Enhancing power distribution systems with renewable energy: a new configuration approach
2025-04-09
(Press-News.org)
A groundbreaking study presents a comprehensive approach to restructuring medium-level voltage (MLV) distribution systems that enhances reliability while reducing both energy losses and carbon emissions.
The study introduces an innovative "N+1 bus configuration" for radial distribution systems (RDS) - a simple yet powerful modification to conventional power networks that adds just one additional tie line to existing systems. This seemingly minor change delivers remarkable improvements in system performance when combined with distributed renewable energy resources (DER).
The research team conducted extensive testing on both real-time radial distribution systems and standard IEEE test systems, evaluating multiple performance metrics:
- Voltage stability: The N+1 configuration demonstrated superior voltage performance across all buses
- Line carrying capacity: All lines operated comfortably below 75% of capacity
- System losses: Total power losses were reduced to just 0.379% of total power flow
- Contingency ranking: The new configuration showed significantly improved resilience during line outage scenarios
A key contribution of this research is its thorough contingency ranking analysis, which evaluates how well the system performs when individual components fail - a critical consideration for institutional power systems where reliability is paramount. "The impact of line outages is dramatically reduced in the N+1 bus system," the researchers explain. "For example, when the line connecting buses 2 and 3 fails, the severity ranking improves from 3 to 9 for voltage performance and from 2 to 3 for flow performance compared to conventional systems."
Beyond the technical improvements, the study quantifies significant environmental benefits from the proposed configuration:
- Carbon reduction: The N+1 configuration reduces CO2 emissions by approximately 14.62 metric tons compared to 9.014 metric tons in conventional systems
- Resource optimization: The approach enables more efficient sizing and utilization of renewable energy sources
To ensure the reliability of their findings, the researchers employed multiple analytical approaches, including MiPower tool modeling, Grey Wolf Optimization (GWO) algorithm, and IEEE standard test systems. The results consistently showed that the N+1 configuration outperformed conventional approaches across all metrics and testing methodologies.
The researchers suggest that their approach could be extended to commercial buildings and other types of distribution systems. Future studies could examine:
- Performance in commercial distribution systems with multiple renewable feed points
- Additional optimization of renewable resource placement and sizing
- Integration with smart grid technologies for dynamic reconfiguration
- Economic analysis of implementation costs versus operational savings
This research represents a significant step forward in making institutional power systems more reliable, efficient, and environmentally sustainable through thoughtful integration of renewable energy sources and strategic network reconfiguration.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-04-09
For millions of deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals around the world, communication barriers can make everyday interactions challenging. Traditional solutions, like sign language interpreters, are often scarce, expensive and dependent on human availability. In an increasingly digital world, the demand for smart, assistive technologies that offer real-time, accurate and accessible communication solutions is growing, aiming to bridge this critical gap.
American Sign Language (ASL) is one of the most widely used sign languages, consisting of distinct hand gestures that represent letters, ...
2025-04-09
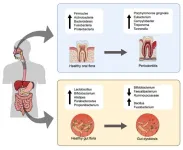
There is growing recognition in medicine that what happens in one part of the body can ripple through others. That idea is now being explored in a surprising place: the mouth. A new review by an international group of researchers has examined the mounting evidence linking periodontal disease—commonly known as gum disease—to chronic liver conditions, including cirrhosis, metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD), and alcohol-related liver disease. Though the mouth and liver are separated ...
2025-04-09
The Korea Institute of Energy Research (President Yi Chang-keun, hereinafter referred to as “KIER”) has successfully developed ultra-lightweight flexible perovskite/CIGS tandem solar cells and achieved a power conversion efficiency of 23.64%, which is the world’s highest efficiency of the flexible perovskite/CIGS tandem solar cells reported to date. The solar cells developed by the research team are extremely lightweight and can be attached to curved surfaces, making it a promising candidate for future applications in buildings, vehicles, aircraft, and more.
Crystalline silicon-based single-junction solar cells ...
2025-04-09
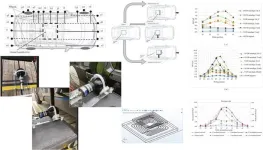
A comprehensive study has examined the magnetic field emissions (MFE) from vehicle-mounted wireless power transfer (WPT) systems, providing critical insights for ensuring user safety during electric vehicle charging. As wireless charging technology gains popularity for fleet vehicles and accessibility applications, understanding and controlling electromagnetic field exposure becomes increasingly important.
Researchers conducted extensive physical measurements around a vehicle equipped with an in-house designed WPT system, examining how various factors affect magnetic field emissions where users might be positioned during charging operations. The study specifically investigated:
- ...
2025-04-09
Cancer diagnoses traditionally require invasive or labor-intensive procedures such as tissue biopsies. Now, research published in ACS Central Science reveals a method that uses pulsed infrared light to identify molecular profiles in blood plasma that could indicate the presence of certain common cancers. In this proof-of-concept study, blood plasma from more than 2,000 people was analyzed to link molecular patterns to lung cancer, extrapolating a potential “cancer fingerprint.”
Plasma is the liquid portion of blood, depleted of any ...
2025-04-09
Wear and tear on plastic products releases small to nearly invisible plastic particles, which could impact people’s health when consumed or inhaled. To make these particles biodegradable, researchers created plastics from plant starch instead of petroleum. An initial study published in ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry shows how animals consuming particles from this alternative material developed health problems such as liver damage and gut microbiome imbalances.
“Biodegradable starch-based plastics may not be as safe and health-promoting as originally assumed,” ...
2025-04-09
Iron and its alloys, such as steel and cast iron, dominate the modern world, and there’s growing demand for iron-derived products. Traditionally, blast furnaces transform iron ore into purified elemental metal, but the process requires a lot of energy and emits air pollution. Now, researchers in ACS Energy Letters report that they’ve developed a cleaner method to extract iron from a synthetic iron ore using electrochemistry, which they say could become cost-competitive with blast furnaces.
"Identifying oxides which can be converted to iron metal at low temperatures is an important ...
2025-04-09
University of Oregon chemists are bringing a greener way to make iron metal for steel production closer to reality, a step towards cleaning up an industry that’s one of the biggest contributors to carbon emissions worldwide.
Last year UO chemist Paul Kempler and his team reported a way to create iron with electrochemistry, using a series of chemical reactions that turn saltwater and iron oxide into pure iron metal.
In their latest work, they’ve optimized the starting materials for the process, identifying which kinds of iron oxides will make the chemical reactions the most cost-effective. That’s a key ...
2025-04-09
Plastics are everywhere—from packaging and textiles to electronics and medical devices. As plastic waste breaks down, it releases microscopic particles that can penetrate our ecosystems, hinder plant growth, and potentially transfer harmful pollutants to organisms, including humans. Therefore, these plastic particles are a potential threat to the ecosystem, especially in their nanoparticulate form (1–100 nm diameter), which can penetrate the environment through different routes, including the soil beneath our feet.
With this in mind, a team of researchers from Japan set out to study the migration behavior of nanoplastics ...
2025-04-09
Coupling reactions are among the most transformative tools in organic chemistry, enabling the formation of crucial chemical bonds in pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and advanced materials. Since their introduction, they have been one of the backbones of modern organic synthesis. However, these methods have long relied on environmentally taxing transition metal catalysts, such as palladium, which are often scarce, costly, and generate unwanted byproducts.
The limitations of conventional coupling methods have prompted researchers to seek alternative strategies that better align with the principles of green and sustainable chemistry ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Enhancing power distribution systems with renewable energy: a new configuration approach