(Press-News.org)
Ikoma, Japan—People seeking to feel fully immersed in virtual environments will soon be able to experience a revolutionary approach to spatial computing that bridges the gap between real and digital worlds. A collaborative research team from NTT DOCOMO, Inc. and Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST), Japan, has developed a novel mixed reality (MR) technology that transforms how users interact with virtual spaces by using everyday real-world doors as natural transition points.
Virtual reality (VR) and MR technologies have long faced a critical challenge—creating a truly immersive experience that feels natural and intuitive. Existing spatial computing applications in VR and MR typically use artificial barriers or abrupt transitions between real and virtual spaces, breaking user immersion and creating a disjointed experience.
To this end, the research team, led by Dr. Daiki Hagimori from NTT DOCOMO, Inc., and Professor Kiyoshi Kiyokawa from NAIST, developed a solution to address this problem. The team includes Hideaki Uchiyama, Monica Perusquía-Hernández, and Yutaro Hirao from NAIST. Through a sophisticated software system compatible with Apple Vision Pro and similar head-mounted displays, the team managed to create seamless transitions between physical and virtual rooms.
Highlighting the unique feature of their technology, Prof. Kiyokawa explains, “To date, no system enables users to physically operate real doors—including all associated sensory feedback—as entry points to virtual spaces.”
The new technology allows users to select a real-world door within their MR interface by simply marking two of its corners. Once identified, the door becomes a smart portal between physical and virtual environments. As the user opens the door, the system dynamically renders a virtual space beyond the door, creating an unprecedented sense of natural transition by leveraging existing physical architecture.
The developed system uses advanced hand movement recognition that does not require users to focus specifically on the door handle, making the interaction intuitive and seamless. Moreover, after the user enters the virtual space, the open door seen from inside still looks like a dynamic window back to the real world. “By incorporating academic expertise from NAIST into the technology that was under development by NTT DOCOMO, a refined system was created,” shared Dr. Hagimori.
This technology offers transformative potential across multiple industries. While in the tourism industry, users could virtually step through a door into destinations around the world, applications in real estate would allow potential buyers to take immersive property tours. Entertainment and art industries could create new forms of interactive storytelling where physical spaces become gateways to rich virtual worlds.
As Prof. Kiyokawa puts it, “Our goal is to develop what we call ‘Personalized Reality’—systems capable of creating dynamic experiences tailored to each individual.” They plan to showcase this novel MR technology at Keihanna Expo in Yumeshima, part of Expo 2025 in Osaka, Kansai, Japan, on Wednesday, 23 April, and Friday, 19 September 2025, offering visitors a firsthand experience of this innovative approach to spatial computing. Moving forward, NTT DOCOMO, Inc., and NAIST will continue collaborating to refine this technology and explore its potential applications across various sectors.
###
Information about the Cybernetics and Reality Engineering Laboratory can be found at the following website: https://carelab.info/en/
About Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST)
Established in 1991, Nara Institute of Science and Technology (NAIST) is a national university located in Kansai Science City, Japan. In 2018, NAIST underwent an organizational transformation to promote and continue interdisciplinary research in the fields of biological sciences, materials science, and information science. Known as one of the most prestigious research institutions in Japan, NAIST lays a strong emphasis on integrated research and collaborative co-creation with diverse stakeholders. NAIST envisions conducting cutting-edge research in frontier areas and training students to become tomorrow's leaders in science and technology.
About NTT DOCOMO, Inc.
Founded in 1992, NTT DOCOMO, Inc., is Japan's largest telecommunications company, providing over 73 million customers with innovative and secure mobile services through advanced wireless networks, including LTE and LTE-Advanced. As a leader in 5G network development, DOCOMO aims to deploy these networks using technologies such as network function virtualization in the 2020s. The company is also active in NFC, IoT solutions, and the global standardization of mobile technologies. Through its +d initiatives, DOCOMO collaborates with businesses to create new services. In 1999, DOCOMO launched the world's first mobile internet platform and has since played a pivotal role in advancing mobile communication standards such as W-CDMA and LTE.
END
PHILADELPHIA – The American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) is pleased to announce the recipients of the 2025 AACR June L. Biedler Prize for Cancer Journalism in the following categories:
Magazine
“Targeting Cancer, Sparing Patients”
By Jyoti S. Madhusoodanan (Photo), Scientific American
Newspaper
“Fighting stigma, fighting cancer: The rising threat of male breast cancer in Kenya”
By Pauline Ongaji Ogada (Photo), Nation
Online/Multimedia
“Farewell, my stomach”
By Teresa Firmino (Photo) and Joana Martins Gonçalves (Photo), Publico
“Women ...
It’s becoming increasingly commonplace for people to develop intimate, long-term relationships with artificial intelligence (AI) technologies. At their extreme, people have “married” their AI companions in non-legally binding ceremonies, and at least two people have killed themselves following AI chatbot advice. In an opinion paper publishing April 11 in the Cell Press journal Trends in Cognitive Sciences, psychologists explore ethical issues associated with human-AI relationships, including their potential to disrupt human-human relationships and give harmful advice.
“The ...
Vancouver, BC, April 11, 2025 – A new study finds that, unlike countries across the UK and Europe, abortion rates did not spike in Ontario, Canada from 2020-2022.
Following decades-long declines in nearly all high-income settings, abortion rate trends reversed between 2020 and 2022 in many countries. For example, 2022 and 2023 saw the highest abortion rates on record in Scotland, England, and Wales.
Researchers from the University of British Columbia and ICES found that, after accounting for changes in the abortion rate when the ...
Tropical cyclones are hurricanes that brew over the tropical ocean and can travel over land, inundating coastal regions. The most extreme cyclones can generate devastating storm tides — seawater that is heightened by the tides and swells onto land, causing catastrophic flood events in coastal regions. A new study by MIT scientists finds that, as the planet warms, the recurrence of destructive storm tides will increase tenfold for one of the hardest-hit regions of the world.
In a study that will appear in One Earth, the scientists ...
About The Study: In this large U.S. cohort study of children and adolescents, SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with a higher risk of adverse postacute kidney outcomes, particularly among those with preexisting chronic kidney disease or acute kidney injury, suggesting the need for vigilant long-term monitoring.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Yong Chen, PhD, email ychen123@pennmedicine.upenn.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website ...
About The Study: In this cohort study of children hospitalized with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in 2022 and 2023, severe RSV disease was more likely among those age 2 or older with pulmonary and neurologic, neuromuscular, or developmental conditions. For children younger than 2 years, age younger than 6 months and prematurity were the main risk factors. These findings support prevention strategies for all younger children, including premature infants, with potential benefit for children age 2 or older ...
A Northwestern University-led international team of scientists has, for the first time, directly observed catalysis in-action at the atomic level.
In mesmerizing new videos, single atoms move and shake during a chemical reaction that removes hydrogen atoms from an alcohol molecule. By viewing the process in real time, the researchers discovered several short-lived intermediate molecules involved in the reaction as well as a previously hidden reaction pathway.
The observations were made possible by single-molecule atomic-resolution time-resolved electron microscopy (SMART-EM), a powerful instrument that enables researchers to watch individual ...
The University of Virginia has named Mark T. Esser, PhD, a premier expert in the development of new medical treatments and tests, to lead the upcoming Paul and Diane Manning Institute of Biotechnology and bring to life the institute’s ambitious plans for a healthier tomorrow for people across the world.
In his role as the inaugural chief scientific officer and head of the Manning Institute, Esser will be charged with capitalizing on the cutting-edge biomedical research under way at UVA and UVA Health to tackle some of the greatest challenges in medicine and accelerate the development of new treatments and cures.
In ...
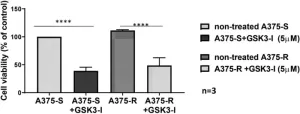
“Inhibitors of GSK3β reduce the cell viability of BRAFi-resistant melanoma cell lines and thus may holds promise as a novel strategy to overcome BRAFi resistance and melanoma progression.”
BUFFALO, NY – April 11, 2025 – A new research perspective was published in Oncotarget, Volume 16, on April 4, 2025, titled “GSK3β activation is a key driver of resistance to Raf inhibition in BRAF mutant melanoma cells.”
In this work, first author Diana Crisan and corresponding author Abhijit Basu from the University Hospital Ulm led ...
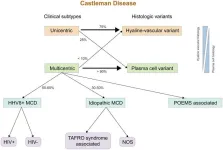
Castleman disease (CD) is a rare, non-clonal lymphoproliferative disorder that manifests with a wide range of histologic and clinical features. It is classified clinically into unicentric (UCD) and multicentric (MCD) forms and histopathologically into hyaline vascular (HV-CD), plasma cell (PC-CD), and mixed types. UCD typically presents as an isolated lymph node enlargement, often asymptomatic, whereas MCD involves multiple nodal sites and systemic symptoms. MCD may be associated with human herpesvirus 8 (HHV8), idiopathic origins (iMCD), POEMS syndrome, or TAFRO ...