(Press-News.org) Local climate can be used to predict the venom characteristics of a deadly snake that is widespread in India, helping clinicians to provide targeted therapies for snake bite victims, according to a study publishing April 10 in the open-access journal PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases by Kartik Sunagar and colleagues at the Indian Institute of Science.
Russell’s viper (Daboia russelii) is found across the Indian subcontinent and is responsible for over 40% of snake bite-related deaths in India each year. Its venom is extremely variable, and snake bites cause different symptoms in different regions of India. The toxic effects of snake venom are caused by the concentrations of different enzymes, which can be influenced by many factors, including prey availability and climate. However, the factors driving variation in Russell’s viper venom are unknown.
To investigate, researchers analyzed venom samples from 115 snakes collected in 34 locations across India. They tested the activity of venom toxins, including enzymes that break down proteins, phospholipids and amino acids. Next, they used historical climate data to understand the relationship between venom composition and the local climate where the snakes were caught. They found that temperature and rainfall partly explained regional variation in snake venom composition. Protease activity showed the closest relationship to climate variables, whereas the activity of animo acid oxidases was unaffected by climate. Snakes in drier regions of India tended to have higher protease activity. The researchers used this data to create a map of expected venom types across Russell’s viper’s range in India, which could be used to predict the clinical symptoms of snake bites in different regions.
The venom maps developed in this study could help clinicians select the most appropriate treatment for patients with snake bites, or to develop targeted therapies such as toxin-specific antibodies, the authors say.
Author Kartik Sunagar adds: “Russell's viper is arguably the clinically most important snake species in the world. It kills and maims more people than any other snake species. As a result, it is important to precisely unravel the composition, activity, and potency of Russell's viper venoms and understand the role of biotic and abiotic factors in shaping them. Recent studies from our lab have shed light on the influence of biotic factors, such as developmental shifts in diet, on Russell's viper venom composition and toxicity. However, the effects of abiotic or environmental factors remained unstudied. Here, we highlight, for the first time, the role of climatic conditions, such as temperature, humidity and rainfall, in driving the biochemical functions of Russell's viper venoms.”
####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases: https://plos.io/4jnlC5q
Citation: Sarangi N, Laxme RRS, Sunagar K (2025) Significant Serpents: Predictive Modelling of Bioclimatic Venom Variation in Russell’s Viper. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 19(4): e0012949. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pntd.0012949
Author Countries: India
Funding: KS was supported by the Wellcome Trust DBT India Alliance Fellowship (IA/I/19/2/504647). RRSL was supported by the Prime Minister’s Research Fellowship (PMRF) from the Ministry of Human Resource Development (MHRD). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Venom characteristics of a deadly snake can be predicted from local climate
In dryer regions of India, the venom of Russell’s vipers contains more protein-degrading enzymes
2025-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Brain pathway links inflammation to loss of motivation, energy in advanced cancer
2025-04-10
The fatigue and lack of motivation that many cancer patients experience near the end of life have been seen as the unavoidable consequences of their declining physical health and extreme weight loss. But new research from Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis challenges that long-held assumption, showing instead that these behavioral changes stem from specific inflammation-sensing neurons in the brain.
In a study published April 11 in Science, the researchers report that they identified a direct connection between cancer-related inflammation ...
Researchers discover large dormant virus can be reactivated in model green alga
2025-04-10
Researchers had been studying the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii for decades without seeing evidence of an active virus within it — until a pair of Virginia Tech researchers waded into the conversation.
Maria Paula Erazo-Garcia and Frank Aylward not only found a virus in the alga but discovered the largest one ever recorded with a latent infection cycle, meaning it goes dormant in the host before being reactivated to cause disease.
“We’ve known about latent infections for a long time,” said Aylward, associate professor in the Department of Biological Sciences. ...
New phase of the immune response uncovered
2025-04-10
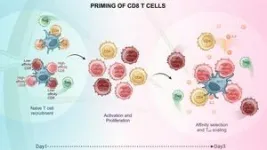
The research groups led by Wolfgang Kastenmüller and Georg Gasteiger employed innovative microscopy techniques to observe how specific immune cells, known as T-cells, are activated and proliferate during a viral infection. Their findings revealed novel mechanisms: the immune system amplifies its defense cells in a far more targeted way than previously believed.
T-Cells Proliferate and Specialize During the Immune Response
T-cells are crucial defense cells in the immune system. To effectively ...
Drawing board rather than salt shaker
2025-04-10
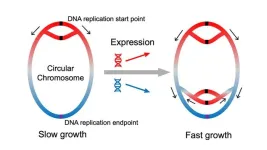
Bioinformaticians from Heinrich Heine University Düsseldorf (HHU) and the university in Linköping (Sweden) have established that the genes in bacterial genomes are arranged in a meaningful order. In the renowned scientific journal Science, they describe that the genes are arranged by function: If they become increasingly important at faster growth, they are located near the origin of DNA replication. Accordingly, their position influences how their activity changes with the growth rate.
Are genes distributed randomly along the bacterial chromosome, as if scattered from a salt shaker? This opinion, which is held by a majority of researchers, has ...
Engineering invites submissions on AI for engineering
2025-04-10
Artificial intelligence (AI) is playing an increasingly pivotal role in revolutionizing the field of engineering, triggering a new era of technological and industrial evolution. A series of recent breakthroughs in areas like natural language processing, computer vision, and machine learning, with the Nobel Prize-winning work in artificial neural networks and protein structure prediction serving as prime examples, have effectively bridged the gap between the physical and digital worlds. The emergence of general AI technologies, especially large language models, has given rise ...
In Croatia’s freshwater lakes, selfish bacteria hoard nutrients
2025-04-10
Bacteria play key roles in degrading organic matter, both in the soil and in aquatic ecosystems. While most bacteria digest large molecules externally, allowing other community members to share and scavenge, some bacteria selfishly take up entire molecules before digesting them internally. In a paper publishing April 10 in the Cell Press journal Cell Reports, researchers document “selfish polysaccharide uptake” in freshwater ecosystems for the first time. In Croatia’s Kozjak and Crniševo Lakes, they found that nutrient hoarding allows selfish species ...
Research suggests our closest neighboring galaxy may be being torn apart
2025-04-10
A team led by Satoya Nakano and Kengo Tachihara at Nagoya University in Japan has revealed new insights into the motion of massive stars in the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC), a small galaxy neighboring the Milky Way. Their findings suggest that the gravitational pull of the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), the SMC’s larger companion, may be tearing the smaller one apart. This discovery reveals a new pattern in the motion of these stars that could transform our understanding of galaxy evolution and interactions. The results were published ...
Researchers identify factors in early-life linked to body fat in South Asian children
2025-04-10
Researchers at McMaster University have identified six key factors in the first three years of life that influence the trajectory of obesity in South Asian children.
The findings offer parents, primary care practitioners and policymakers new insights into addressing childhood obesity for a group of children who have a higher prevalence of abdominal fat and cardiometabolic risk factors, as well as a predisposition to diabetes.
“We know that current measures of childhood obesity such as the body mass index (BMI) don’t work well for South Asians because of the so called ‘thin-fat’ phenotype: South Asian newborns are characterized as low birth weight, but proportionally ...
Environment: Less than 10% of global plastics manufactured from recycled materials
2025-04-10
Only 9.5% of plastic materials produced globally in 2022 were manufactured from recycled materials. The findings, reported in Communications Earth & Environment, are part of a comprehensive analysis of the global plastics sector, which also reveals a large increase in the amount of plastic being disposed of by incineration and substantial regional differences in plastic consumption.
Plastic production has increased from two million tonnes per year in 1950 to 400 million tonnes per year in 2022 and ...
Influenza vaccination among people with Medicare by race and ethnicity, education, and rurality
2025-04-10
About The Study: In this cross-sectional survey study, although overall influenza vaccination rates changed little from 2019 to 2022, they increased substantially for Black and Hispanic older adults, particularly those in rural areas, and decreased for some groups of white older adults. Determining the reasons for these divergent changes in influenza vaccination rates is a high priority for future research.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Marc N. Elliott, PhD, email elliott@rand.org.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2025.4462)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Venom characteristics of a deadly snake can be predicted from local climateIn dryer regions of India, the venom of Russell’s vipers contains more protein-degrading enzymes