01
NEW YORK, April 1, 2025 — Researchers at the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) and at Florida International University report in the journal Science their insights on the emerging field of complex frequencies excitations, a recently introduced scheme to control light, sound and other wave phenomena beyond conventional limits. Based on this approach, they outline opportunities that advance fundamental understanding of wave-matter interactions and usher wave-based technologies into a new era.
In conventional light wave- and sound wave- based systems such as wireless cell phone technologies, microscopes, speakers ...
New research finds novel drug target for acute myeloid leukemia, bringing hope for cancer patients
2025-04-01
A team of scientists from The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) has identified a promising new drug target for acute myeloid leukemia (AML), a deadly blood cancer with a five-year survival rate of just 30%, according to the National Cancer Institute. Their study, published in Cell Stem Cell in February, highlights the crucial role of a protein called paraspeckle component 1 (PSPC1) in the progression of AML.
An aggressive blood cancer, AML originates ...
New insight into factors associated with a common disease among dogs and humans
2025-04-01
The pathogens Giardia duodenalis and Cryptosporidium are common causes of sometimes-fatal intestinal diseases in humans, other mammals and birds worldwide.
Now, findings from researchers at Texas A&M University provide new, evidence-based insight into minimizing the risk of these diseases at canine facilities.
“In adult, healthy humans and animals, these diseases usually cause diarrhea and occasionally other minor ailments, but for infants, puppies and the immunocompromised, infection could be deadly,” said Loni Taylor, PhD, DVM, an epidemiologist with the Texas A&M University School of Public Health, who led ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
[Press-News.org] Inability to pay for healthcare reaches record high in U.S.Affordability gap widens for low-income households, Black and Hispanic Americans