(Press-News.org) Research Highlights:
New research suggests that participating in at least 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity in just two days had similar health benefits as distributing the activity throughout the week.
People who followed the “weekend warrior” approach, condensing physical activity into one or two days each week, had a significantly lower risk of death from all causes, cardiovascular disease and cancer, similar to those who engaged in activity throughout the week.
The study examined the physical activity of more than 93,000 participants in a large U.K. biomedical database who wore wrist accelerometers to track their physical activity.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Wednesday, April 2, 2025
DALLAS, April 2, 2025 — Being physically active for one to two days a week, often called a “weekend warrior,” may provide comparable health and life-prolonging benefits as smaller doses of daily physical activity if the physical effort is moderate to vigorous and totals 150 minutes a week in line with recommended guidelines for weekly physical activity, according to new research published today in the Journal of the American Heart Association, an open access, peer-reviewed journal of the American Heart Association.
“You don’t need to exercise every day to stay healthy. As long as you get 150 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity per week — whether packed into one to two days or spread out — you can significantly reduce your risk of dying from cardiovascular disease, cancer or other causes,” said study corresponding author Zhi-Hao Li, Ph.D., an epidemiologist in the School of Public Health at Southern Medical University in Guangzhou, China.
“This message is encouraging news for busy people who struggle to fit in daily workouts but can manage a concentrated burst of activity on weekends or over a couple of days,” Li said. “The research provides reassuring evidence that even sporadic physical activity can have lasting health benefits, making it easier for people to prioritize their well-being amid busy schedules.”
To achieve health benefits, both the World Health Organization and the American Heart Association recommend that throughout a week adults engage in 150 to 300 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity, or 75 to 150 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity, or an equivalent combination of moderate and vigorous-intensity activity.
Researchers examined health and physical activity data for more than 93,000 people in a large biomedical database in the U.K. to explore how different physical activity patterns may affect the risk of dying from all causes, specifically cardiovascular disease and cancer. They reviewed physical activity data collected from wrist accelerometers, devices that measure movement and are likely more accurate than asking participants about their activity.
The study categorized the data into three groups: “active weekend warrior” — people who completed most of their exercise in one or two days; “active regular” — those who spread their activity throughout the week; and “inactive” — participants who did not complete the recommended minimum of 150 minutes of weekly physical activity.
Compared to the inactive group, the weekend warrior and active regular groups had a significantly lower risk of death from all causes, cardiovascular disease and cancer if they completed 150 minutes of physical activity a week.
The analysis also found:
For weekend warriors, the risk of death from all causes was 32% lower; the risk of death from cardiovascular disease was 31% lower; and the risk of death from cancer was 21% lower.
Among participants in the active regular group, the risk of death from all causes was 26% lower; the risk of death from cardiovascular disease was 24% lower; and the risk of death from cancer was 13% lower.
No significant differences in the risk of death surfaced between the weekend warrior vs. the active regular group.
While the new research aligns with previous studies, it is the first to analyze the relationship between physical activity patterns measured by accelerometers and the risk of death from cardiovascular disease and cancer.
Some of the findings surprised the research team, who initially expected that spreading activity throughout the week would be more beneficial. They did not anticipate that weekend warriors’ condensed physical activity would reduce the risk of death from disease.
“This reinforces the idea that meeting the 150-minutes of physical activity per week guideline is key to longevity, regardless of the activity pattern,” Li said. “Any activity — whether structured exercise such as jogging or daily tasks such as gardening — can be included if the intensity is moderate to vigorous.”
American Heart Association expert volunteer Keith Diaz, Ph.D., said the findings emphasize that the total volume of physical activity is the crucial factor for health benefits, rather than how it is distributed across a week. Diaz, the Florence Irving Associate Professor of Behavioral Medicine at Columbia University Medical Center in New York, was not involved in this research.
“Many people struggle to fit in daily exercise during the workweek; however, this research shows that even if you can only be active on the weekends, you can still gain meaningful health benefits,” said Diaz, a member of the Association’s Physical Activity Science Committee.
“One important caveat to remember is that trying to fit 150 minutes of exercise into just one or two days can be a lot on your body,” he added. “Some research suggests that weekend warriors have a slightly higher risk of musculoskeletal injuries compared to those who exercise more regularly. However, the benefits of exercising just on the weekend far outweigh the potential risks. If you are going to be a weekend warrior, make sure you do proper warm-ups and build up and progress to higher volumes of activity over time. This will help to reduce your risk of injuries.”
The study had several limitations, including that physical activity was only measured at baseline; participants lived in the U.K. and most were white, so the results may not apply to other populations. The researchers said future studies should be conducted to confirm these results in more diverse groups of people throughout the world and with more consideration for contradictory factors such as genetic predisposition or environmental exposures that may influence physical activity and the outcomes.
Study details, background and design:
The research data focused on seven days of accelerometer-measured physical activity from 2013 to 2015 for 93,409 participants, aged 37 to 73, enrolled in the UK Biobank.
More than 56% of the participants were women, 97% were white and their average age was 62 years old.
Based on accelerometer data, more than 42% of participants were classified as weekend warrior, about 24% as active regular and nearly 34% as inactive.
The accelerometers captured a range of activities, including walking, jogging, stationary cycling, elliptical exercises, household chores, gardening and leisure activities such as dancing.
During eight years of follow-up, nearly 4,000 adults died from all causes, including about 17% from cardiovascular disease and about 45% from cancer.
Compared to the inactive participants, those who exercised during two days each week were more likely to be men, younger, have a college degree, non-smokers, non-drinkers, less likely to have Type 2 diabetes and/or to have lower body mass index (an indicator of body fat to determine healthy weight).
Co-authors, disclosures and funding sources are listed in the manuscript.
Studies published in the American Heart Association’s scientific journals are peer-reviewed. The statements and conclusions in each manuscript are solely those of the study authors and do not necessarily reflect the Association’s policy or position. The Association makes no representation or guarantee as to their accuracy or reliability. The Association receives more than 85% of its revenue from sources other than corporations. These sources include contributions from individuals, foundations and estates, as well as investment earnings and revenue from the sale of our educational materials. Corporations (including pharmaceutical, device manufacturers and other companies) also make donations to the Association. The Association has strict policies to prevent any donations from influencing its science content. Overall financial information is available here.
Additional Resources:
Multimedia is available on the right column of release link
After April 2, 2025, view the manuscript online.
AHA news release: Short, intense bursts of exercise more effective after stroke than steady, moderate exercise (Aug. 2024)
AHA health information: How much physical activity do you need? (Infographic)
AHA health information: Breaking Down Barriers to Fitness
AHA health information: Walking
AHA health initiative: April 2 is National Walking Day.
Follow AHA/ASA news on X @HeartNews
Follow news from the Journal of the American Heart Association @JAHA_AHA
###
About the American Heart Association
The American Heart Association is a relentless force for a world of longer, healthier lives. Dedicated to ensuring equitable health in all communities, the organization has been a leading source of health information for more than one hundred years. Supported by more than 35 million volunteers globally, we fund groundbreaking research, advocate for the public’s health, and provide critical resources to save and improve lives affected by cardiovascular disease and stroke. By driving breakthroughs and implementing proven solutions in science, policy, and care, we work tirelessly to advance health and transform lives every day. Connect with us on heart.org, Facebook, X or by calling 1-800-AHA-USA1.
END
Being physically active, even just a couple of days a week, may be key to better health
2025-04-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
High-fat diet promote breast cancer metastasis in animal models
2025-04-02
CNIO researchers discover that, in mice that eat a lot of fat, cancer cells travelling through the blood surround themselves with platelets, which act as an armor-like protection as they spread.
In addition, in animals with a fatty diet it is easier for tumor cells to 'nest' in other organs and give rise to metastasis of the primary tumor.
“These results anticipate a future in which dietary changes, together with the control of platelet activity, will complement antitumor treatments,” says Héctor Peinado, of the Spanish National Cancer Research Center (CNIO).
The study is published ...
A router for photons
2025-04-02
Applied physicists at the Harvard John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences (SEAS) have created a photon router that could plug into quantum networks to create robust optical interfaces for noise-sensitive microwave quantum computers.
The breakthrough is a crucial step toward someday realizing modular, distributed quantum computing networks that leverage existing telecommunications infrastructure. Comprising millions of miles of optical fiber, today’s fiber-optic networks send information between computing clusters as pulses ...
Nurses and AI collaborate to save lives, reduce hospital stays
2025-04-02
NEW YORK, NY (April 2, 2025)--
April 2, 2025—An AI tool that analyzes nurses’ data and notes detected when patients in the hospital were deteriorating nearly two days earlier than traditional methods and reduced the risk of death by over 35%, found a year-long clinical trial of more than 60,000 patients led by researchers at Columbia University.
The new AI tool, CONCERN Early Warning System, uses machine learning to analyze nursing documentation patterns to predict when a hospitalized patient is deteriorating before the change is reflected in vital signs, allowing for timely, life-saving ...
Multi-resistance in bacteria predicted by AI model
2025-04-02
An AI model trained on large amounts of genetic data can predict whether bacteria will become antibiotic-resistant. The new study shows that antibiotic resistance is more easily transmitted between genetically similar bacteria and mainly occurs in wastewater treatment plants and inside the human body.
"By understanding how resistance in bacteria arises, we can better combat its spread. This is crucial to protect public health and the healthcare system's ability to treat infections," says Erik Kristiansson, Professor at the Department of Mathematical Sciences at Chalmers University of Technology and the University of Gothenburg in Sweden.
Antibiotic ...
Tinker Tots: A citizen science project to explore ethical dilemmas in embryo selection
2025-04-02
EMBARGOED UNTIL 09:00 BST WEDNESDAY 2 APRIL
Tinker Tots: A Citizen Science Project to Explore Ethical Dilemmas in Embryo Selection
Researchers at the University of Oxford, University of Exeter, and the National University of Singapore Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine present a new, interactive study.
Oxford, 2 April 2025: When choosing an embryo for implantation during in vitro fertilization (IVF), would you consider its chances of developing a health condition? What about traits like creativity, intelligence, ...
Sensing sickness
2025-04-02
Beekeepers in the United States lost more than 55 percent of managed colonies last year—the highest loss rate since the Apiary Inspectors of America began determining them in 2011. A new study from University of Vermont scientists and international collaborators supports a novel method for testing hygienic behavior in honey bees that could promote breeding more disease resistant colonies in the future.
“Beekeepers are losing bees at a rate that they say is unsustainable,” says Samantha Alger, director of the Vermont Bee Lab at the UVM and lead author of the study. “In the ‘80s, beekeepers lost colonies ...
Cost to build multifamily housing in California more than twice as high as in Texas
2025-04-02
Building multifamily housing in California is more than twice as expensive as it is in Texas, with much of the difference driven by state and local policies that contribute to long permitting and construction timelines, and higher local development fees, according to a new RAND report based on cost information from more than 100 completed apartment projects.
The high cost of housing and its associated effect on homelessness is a defining policy issue in California.
The cost of building multifamily housing is 2.3 times higher in California than Texas and 1.5 times higher than in Colorado, ...
Program takes aim at drinking, unsafe sex, and sexual assault on college campuses
2025-04-02
PISCATAWAY, NJ – A prevention program that teaches college students about the links between risky drinking and sexual assault—and how to protect themselves and their friends—has shown early promise, according to a new report in the Journal of Studies on Alcohol and Drugs.
It’s well known that alcohol and sex can sometimes be a dangerous mix for young adults. Alcohol intoxication raises the odds of having unprotected sex and, possibly, contracting a sexually transmitted disease or having an unplanned pregnancy. Drinking can also increase the risk of falling victim to sexual assault or becoming the perpetrator.
Yet college prevention programs have traditionally ...
Inability to pay for healthcare reaches record high in U.S.
2025-04-02
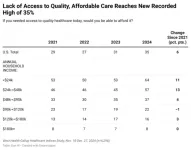
WASHINGTON, D.C. – April 2, 2025 – The inability to pay for healthcare in the U.S. has reached a new high, with more than one-third of Americans (35%), or an estimated 91 million people, reporting that they could not access quality healthcare if they needed it today, according to the latest West Health-Gallup Healthcare Affordability Index. The Index has been tracking healthcare affordability and access in the U.S. since 2021.
Rates were higher among Black and Hispanic Americans, with 46% and 52%, respectively, reporting ...
Science ‘storytelling’ urgently needed amid climate and biodiversity crisis
2025-04-02
Scientists should experiment with creative ways of communicating their work to inspire action to protect the natural world, researchers say.
Scientists primarily publish their work in academic journals, where writing is expected to be technical, objective and dispassionate – making it unlikely to appeal to, or be easily understood by non-experts.
The researchers – from the University of Exeter – argue for science “translated into stories”, with benefits both for science and wider society.
They suggest ways that scientists can tell powerful, passionate stories without compromising the objectivity of science.
“As ...