(Press-News.org) Popular CT Scans Could Account for 5% of All Cancer Cases A Year
Radiation from imaging could lead to lung, breast and other future cancers, with 10-fold increased risk for babies
CT scans may account for 5% of all cancers annually, according to a new study out of UC San Francisco that cautions against overusing and overdosing CTs.
The danger is greatest for infants, followed by children and adolescents. But adults also are at risk, since they are the most likely to get scans.
Nearly 103,000 cancers are predicted to result from the 93 million CTs that were performed in 2023 alone. This is 3 to 4 times more than previous assessments, the authors said.
The study, which was funded by the National Institutes of Health, appears April 14 in JAMA Internal Medicine.
“CT can save lives, but its potential harms are often overlooked,” said first author Rebecca Smith-Bindman, MD, a UCSF radiologist and professor of epidemiology and biostatistics and obstetrics, gynecology and reproductive sciences.
“Given the large volume of CT use in the United States, many cancers could occur in the future if current practices don’t change,” said Smith-Bindman, who is also a member of the Philip R. Lee Institute for Health Policy Studies and directs the Radiology Outcomes Research Lab.
“Our estimates put CT on par with other significant risk factors, such as alcohol consumption and excess body weight,” she said. “Reducing the number of scans and reducing doses per scan would save lives.”
Benefits and potential dangers
Computed tomography (CT) is both indispensable and widely used to detect tumors and diagnose many illnesses. Since 2007, the number of annual CT exams has surged by 30% in the U.S.
But CTs expose patients to ionizing radiation – a carcinogen – and it’s long been known that the technology carries a higher risk of cancer.
To assess the public health impact of current CT use, Smith-Bindman's study estimates the total number of lifetime cancers associated with radiation exposure in relation to the number and type of CT scans performed in 2023.
Researchers analyzed 93 million exams from 61.5 million patients in the U.S. The number of scans increased with age, peaking in adults between 60 to 69 years old. Children accounted for 4.2% of the scans. The researchers excluded tests in the patient’s last year of life because it was unlikely to lead to cancer.
Future cancers from radiation exposure
Adults 50 to 59 had the highest number of projected cancers: 10,400 cases to women, 9,300 to men.
The most common adult cancers were lung, colon, leukemia, bladder and breast. The most frequently projected cancers in children were thyroid, lung and breast.
The largest number of cancers in adults would come from CTs of the abdomen and pelvis, while in children they came from CTs of the head. Projected cancer risks were highest among those who underwent CT when they were under 1 year old. They were 10 times more likely to get cancer compared to others in the study.
The researchers said some CT scans are unlikely to help patients and are overused, such as those for upper respiratory infections or for headaches without concerning signs or symptoms. They said patients could lower their risk by getting fewer of these scans, or by getting lower dose scans.
“There is currently unacceptable variation in the doses used for CT, with some patients receiving excessive doses,” Smith-Bindman said.
Co-author Malini Mahendra, MD, a UCSF assistant professor of Pediatric Critical Care, said it was important that families understand the risk of developing cancer from pediatric scans.
“Few patients and their families are counseled about the risk associated with CT examinations,” she said. “We hope our study’s findings will help clinicians better quantify and communicate these cancer risks, allowing for more informed conversations when weighing the benefits and risks of CT exams.”
Authors: From UCSF, authors are Philip W. Chu; Hana Azman Firdaus; Carly Stewart; Matthew Malekhedayat; and Malini Mahendra, MD. Joint senior authors are Diana L. Miglioretti, PhD, of UC Davis and Kaiser Permanente Washington Health Research Institute, and Amy Berrington de Gonzalez, DPhil, of The Institute of Cancer Research, London. Other authors are Susan Alber, PhD, of UC Davis; and Wesley E. Bolch, PhD of the University of Florida.
Disclosures: Please see the paper.
Funding: The research was supported in part by awards from the National Cancer Institute (1R01CA181191-O1A1), the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (CD-1304-7043).
About UCSF: The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) is exclusively focused on the health sciences and is dedicated to promoting health worldwide through advanced biomedical research, graduate-level education in the life sciences and health professions, and excellence in patient care. UCSF Health, which serves as UCSF's primary academic medical center, includes top-ranked specialty hospitals and other clinical programs, and has affiliations throughout the Bay Area. UCSF School of Medicine also has a regional campus in Fresno. Learn more at ucsf.edu, or see our Fact Sheet.
###
END
Popular CT scans could account for 5% of all cancer cases a year
2025-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Deep-sea mining risks leads study to urge shift to circular solutions
2025-04-14
Deep-sea mining (DSM) not only poses significant environmental, social, and economic risks that may have far-reaching implications for coastal communities and Small Island Developing States (SIDS), it is also likely to negatively affect the business community, including insurers and investors, says a new study by researchers from the University of British Columbia and the Dona Bertarelli Philanthropy.
DSM operations are expected to increase the negative impact on environmental indicators by up to 13 per cent, a change categorized as having “great” significance, relative to the “without” DSM scenario, ...
Dynamically controlled flight altitudes in robo-pigeons via locus coeruleus neurostimulation
2025-04-14
Background
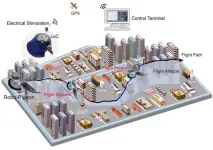
Robo-pigeon / Cyborg pigeon is a new type of hybrid intelligent robotic system developed by combining micro-implantable brain-computer interface (BCI) and micro-electro-mechanical system (MEMS) technologies. By integrating the perception, motion and autonomous intelligence of real pigeons with the high precision, repeatability and controllability of MEMS, a flexible and efficient "biological flight platform" is formed, which has a broad application prospect in key fields such as disaster rescue, national defense security and environmental monitoring.
However, ...
Using AI to monitor inaccessible locations of nuclear energy systems
2025-04-14
Whether it’s for your vehicle or your home, from small-scale uses to the largest, the debate over the most efficient and cost-effective fuels continues. Currently, there’s no shortage of options either.
Nuclear power provides an alternative to more conventional energy options but requires rigorous systems monitoring and safety procedures. Machine learning could make keeping a close eye on key elements of nuclear systems easier and response time to issues faster.
Syed Bahauddin Alam, an assistant professor ...
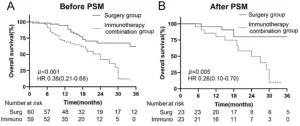
Outcomes for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with pulmonary metastasis: Surgical vs. immunotherapy
2025-04-14
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, with over 70% of patients diagnosed at an advanced stage due to the absence of symptoms. A key characteristic of advanced HCC is extrahepatic metastasis, particularly pulmonary metastasis, which is associated with a poor prognosis.
Although multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) and immune checkpoint inhibitors have limited efficacy when used alone in advanced HCC, their combination can enhance outcomes for patients with pulmonary metastases. Meanwhile, pulmonary metastasectomy ...
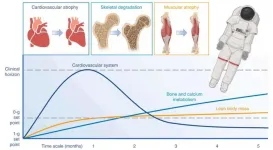
How flexible wearables protect astronauts' health in space
2025-04-14
A review published recently in Wearable Electronics examines the current applications and persistent challenges of flexible wearable technologies in aerospace medicine. As human space exploration progresses toward extended-duration missions, the imperative for real-time monitoring of astronauts' physiological and psychological well-being has become increasingly critical. The unique space environment characterized by microgravity conditions, cumulative radiation exposure, and extreme thermal fluctuations presents multifaceted health risks to crew members.
Flexible wearable systems, equipped ...
Pregnancy complications contribute to cardiovascular risk for overweight women, study finds
2025-04-14
Complications during pregnancy (or adverse pregnancy outcomes), like gestational diabetes and newly developed high blood pressure, act as nature’s stress test and may uncover an individual’s risk for heart disease later in life, according to new research published in the JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology. The study also highlights how weight management before pregnancy may not only improve maternal health but also reduce future cardiovascular disease risk.
The observational study, which ...
Simple medication can save the lives of cardiac patients
2025-04-14
Cardiovascular disease is by far the most common cause of death worldwide, and myocardial infarction is the most common acute event. For those who survive a myocardial infarction, the risk of a new heart attack is greatest in the first year after the initial event because the blood vessels are more sensitive, making it easier for blood clots to develop. Reducing the “bad” cholesterol in the blood stabilises changes in the vessels, decreasing the risk for new events. The current established routine treatment is to treat with high-potency statins, immediately after the infarction. However, the majority ...
Combination of drugs could prevent thousands of heart attacks
2025-04-14
LUND UNIVERSITY/IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON PRESS RELEASE
[Peer-reviewed /Simulation/Modelling / People]
UNDER EMBARGO UNTIL:
Monday 14th April 2025
10:00 am US Eastern Time / 3:00 pm UK Time
Combination of drugs could prevent thousands of heart attacks
Patients who receive an add-on medication soon after a heart attack have a significantly better prognosis than those who receive it later, or not all.
This is according to a new study from researchers at Lund University in Sweden and Imperial College London. ...
New tool for cutting DNA: Promising prospects for biotechnology
2025-04-14
New tool for cutting DNA: promising prospects for biotechnology
An INRS team discovers a new family of enzymes capable of inducing targeted cuts in single-stranded DNA
A few years ago, the advent of technology known as CRISPR was a major breakthrough in the scientific world. Developed from a derivative of the immune system of bacteria, CRISPR enables double strands of nucleotides in deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) to be cut. This makes it possible to specifically modify a targeted gene in plant, animal and human cells. Ultimately, CRISPR became a preferred method in the search for treatments for acquired or hereditary diseases.
Recently, ...
Footprints of tail-clubbed armored dinosaurs found for the first time
2025-04-14
Victoria, BC— For the first time, footprints of armoured dinosaurs with tail clubs have been identified, following discoveries made in the Canadian Rockies. The 100-million-year-old fossilized footprints were found at sites at both Tumbler Ridge, BC, and northwestern Alberta.
There are two main groups of ankylosaurs. Nodosaurid ankylosaurs have a flexible tail and four toes, while ankylosaurid ankylosaurs have a sledgehammer-like tail club, and only three toes on their feet.
Unlike the well-known ankylosaur footprints called Tetrapodosaurus ...