(Press-News.org) A review published in The Laryngoscope indicates that climate change’s effects on pollen seasons and concentrations are contributing to increasing rates of allergic rhinitis, or hay fever.
When investigators assessed research published between 2000 and 2023, they identified 30 studies that reported on the current epidemiological state of allergic rhinitis, described factors related to climate change, and observed how global warming is affecting pollen seasons and allergy symptoms.
Sixteen studies reported longer pollen seasons and/or higher pollen concentrations related to climate change. As an example, total pollen emissions in the U.S. are projected to increase by 16–40% by the end of the century and pollen season length to increase by 19 days. Four studies reported an increase in allergic rhinitis–related health care usage, particularly among low-income residents. Two studies reported that health care professionals want more education on climate change.
“Physicians are uniquely positioned to witness the impact of allergic rhinitis on patient outcomes and can adapt their practice as climate change intensifies,” said corresponding author Alisha R. Pershad, BS, a third-year medical student at the George Washington University School of Medicine and Health Sciences. “As trusted voices in the community, they should leverage their frontline experience to advocate for meaningful change in addressing the climate crisis.”
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/lary.32124
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
The Laryngoscope has been the leading source of information on advances in the diagnosis and treatment of head and neck disorders since 1896. The Laryngoscope is the first choice among otolaryngologists for publication of their important findings and techniques.
About Wiley
Wiley is one of the world’s largest publishers and a trusted leader in research and learning. Our industry-leading content, services, platforms, and knowledge networks are tailored to meet the evolving needs of our customers and partners, including researchers, students, instructors, professionals, institutions, and corporations. We empower knowledge-seekers to transform today’s biggest obstacles into tomorrow’s brightest opportunities. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
How is climate change affecting seasonal allergies?
2025-04-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Does universal preschool lead to better academic outcomes?
2025-04-09
Several states, including Georgia, offer state-funded pre-kindergarten programs to students regardless of their family’s income. New research in Economic Inquiry investigates whether such programs offer long-lasting academic benefits to all students.
Using enrollment lottery data from a large school district in metro Atlanta, investigators found that lottery-winning enrollees of school-based pre-kindergarten entered kindergarten more prepared in both math and reading than non-winning peers. Gains tended to fade by the end of kindergarten, however, and some negative achievement effects ...
Could fish swim bladders be useful in a treatment for heart failure?
2025-04-09
Hydrogels, which are soft materials formed by crosslinking polymers, could have a variety of medical applications. In research published in Advanced Science, investigators developed an injectable hydrogel containing components of fish swim bladders and used it to repair damaged heart tissue.
The fish swim bladder is an organ that aids fish in floating in water and is composed of collagen, glycosaminoglycans, and elastin, closely resembling parts of the human heart.
Experiments revealed that the researchers’ fish swim bladder–based hydrogel enhances cardiac cell adhesion and stretching while promoting new ...
Does cancer treatment affect connections in the brain?
2025-04-09
New research published in the Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging has uncovered changes in brain connectivity during chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer.
In the study of 55 patients with breast cancer and 38 controls without cancer, investigators conducted functional magnetic resonance imaging scans of participants’ brains over several months.
Scans from patients revealed changes in brain connectivity, particularly in the frontal-limbic system (involved in executive functions) and the cerebellar cortex (linked to memory) throughout the course of treatment. These changes got worse and spread more as chemotherapy continued.
“The ...
Unsafe driving during school drop offs at ‘unacceptable’ levels
2025-04-09
Risky driving by parents and other motorists who do the school run is putting children in danger, according to a study published in the peer-reviewed journal Traffic Injury Prevention.
Double parking, not obeying traffic controls and other unsafe behavior occurs at the majority (98%) of elementary schools during morning drop-off times.
The authors analyzed data from more than 500 schools in Canada and say hazardous driving is an “urgent and serious” issue. The most observed misdemeanour was to drop a student ...
RAND survey reveals varied curriculum use and time constraints among public school pre-k teachers
2025-04-09
According to a new RAND survey, over 80% of public school-based pre-kindergarten (pre-K) teachers use multiple curriculum materials. Some combine materials that focus on a particular domain – such as literacy or numeracy – while others use material that covers many domains at once, and some use both. More than two-thirds reported using materials that they created themselves, often in conjunction with commercial curricula.
Most public school-based pre-K educators surveyed believe their instructional materials are high quality, especially ...
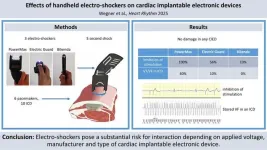
Study finds handheld electro-shockers can pose risk for individuals with cardiac implants
2025-04-09
Philadelphia, April 9, 2025 – Research has found that handheld electro-shockers commonly used for self defense can potentially interact with cardiac implantable electronic devices (CIEDs) such as pacemakers, putting individuals at risk. The study in Heart Rhythm, the official journal of the Heart Rhythm Society, the Cardiac Electrophysiology Society, and the Pediatric & Congenital Electrophysiology Society, published by Elsevier, shows that the individual interactive risk is primarily based on the applied voltage, but also on the manufacturer and type of implanted CIED.
The use of TASER pistols by security forces has been controversial ...
Holograms that can be grabbed and manipulated
2025-04-09
Doctor Elodie Bouzbib, from Public University of Navarra (UPNA), together with Iosune Sarasate, Unai Fernández, Manuel López-Amo, Iván Fernández, Iñigo Ezcurdia and Asier Marzo (the latter two, members of the Institute of Smart Cities) have succeeded, for the first time, in displaying three-dimensional graphics in mid-air that can be manipulated with the hands.
'What we see in films and call holograms are typically volumetric displays,' says Bouzbib, the first ...
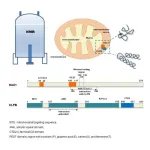
Novel structural insights reveal the mechanism of mitochondrial protein HAX1 interaction with CLPB
2025-04-09
A recent study published in Magnetic Resonance Letters has revealed for the first time the interaction mechanism between the mitochondrial proteins HAX1 and CLPB, filling the research gap between these two key proteins in the field of structural dynamics and functional association. By integrating multiple biophysical techniques, the research team based in Hefei, China, revealed the high-affinity binding properties between the two and their structural basis, which provides new research perspectives for understanding diseases related to abnormal mitochondrial function.
HAX1 and CLPB: from structural differences to functional synergy
HAX1 ...
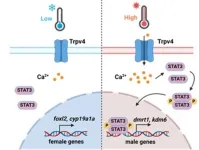
Warm temperature promotes sex change in ricefield eel, a protogynous hermaphrodite freshwater fish
2025-04-09
The ricefield eel (Monopterus albus) is the only protogynous hermaphrodite freshwater fish. While the mechanism underlying the natural sex change in this species has been fascinating scientists for a long time, it remains elusive and mysterious.
In a new study published in Water Biology and Security, a team of researchers in China reported a temperature-induced sex reversal mechanism in ricefield eel.
“We show that warm temperature induces the expression of male sex determination genes in ovarian tissues, ...
3D-printed open-source robot offers accessible solution for materials synthesis
2025-04-09
FLUID, an open-source, 3D-printed robot, offers an affordable and customizable solution for automated material synthesis, making advanced research accessible to more scientists.
A team of researchers led by Professor Keisuke Takahashi at the Faculty of Science, Hokkaido University, have created FLUID (Flowing Liquid Utilizing Interactive Device), an open-source robotic system constructed using a 3D printer and off-the-shelf electronic components.
To demonstrate FLUID’s capabilities, the team used the robot to automate the co-precipitation of cobalt and nickel, creating ...